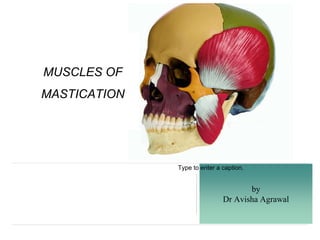
Muscles of mastication powerpoint
- 1. by Dr Avisha Agrawal Type to enter a caption. MUSCLES OF MASTICATION
- 2. CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Types of muscle 3. development of muscle 4. Primary muscle of mastication 5. Secondary muscle of mastication 6. Clinical features 7. Conclusion 8. References
- 3. MASTICATION ❖ Rhythmic opposition and separation of jaws with the involvement of teeth ,lips ,cheeks and tongue for chewing of food in order to prepare it for swallowing and digestion. ❖ Main purpose of mastication is to reduce the size of food particles to a size that is convenient for swallowing (bolus formation) with the help of saliva.
- 4. TYPES OF MUSCLE Type to enter a caption. CARDIACSTRIATED SMOOTH
- 5. PRIMARY ❖ Temporalis muscle ❖ Masseter muscle ❖ Medial pterygoid muscle ❖ Lateral pterygoid muscle SECONDARY ❖ Digastric muscle ❖ Mylohyoid muscle ❖ Geniohyoid muscle 2 groups of muscles of mastication
- 6. DEVELOPMENT The neck is formed by the elongation of the region between the stomatodeum and the pericardium. This is achieved partly, by a ‘descent’ of the developing heart. However this elongation is due mainly to the appearance of a series of mesodermal thickenings on the wall of the cranial most part of the foregut These are called pharyngeal, or branchial arches
- 7. ❖ At this stage the endoderm wall is separated from ectoderm by a wall of mesoderm. ❖ Soon, thereafter the mesoderm comes to be arranged in the form of six bars that run dorso-ventrally in the side wall of the foregut ❖ Each of this bars grow ventrally the floor of the developing pharynx and fuses with the corresponding bar of the opposite side to form a pharyngeal or branchial arch ❖ In the interval between any two adjoining arches ,the endoderm extends outwards in the form of a pouch(endodermal or pharyngeal pouch) to meet the ectoderm which dips into this interval as an ectodermal cleft.
- 8. Arch Nerve of the arch Muscle of the arch First Mandibular Medial and lateral pterygoids,masseter,temporalis mylohyoid ,anterior belly of digastric,digastric, tensor tympani, tensor palate Second Facial Facial muscles,occipitofrontalis,platysma,stylohyoid, post belly of digastric,stapedius,auricular muscles Third Glosso phayrngeal Stylopharngeus Fourth Superior laryngeal Muscles of larynx and pharynx Fifth Recurrent laryngeal
- 9. MASSETER MUSCLE ❖ Masseter muscle is quadrilateral in shape ❖ origin-zygomatic arch and maxillary process of the zygomatic bone ❖ Superficial part-maxillary process of zygomatic bone and the anterior 2/3rd of zygomatic process of maxilla ❖ Deep part- medial aspect of the zygomatic arch and posterior part of its inferior margin. ❖ Fibres- ❖ superficial fibres- pass downwards and backwards at 45 degree ❖ Deep fibers- pass vertically downwards Type to enter a caption.
- 10. ❖ insertion- ❖ Superficial part-into lower part of lateral surface of ramus of mandible ❖ Deep layer-into rest of the ramus of mandible ❖ Innervation- massetric nerve from the anterior trunk of the mandibular nerve ❖ Nerve supply- massetric nerve ❖ Actions-elevation of mandible to close the mouth Type to enter a caption.
- 11. TEMPORALIS ❖ This muscle is large fan shaped that fills much of the temporal fossa. ❖ Origin- bone of temporal fossa and temporal fascia. ❖ Fibres- Ant. Fibres run vertically, middle obliquely, posterior horizontally. All converge and pass through gap deep to zygomatic arch ❖ Insertion- margin and deep surface of coronoid process of mandible and anterior margin of ramus of mandible almost to last molar tooth. ❖ Innervation-deep temporal nerves from the ant trunk of the mandibular nerve. Type to enter a caption.
- 12. ❖ Function- elevates mandible. ❖ Helps in side to side grinding movement ❖ Posterior fibers retract the protruded mandible. Type to enter a caption.
- 13. LATERAL PTERYGOID ❖ Short, conical has upper and lower heads ❖ Origin- ❖ upper head(small) from infratemporal surface and crest of greater wing of sphenoid bone ❖ Lower head (larger)-from lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate ❖ Origin is medial to insertion ❖ Fibres- run backwards and laterally and converge for insertion Type to enter a caption.
- 14. ❖ Insertion - ❖ Pterygoid fovea-on anterior surface of neck of mandible ❖ Ant margin of articular disc and capsule of TMJ ❖ Insertion is posterolateral and at a slightly higher level than origin supply ❖ Nerve supply- branch from ant. Division of mandibular nerve ❖ Actions-depresses mandible to open mouth with supra hyoid muscles ❖ Lateral and medial pterygoid protrude mandible ❖ Right lateral ptergoid and right medial pterygoid turn the chin to left side as a part of grinding movement. Type to enter a caption.
- 15. MEDIAL PTERYGOID ❖ Quadrilateral, has a small superficial and a large deep head ❖ Origin- ❖ Superficial head(small slip)-from tuberosity of maxilla and adjoining bone ❖ Deep head(quite large)-from medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate and adding process of palatine bone. ❖ Fibres-run downwards, backwards and laterally. Type to enter a caption.
- 16. ❖ Insertion-roughened area on the medial surface of angle and adjoining ramus of mandible,mandible, below and behind the mandibular foramen and mylohyoid groove. ❖ Nerve supply-nerve to medial pterygoid,branch of the main trunk of mandibular nerve ❖ Actions- ❖ elevates mandible ❖ Help protrude mandible ❖ Right medial pterygoid with right lateral pterygoid turn the chin to left side. Type to enter a caption.
- 17. MYLOHYOID ❖ Flat triangular muscle, two mylohyoid forms floor of mouth cavity, deep to digastric muscle ❖ Origin- mylohyoid line of mandible ❖ Fibres-run medially and slightly downwards ❖ Insertion ❖ posterior fibres- body of hyoid bone ❖ Middle and anterior fibres-fibres; median raphe,between mandible and hyoid bone Type to enter a caption.
- 18. ❖ Nerve supply-nerve to mylohyoid ❖ Actions-elevates floor of mouth in first stage of deglutition. ❖ Helps in depression of mandible, and elevation of hyoid bone
- 19. GENIOHYOID ❖ Short and narrow muscle lies above medial part of mylohyoid ❖ Origin-inferior mental spine(genial tubercle) ❖ Fibres-run backwards and downwards ❖ insertion-Ant surface of body of hyoid bone ❖ Nerve supply-C1 through hypoglossal nerve Type to enter a caption.
- 20. ❖ Actions- elevates hyoid bone ❖ May depress mandible when hyoid is fixed Type to enter a caption.
- 21. HYOGLOSSUS ❖ It is a muscle of tongue. ❖ It forms important landmarks in this region ❖ Origin-whole length of greater cornea and lateral part of body of hyoid bone ❖ Fibres-run upwards and forwards ❖ Insertion-side of tongue between styloglossus and inf longitude; muscles of tongue ❖ Nerve supply-hypoglossal nerve Type to enter a caption.
- 22. ❖ Actions- depresses tongue makes dorm convex, retracts the protruded tongue Type to enter a caption.
- 24. OKESONS CLASSIFICATION OF MASTICATORY MUSCLE DISORDERS A. Myalgia 1. Local myalgia 2. Myofascial pain 3. Myofascial pain with referral B. Tendonitis C. Myositis D. Spasm 2. Contracture 3. Hypertrophy
- 25. 4. Neoplasm 5. Movement disorders A. Orofacial dyskinesia B. Oromandibular dystonia 6. Masticatory muscle pain attributed to systemic/central pain disorders A. Fibromyalgia/widespread pain
- 26. MYALGIA ❖ It is a pain originating from muscles of mastication and differs from TMJ pain in several ways ❖ It is loosely correlated with jaw function, where as joint pain is a direct function of joint movement. ❖ It is typically delayed in onset ❖ The muscle pain from myalgia is mostly diffuse and slowly waxes and wanes over time. ❖ When asked to locate pain, TMJ pain is located in front of the ear, while myalgia patient will place hands over the entire side of the face
- 27. ❖ Myalgia is diagnosed by clinical examination ❖ Pain can be provoked by digital palpation of the muscles. ❖ patient seek treatment primarily to relieve pain ❖ Causes ❖ Drug-Induced Myalgias ❖ Mycoplasm pneumonia and atypical pneumonia ❖ Disorders of skeletal muscle ❖ Cramps muscle stiffness and exercise intolerance
- 28. ❖ Treatment ❖ NSAIDS and muscle relaxant are the first line of treatment. ❖ Antidepressant therapy is very effective for many of these patients
- 29. MYOFACIAL PAIN DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME ❖ Myofascial pain (MP) is a widespread and universal cause of soft tissue pain. ❖ The central feature of MP syndrome (MPS) is the myofascial trigger point (MTrP), a very small, localized area of muscle contraction that is hard to touch, and that is very tender. ❖ The MTrP is always located on a tight or taut band of muscle. An MTrP that causes pain is always tender to palpation. ❖ When stimulated mechanically by palpation or by needling, it contracts sharply, referred to as local twitch response (LTR). ❖ The taut band limits stretch of a muscle and produces weakness that is rapidly reversed as the trigger point is inactivated.
- 30. ❖ It can activate autonomic activity, such as vasodilation or constriction, goose bumps, or piloerection. ❖ The MTrP, like other physical sources of chronic pain, refers pain to distant sites and leads to central nervous system sensitization. ❖ MTrPs can be spontaneously painful (so-called “active” MTrPs) or they can be nascent or quiescent (so-called “latent” MTrPs), inactive until physical activity converts them to active MTrPs.
- 31. Anterior Supraorbital ridge and downward to incisors teeth Intermediate Posterior Mid temple area an downward to maxillary teeth on the same side backward and upward Pain referred Upper border of zygomatic arch. Above the ear. Palpation
- 32. MANAGEMENT Treatment Description Education Explanation of diagnosis and treatment Reassurance about the generally good prognosis for recovery and natural course Explanation of patients and doctors role in therapy Information to enable patients to perform self care Self care Control parafunctional oral behaviours Provide information on jaw care associated with daily activities Physical therapy Education regarding biomechanics of jaw,jaw, neck and head posture and integrated movement pattern Passive modalities(heat and cold therapy, ultrasound,laser and TENS)for pain passive stretching and range of motion exercises Posture therapy to regain a neutral zone. General exercise and conditioning program intraoral appliance therapy Cover all the teeth on the arch the appliance is seated on Adjust to achieve simultaneous contact against opposing teeth Adjust to stable comfortable mandibular posture Does not alter mandibular position Use during sleep and rely on behavioural methods for waking hours
- 33. behavioral/relaxation technique Relaxation therapy Hypnosis Biofeedback Cognitive behavioural therapy
- 34. MYOSITIS ❖ refers to any condition causing inflammation in muscles. ❖ Weakness, swelling, and pain are the most common myositis symptoms. ❖ Myositis causes include infection, injury, autoimmune conditions, and drug side effects. Treatment of myositis varies according to the cause. ❖ Causes ❖ Inflammatory condition ❖ Infection ❖ Drugs ❖ Injury
- 35. Inflammatory conditions causing myositis may require treatment with drugs that suppress the immune system, including: • Prednisone • Azathioprine (Imuran) • Methotrexate
- 36. TRISMUS ❖ The word Trismus is Latin term derived from the Greek word “Trismos” which means grinding / rasping. ❖ In lay terms Trismus means limitation of mouth opening due to reduced mandible mobility. ❖ Two bones form the boundaries of oral cavity (maxilla and mandible). ❖ Out of these two maxilla is fixed and is not mobile, where as mandible is capable of upwards and downwards mobility with a limited forward and backward mobility too. ❖ The maximal interincisal opening (MIO) of at least 35mm is used as a cutoff point to determine Trismus. ❖ Less than 5 mm of MIO indicates complete ankylosis.
- 37. ❖Roughly put the mouth opening should permit a minimum of three fingers when inserted sideways. ❖Since the movement of the mandible occurs around Temporomandibular joint Kazanjian classified anky ❖True ankylosis of TM joint is usually caused due to pathology involving the joint ❖while the term false ankylosis is used to describe restrictions of movement resulting from extra articula ❖It is this type of false ankylosis which clinicians commonly term as Trismus
- 38. Etiology of Trismus may be classified into: 1. Infection 2. Trauma 3. Dental treatment 4. TM joint disorders 5. Tumors and oral care include benign and 6. malignant lesions involving oral cavity 7. and submucous fibrosis Type to enter a caption.
- 39. 6. Drug induced 7. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy 8. Congenital disorders 9. Miscellaneous disorders include Hysteria, Lupus erythematosus
- 41. MANAGEMENTConservative medical management for acute trismus: 1. Heat therapy – By placing moist hot towels on the affected area for 10-20 minutes / hour. 2. Analgesics – Aspirin is adequate. Narcotic analgesic may be indicated if the discomfort is too much. 3. Soft diet 4. Muscle relaxants – Benzodiazepines 11 2.5 – 5 mg three times a day may be indicated in patients with excessive masticatory muscle spasm 5. Physiotherapy can be started after cessation of the acute phase. Antibiotics is indicated only if trismus has been attributed to infection.
- 42. HYPERTROPHY Hypertrophy of muscle refers to an increase in size of individual muscle fibres. Masticatory muscle hypertrophy can affect all the muscles of mastication, several muscles or just one muscle. It can occur either bilaterally or unilaterally, and most commonly the masseter muscles alone are affected. The involved muscles, which are variably enlarged and can be up to three times the normal size, are otherwise normal on all imaging studies. Type to enter a caption.
- 43. ❖ Masseter muscle hypertrophy (MMH) may present as unilateral or bilateral, benign increase in size of masseter muscle. ❖ Its aetiology remains unexplained. ❖ It is most commonly seen in late adolescence and early adulthood, affects both males and female but has slight male predominance. ❖ Very little information concerning this entity has appeared in dental literature because MMH in itself is only occasionally associated with dental problems such as attrition, periodontal breakdown or temperomandibular joint problem. ❖ Unilateral or bilateral hypertrophy of the masseter muscle is ❖ characterised by an increase in the volume of the muscle mass.
- 44. ❖ Clinically, patient may present with the complaint of unaesthetic appearance due to facial asymmetry or ‘square’ face appearance. ❖ Some patients complain of pain, headache, muscle stress, trismus and intermittent masticatory claudication. ❖ The radiographic findings associated with MMH are the bone spurs at the angle of mandible6 or flaring of mandibular angle and hyperostosis of mandibular ramus.
- 45. ❖ CT and MRI scans provide useful diagnostic information regarding this condition. ❖ This entity must be carefully differentiated from unilateral compensatory hypertrophy (due to hypertrophy or hyperplasia in the contralateral side), masseter tumour, salivary gland disease, parotid tumour, parotid inflammatory disease, masseter muscle intrinsic myopathy, lipoma, vascular tumours, benign and malignant mandible tumours and metabolic disorders.
- 46. TREATMENT A longer acting, more reliable method of obtaining masticatory muscle relaxation can be achieved by injecting measured doses of botulinum toxin (BTX) into specific sites in the major muscles of mastication.12–14. These doses are sufficient to shut down the efferent response from spindle cells within the muscles that are implicated in initiating and potentiating the sympathetic dystonic cycle. Type to enter a caption.
- 47. ❖ The effect of BTX is to act as a governor on sympathetically driven trigeminal innervation to the masticatory muscles.The obvious treatment goal is to reduce spasm but not to interfere with normal function.15 A reduction in dystonia and pain with optimization of function is easily achievable with a site-specific and dose-specific BTX injection protocol. ❖ BTX, a natural protein, is one of the most potent biological substances known. ❖ The toxin inhibits the release of acetylcholine (ACH), a neurotransmitter responsible for the activation of muscle contraction and glandular secretion.
- 48. ❖ BTX is synthesized as a large single-chain peptide. ❖ Activation requires a two-step modification in the tertiary structure of the protein. ❖ This process converts the single- chain neurotoxin to a di-chain neurotoxin comprising a 100,000-Da heavy chain (HC) linked by a disulfide bond to a 50,000-Da light chain (LC). BTX acts at the neuromuscular junction where it exerts its effect by inhibiting the release of ACH from the presynaptic nerve terminal. ❖ ACH is contained in vesicles, and several proteins (vesicle-associated membrane protein [VAMP], synaptosome-associated protein 25 kDA [SNAP-25], and syntaxin) are required to release these vesicles through the axon terminal membrane.
- 49. ❖ BTX binds to the presynap- tic terminal via the HC. ❖ The toxin is then internalized and the HC and LC are separated. ❖ The LC from BTX-A cleaves SNAP-25, the LCs from serotypes B and F cleave VAMP, and that from serotype C cleaves syntaxin.23 ❖ This disrupts ACH release and subsequent neuro- muscular transmission, resulting in weakness of the injected muscle.
- 50. ORAL DYSKINESIA ❖ Oral dyskinesias are abnormal ,involuntary movements of the tongue, lips and jaw. ❖ The term tar dive dyskinesia was introduced in 1964 to describe a dyskinesia associated with antipsychotic medication ❖ The prevalence of tar dive dyskinesia in patients treated chronically with conventional antipsychotic medication is estimated to be approx 20% ❖ Oral dyskinesias may be a factor contributing to muscle stiffness, TMJ degenerative changes, mucosal lesions, damage to teeth, and dental prostheses. ❖ Tar dive dyskinesia has been reported to cause facial pain ❖ Complete loss of teeth is considered to be one cause of oral dyskinesia ❖ Ill fitting dentures or lack of replacements may initiate dyskinesia.
- 51. ❖ Dyskinesias are characterised clinically by the observation of involuntary muscles and the effects of these movements on the jaw muscles,TMJ,oral mucosa,and teeth. ❖ Emphasis on mangement is prevention because no treatment is predictably effective and safe ❖ Tardive dyskinesia may be persistent even after drug therapy is stopped ❖ Palliative treatment using tetrabenzaine, a central monoamine depleter, clonazepam and baclofen has been tried.
- 52. OROMANDIBULAR DYSTONIA ❖ Oro mandibular dystonia produces involuntary and excessive contractions of tongue, lip and jaw muscles. ❖ The etiology and pathophysiology are unknown. ❖ The proposed mechanism is related to defective inhibitory control of the basal ganglia of the forebrain, thalamus and brain stem. ❖ Injection of botulinum toxin has been used in the cases of oromandibular dystonia
- 53. BRUXISM The term ‘la bruxomanie’ was first introduced by Marie Pietkiewicz in 1907 [3]. It was latter adopted as ‘bruxism’ to describe gnashing and grinding of the teeth occurring without a functional purpose. Type to enter a caption.
- 54. ❖ Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms (GPT-8) [4] defines bruxism as parafunctional grinding of teeth or an oral habit consisting of involuntary rhythmic or spasmodic non functional gnashing, grinding or clenching of teeth in other than chewing movements of the mandible which may lead to occlusal trauma. ❖ Bruxism can occur during wakefulness or during sleep.
- 55. ❖ Bruxism during daytime is commonly a semivoluntary ‘clenching’ activity and is also known as ‘Awake Bruxism’ (AB) or Diurnal Bruxism (DB). ❖ AB can be associated with life stress caused by familial responsibility or work pressure. Bruxism during sleep either during daytime or during night is termed as ‘Sleep Bruxism’ (SB). ❖ SB is an oromandibular behavior that is defined as a stereotyped movement disorder occurring during sleep and characterized by tooth grinding and/or clenching [5]. ❖ Sleep bruxism was recently classified as sleep related movement disorder according to recent classification of Sleep Disorders.
- 56. ❖ Prevalence rate of AB and SB is about 20 and 8–16% respectively in adult population. ❖ AB is found to occur predominantly among females while no such gender difference is seen for sleep bruxism. ❖ Onset of SB is about 1 year of age soon after the eruption of deciduous incisors. ❖ The disorder is appearing more frequently in the younger population. ❖ The prevalence in children is between 14 to 20%. ❖ In adults aged above 60 years and over only 3% are being aware of frequent grinding.
- 57. Management Bite plane Occlusal splints
- 58. MASTICATOR SPACE ❖ The masticator space contains the mastication muscles, ramus of the mandible, and mandibular nerve. ❖ Because clinical assessment of lesions in this space may be difficult, CT and MR imaging is important for the characterisation and mapping of the pathology. ❖ Inflammatory conditions of the space are particularly common and are usually odontogenic in origin. ❖ Lymphovascular malformations are also common, particularly in children. ❖ Benign and malignant tumours may arise from the different contents of the space, and malignant tumours may appear well defined and confined by the fascia, without signs of aggressiveness. ❖ Tumours of the pharynx and parotid gland may also invade the MS. ❖ PNS can also occur with malignancies arising within this space.
- 59. Type to enter a caption. ❖ Masticator spaces are paired supra-hyoid cervical spaces on each side of the face that extend from the angle of the mandible to the parietal calvarium. ❖ Each space is delineated by a superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia (SLDCF). ❖ At the lower border of the mandible, the SLDCF splits into two layers: an inner layer that extends deep to the medial pterygoid muscle and attaches to the skull base medial to the foramen ovale and an outer or superficial layer that covers the masseter muscle, attaches to the zygomatic arch, and then continues superiorly to encase the temporalis muscle. ❖ These two layers fuse along the anterior and posterior borders of the mandibular ramus, enveloping the space. ANATOMY
- 60. PATHOLOGY ❖ odontogenic abscess ❖ osteomyelitis ❖ direct spread of squamous cell carcinoma ❖ lymphoma ❖ minor salivary gland tumours ❖ muscle sarcoma ❖ bone sarcoma ❖ osteoradionecrosis ❖ schwannoma ❖ neurofibroma ❖ benign masseteric hypertrophy ❖ accessory parotid tissue
- 61. CONCLUSION Mastication is oral motor behavior reflecting central nervous system commands, and many peripheral sensory inputs to modulate the rhythmic jaw movements. Since tooth guidance has an enormous influence on muscle activity during chewing and swallowing, it is advisable to make restorations and replacements as much compatible as possible, with the functional movement patterns of the patient, rather than expect the patterns of the mastication to adapt to the new made replacements.
- 62. REFERENCES ❖ Kamble V, Mitra K. A Rare Association of Bilateral and Unilateral Masseter Hypertrophy with Hypertrophy of Pterygoids. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR. 2016 Feb;10(2):TJ03. ❖ B.D chaurasia-human anatomy pg 144-148 ❖ Inderbir singh- human embryology tenth edition ❖ Grays’s Anatomical basis of clinical practice 39th edition. Elsevier under the Churchill Livingstone publication. ❖ Rispoli DN Benign masseter muscle hypertrophy. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2008;74(5): 790-3.