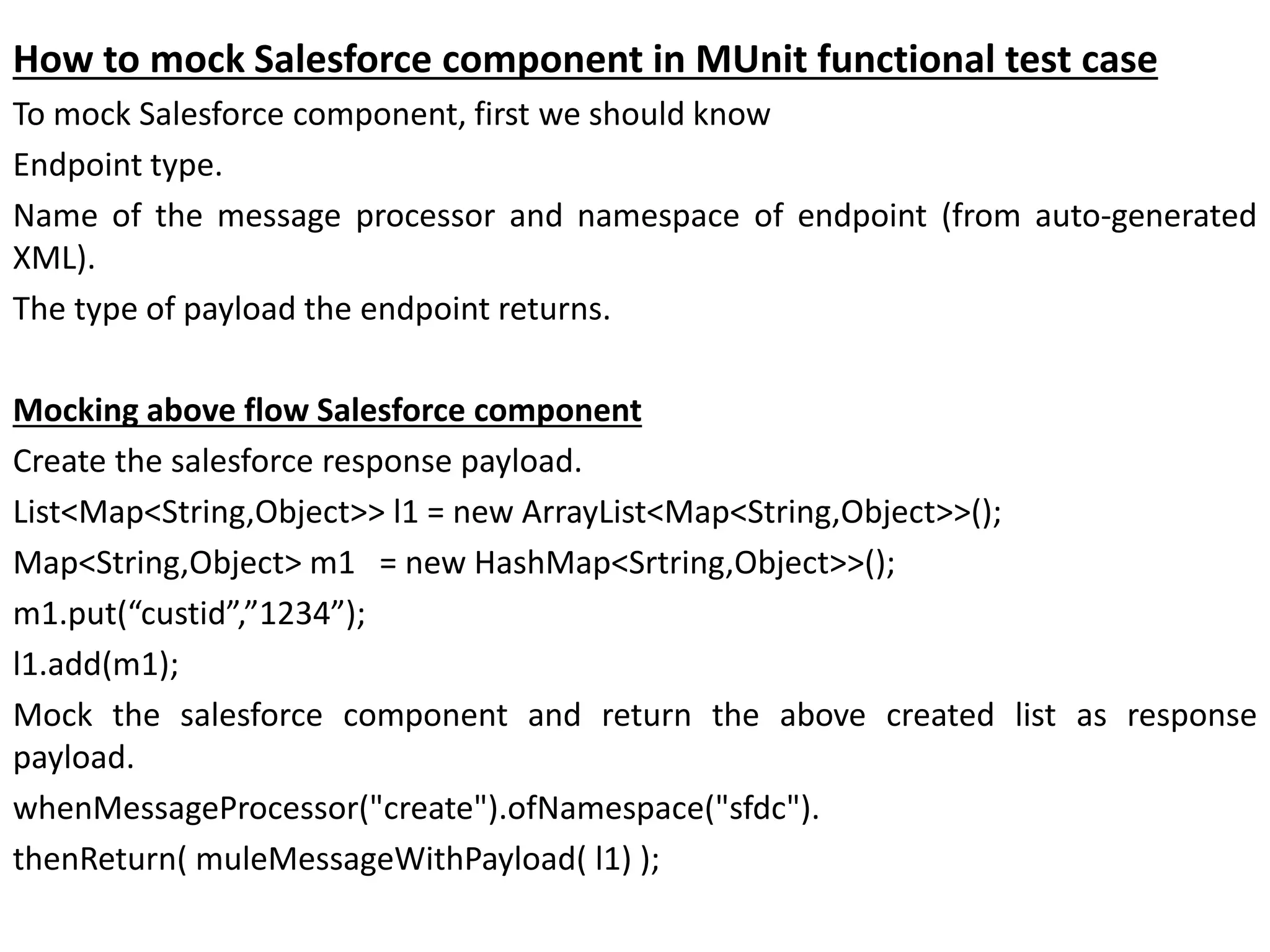
This document discusses writing functional test cases for Mule flows using JUnit and MUnit frameworks. With JUnit, test cases directly connect to original components like databases and APIs, modifying real data. MUnit allows mocking components to avoid this. The document provides examples of test cases using JUnit that connect directly to Salesforce and SAP, modifying real data. It then presents a solution using MUnit, showing how to mock the Salesforce component to return sample data without connecting to the real system. MUnit test cases are able to fully isolate tests by mocking components.








![Sample flow
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <mule xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http"
xmlns:tracking="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/tracking"
xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" version="EE-3.6.1"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/tracking
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/tracking/current/mule-tracking-ee.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd">
<http:listener-config name="HTTP_Listener_Configuration" host="0.0.0.0" port="9090" doc:name="HTTP Listener
Configuration"/> <flow name="exampleFlow"> <http:listener config-ref="HTTP_Listener_Configuration" path="/"
allowedMethods="GET" doc:name="HTTP"/> <set-payload
value="#[message.inboundProperties['http.query.params']['url_key']]" doc:name="Set Original Payload"/> <flow-ref
name="exampleFlow2" doc:name="exampleFlow2"/> <choice doc:name="Choice"> <when
expression="#[flowVars['my_variable'].equals('var_value_1')]"> <set-payload value="#['response_payload_1']"
doc:name="Set Response Payload"/> </when> <otherwise> <set-payload value="#['response_payload_2']"
doc:name="Set Response Payload"/> </otherwise> </choice> </flow> <flow name="exampleFlow2"> <choice
doc:name="Choice"> <when expression="#['payload_1'.equals(payload)]"> <flow-ref name="exampleSub_Flow1"
doc:name="exampleSub_Flow1"/> </when> <otherwise> <flow-ref name="exampleSub_Flow2"
doc:name="exampleSub_Flow2"/> </otherwise> </choice> </flow> <sub-flow name="exampleSub_Flow1"> <set-
variable variableName="my_variable" value="#['var_value_1']" doc:name="my_variable"/> </sub-flow> <sub-flow
name="exampleSub_Flow2"> <set-variable variableName="my_variable" value="#['var_value_2']"
doc:name="my_variable"/> </sub-flow> </mule>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/munitjunittestcase-150725143723-lva1-app6892/75/Munit-junit-test-case-15-2048.jpg)

![Example
Mocking Salesforce test case using Munit
mflow
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core" xmlns:vm="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm"
xmlns:sfdc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/sfdc" xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:core="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
version="EE-3.4.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm/current/mule-
vm.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/sfdc http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/sfdc/5.0/mule-sfdc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd">
<vm:endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" path="CREATE_CSTMR_VM" name="CREATE_CSTMR_VM"
doc:name="VM"/>
<vm:endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" path="INSERT_PERSON_ACT_VM" name="INSERT_PERSON_ACT_VM"
doc:name="VM"/>
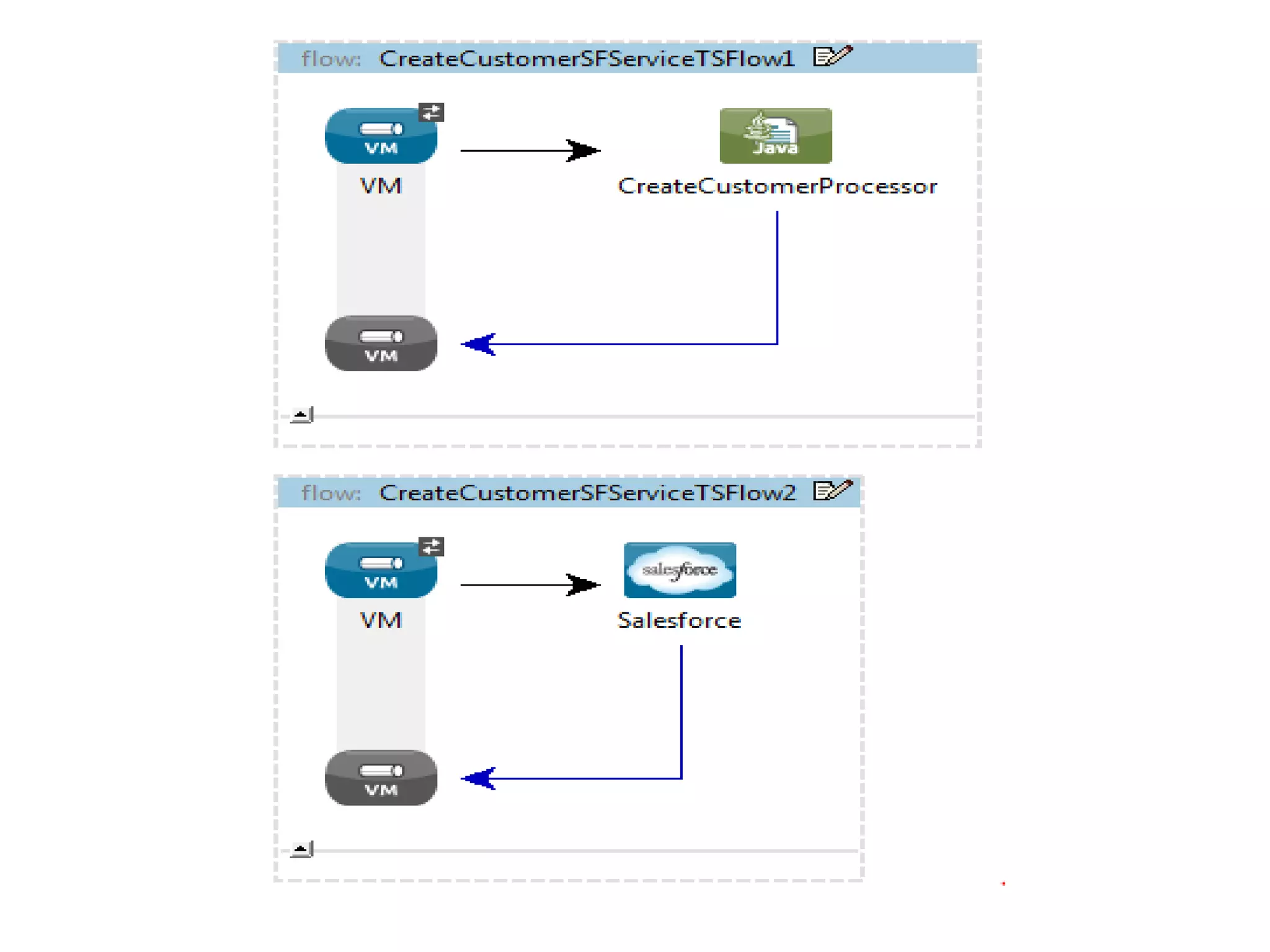
<flow name="CreateCustomerSFServiceTSFlow1" doc:name="CreateCustomerSFServiceTSFlow1">
<vm:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" ref="CREATE_CSTMR_VM" doc:name="VM"/>
<component class="com.vertu.services.ecom.maintaincustmr.processor.CreateCustomerProcessor"
doc:name="CreateCustomerProcessor"/>
</flow>
<flow name="CreateCustomerSFServiceTSFlow2" doc:name="CreateCustomerSFServiceTSFlow2">
<vm:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" ref="INSERT_PERSON_ACT_VM" doc:name="VM"/>
<sfdc:create config-ref="ECOM_SALESFORCE_CONNECTOR" type="#[payload.Type]" doc:name="Salesforce">
<sfdc:objects ref="#[payload.Object]"/>
</sfdc:create>
</flow>
</mule>
Here we have a Salesforce component to create the customer in
Salesforce and return the customer-id as payload. So in
functional test case we should mock this component without](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/munitjunittestcase-150725143723-lva1-app6892/75/Munit-junit-test-case-17-2048.jpg)




![Mocking Database component test case using
MUnit
Mflow:
<flow name="CheckAcctIDFlow" doc:name="CheckAcctIDFlow">
<vm:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-
response" ref="FETCH_ACT_GUID_VM1"
doc:name="FETCH_ACT_GUID_VM1"/>
<logger
message="#[message.inboundProperties['ACCT_GUID']]"
level="INFO" doc:name="Logger"/>
<jdbc-ee:outbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-
response" queryKey="Get_ACC_ID" queryTimeout="-1"
connector-ref="CDMR_JDBC_CONNECTOR"
doc:name="Get_ACCT_ID"/>
</flow>
• Here we have a database component used to select and
return the account-id from database. So we need to mock this
component in functional test case.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/munitjunittestcase-150725143723-lva1-app6892/75/Munit-junit-test-case-23-2048.jpg)