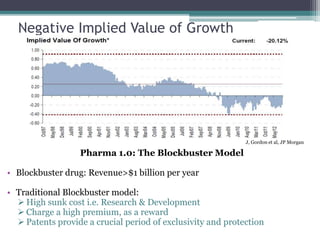
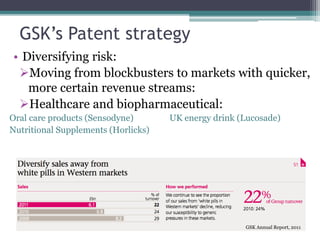
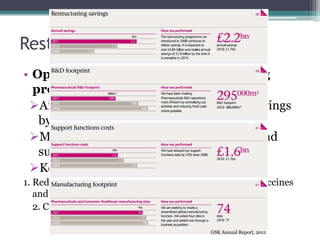
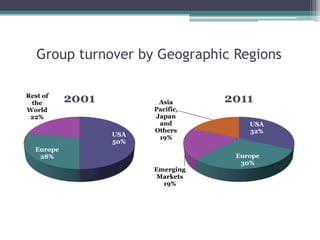
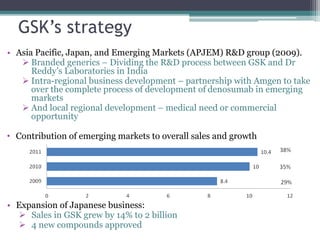
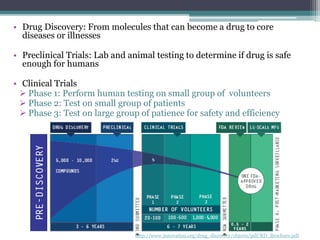
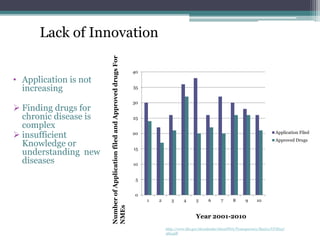
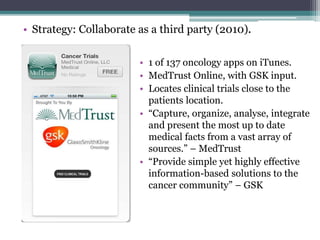
The document discusses the evolving challenges in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly focusing on the dangers of the traditional blockbuster model due to weakening patent protections and the rise of generics. It outlines GlaxoSmithKline's (GSK) strategies to adapt, including diversifying into new markets, collaborating with generic firms, and restructuring for operational excellence. The document also highlights the shift towards digital healthcare technology and the need for pharmaceutical companies to innovate to remain competitive in a changing market landscape.