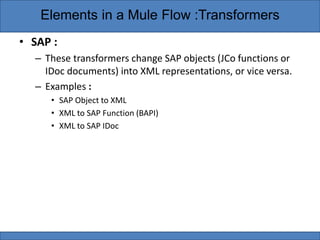
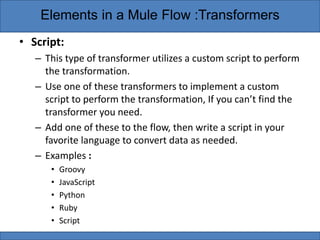
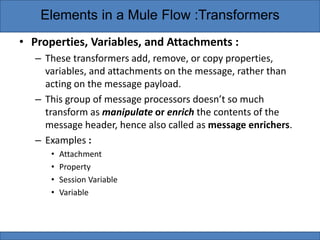
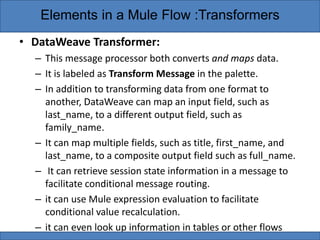
Transformers are elements in Mule flows that prepare messages for further processing by altering message properties, variables, or payloads. Mule provides standard transformers to handle common data transformation scenarios with minimal configuration. Transformers can be categorized as Java object, content, SAP, script, or properties/variables/attachments depending on what types of changes they make to messages. DataWeave is also a transformer that can both convert data formats and map fields, as well as perform conditional routing and expressions.