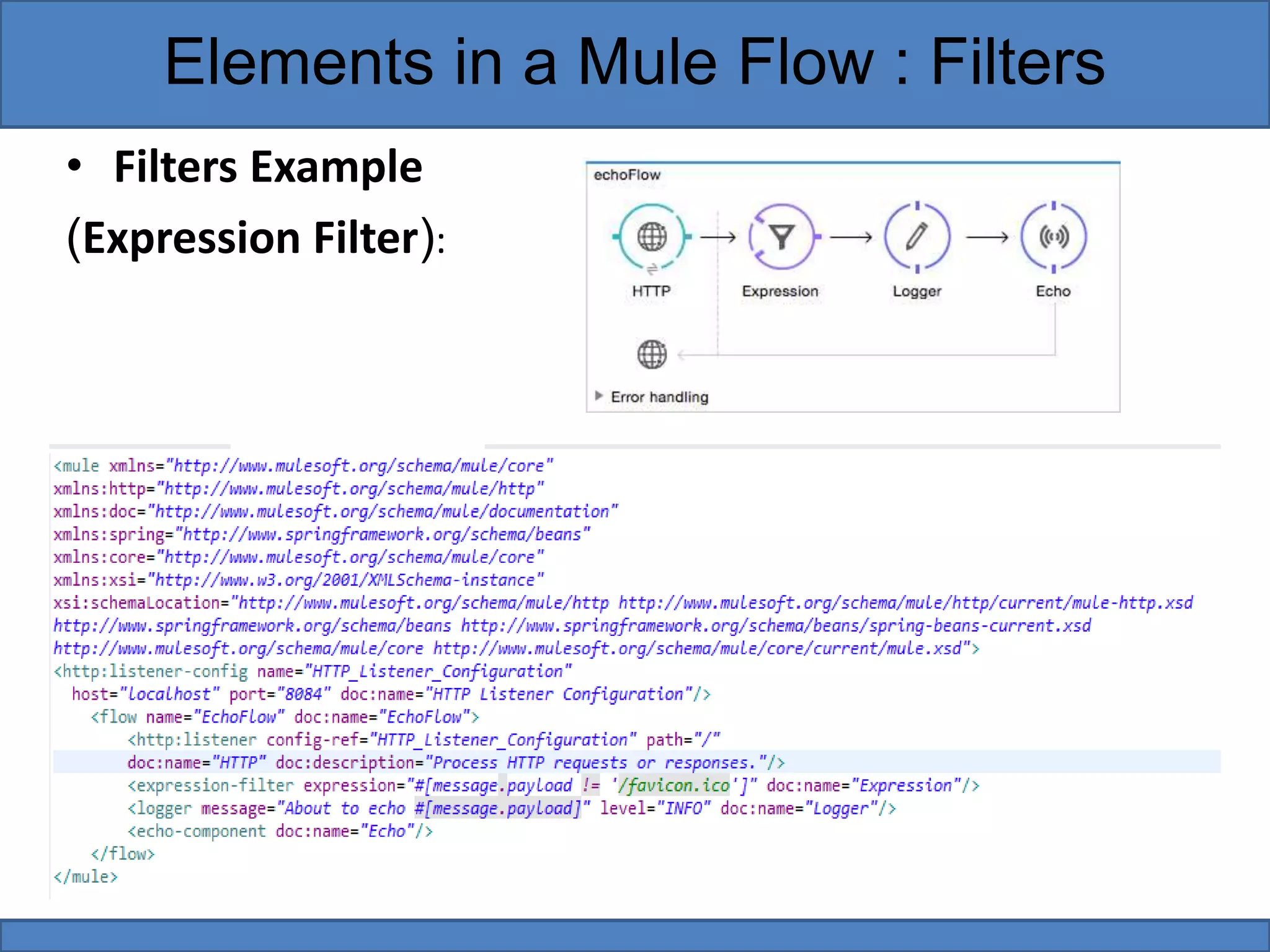
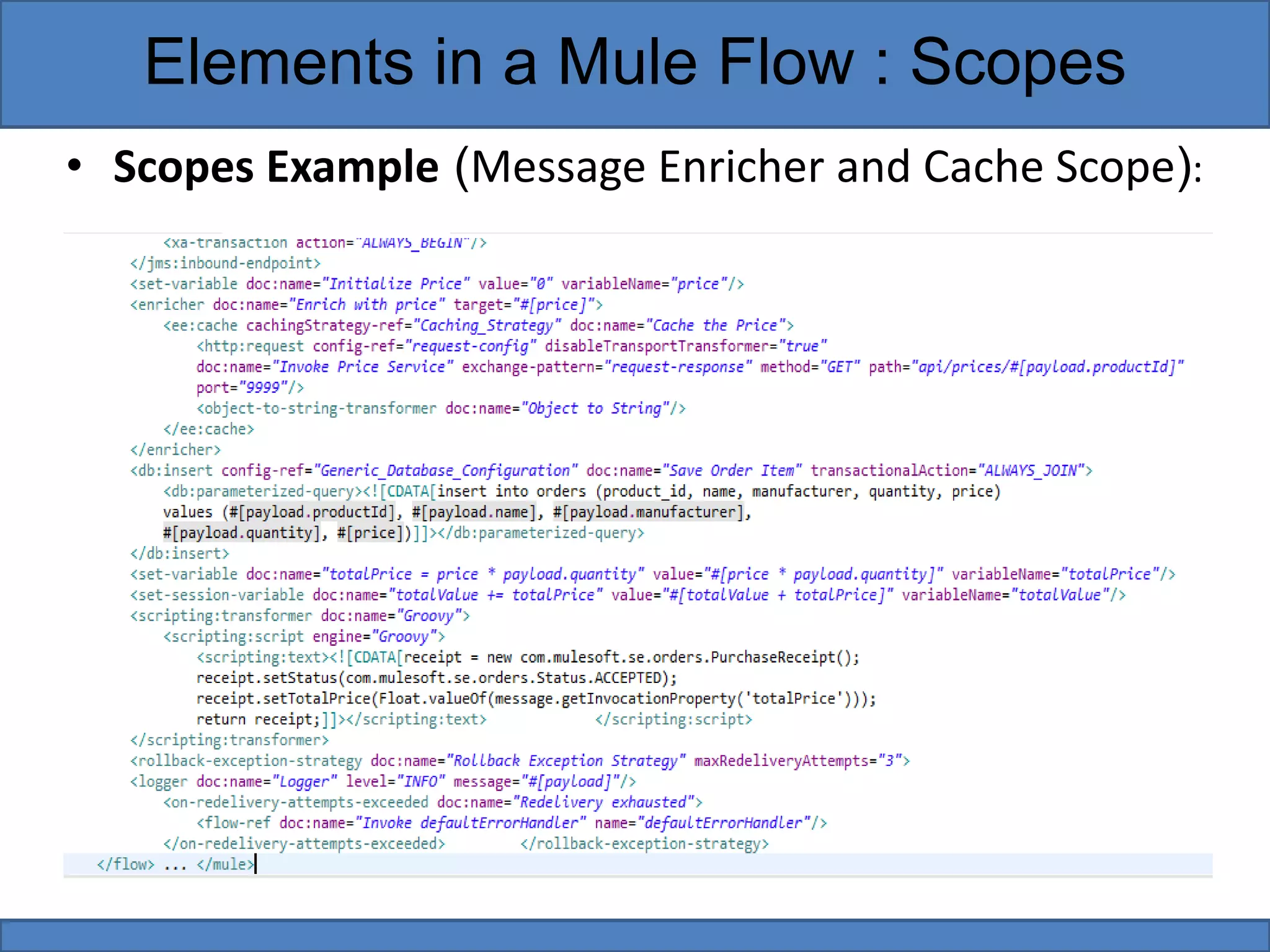
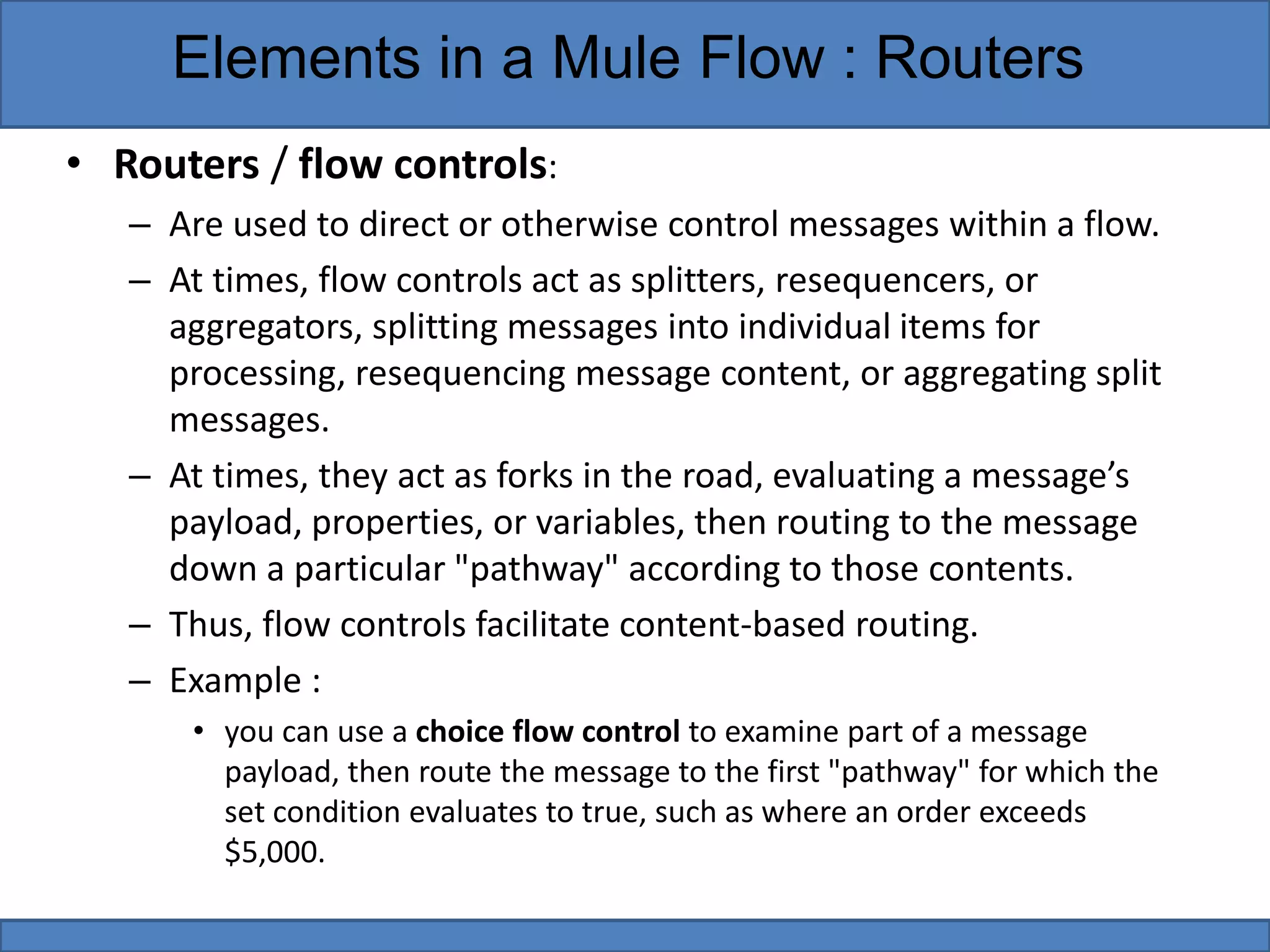
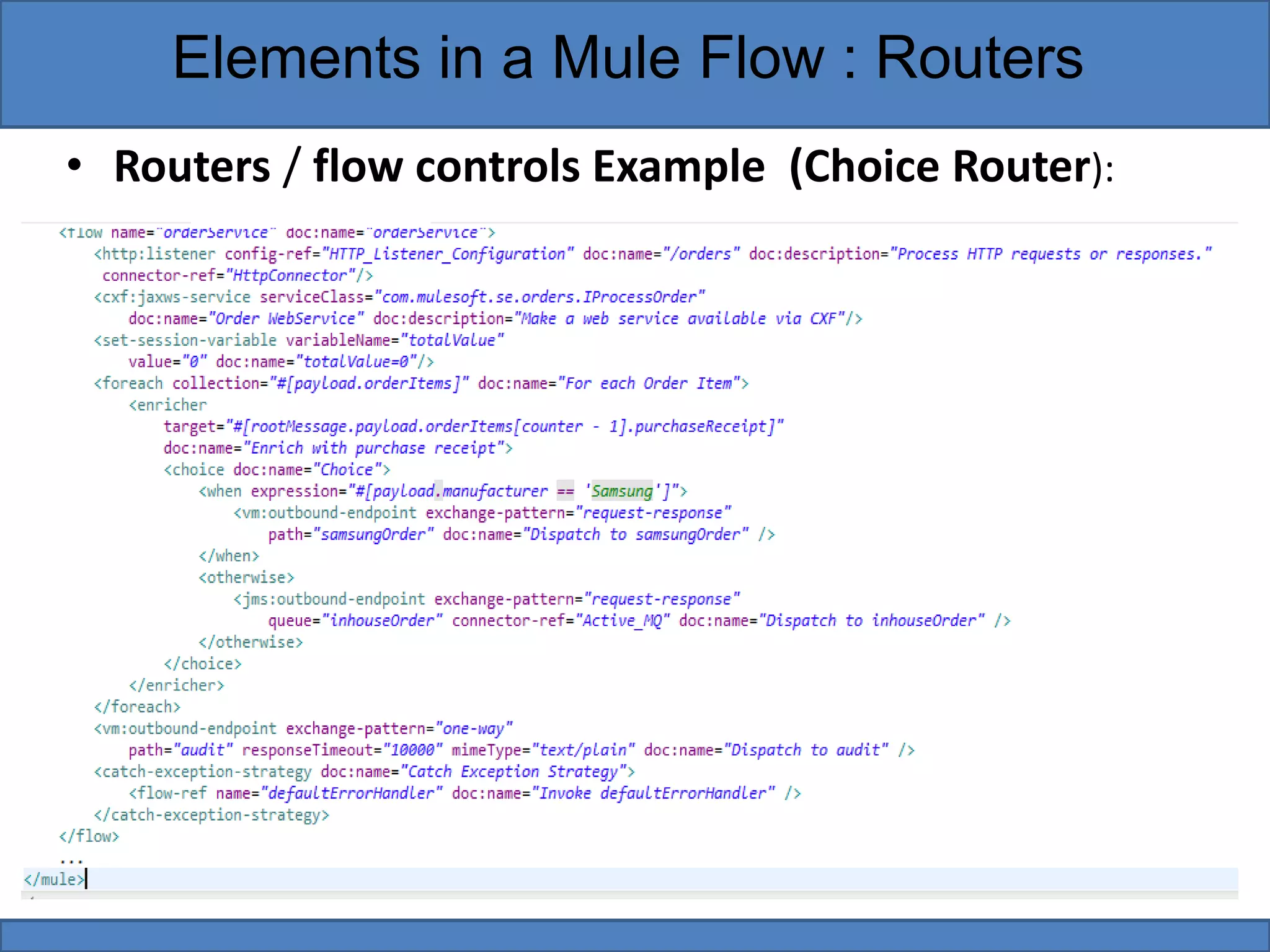
Mule flows contain three main types of elements: filters, scopes, and routers. Filters evaluate messages to determine if they can proceed in the flow. Scopes encapsulate message processors to execute them as a single unit. Routers direct and control messages by splitting, resequencing, aggregating, or routing them based on content. Examples provided demonstrate using filters to reject messages, scopes to add enrichments, and routers to choose processing pathways.