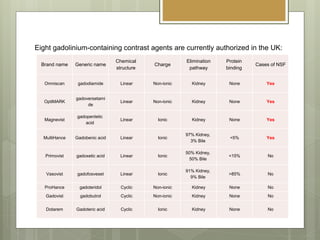
- Contrast agents are substances used in MRI to increase contrast between tissues. Gadolinium is commonly used as it has 7 unpaired electrons giving it a strong magnetic moment. However, gadolinium is toxic so it must be bound to chelate molecules.
- Some gadolinium-based contrast agents have been linked to Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF), a rare condition causing fibrosis of skin and tissues. NSF seems to occur when free gadolinium ions are released from the chelate in patients with kidney problems who cannot eliminate the agent quickly.
- To reduce risks, health regulators now classify agents as high, medium, or low risk for NSF. Strict guidelines around