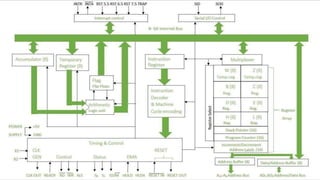
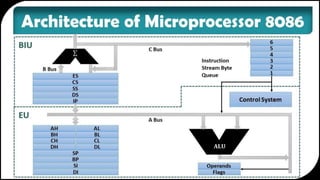
The document discusses the evolution of microprocessor architectures from the 8085 to the 8086. It describes the key features and limitations of the 8085 architecture, including its 8-bit data bus, 16-bit address bus, and limited memory capabilities. It then outlines the introduction of the 8086 architecture by Intel in 1978, which expanded the data bus to 16-bits, address bus to 20-bits, and memory to 1MB. A comparison of the two architectures shows that while the 8086 had improved processing speed and instruction set, its segmented memory addressing was slower.