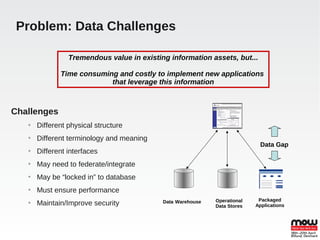
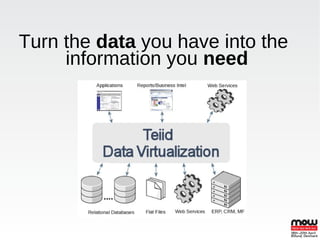
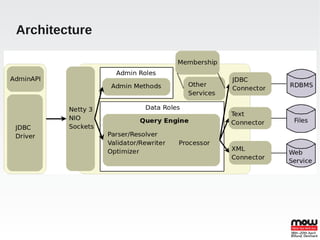
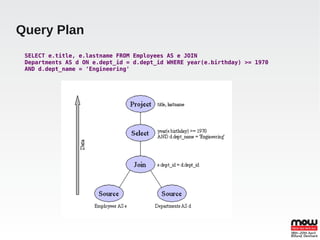
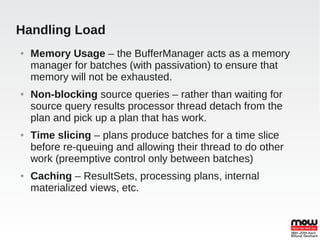
EDS is an open source data virtualization system that allows applications to access and integrate data from multiple heterogeneous data sources through a relational abstraction. It focuses on real-time integration performance, full integration via SQL and procedures, and providing JDBC access. This enables data services and integration of legacy and JPA applications. EDS uses query optimization techniques like access pattern pushdown, dependent and optional joins, and caching to improve performance. It handles large loads through memory buffering, non-blocking source queries, time slicing, and various caching mechanisms. Transactions can be global, local, or at the command level using JTA.