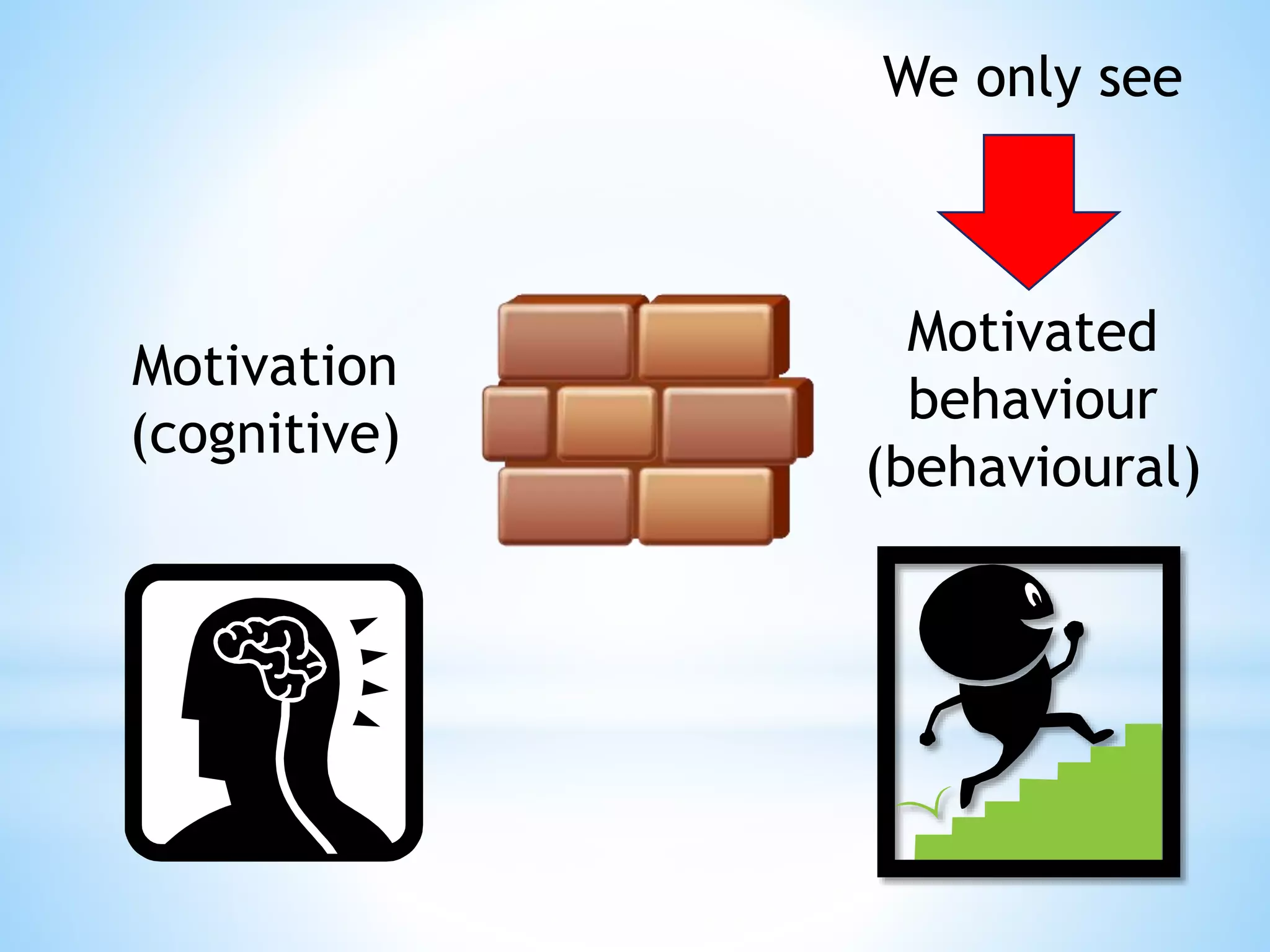
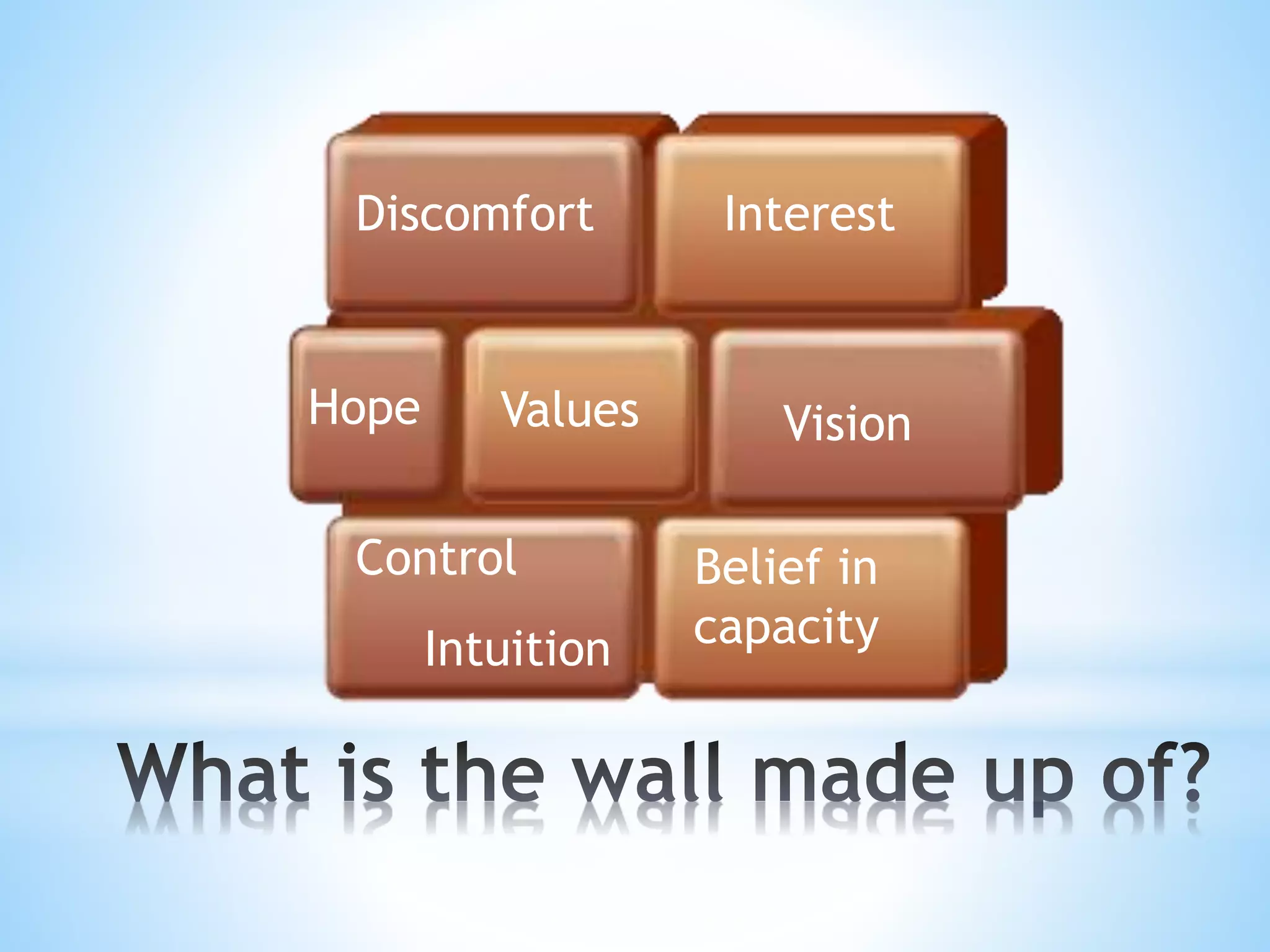
Jo Sherring is an occupational therapist and mental health clinician who is the managing director of The Maya Academy. The document discusses various factors that influence motivation such as interest, discomfort, hope, vision, belief in values, control, and intuition capacity. It provides commentary on each factor and how to help clients overcome barriers to enacting desired changes. The Maya Academy provides free videos, commentaries, posters, and tools and will soon offer courses to help break down walls and facilitate motivation.