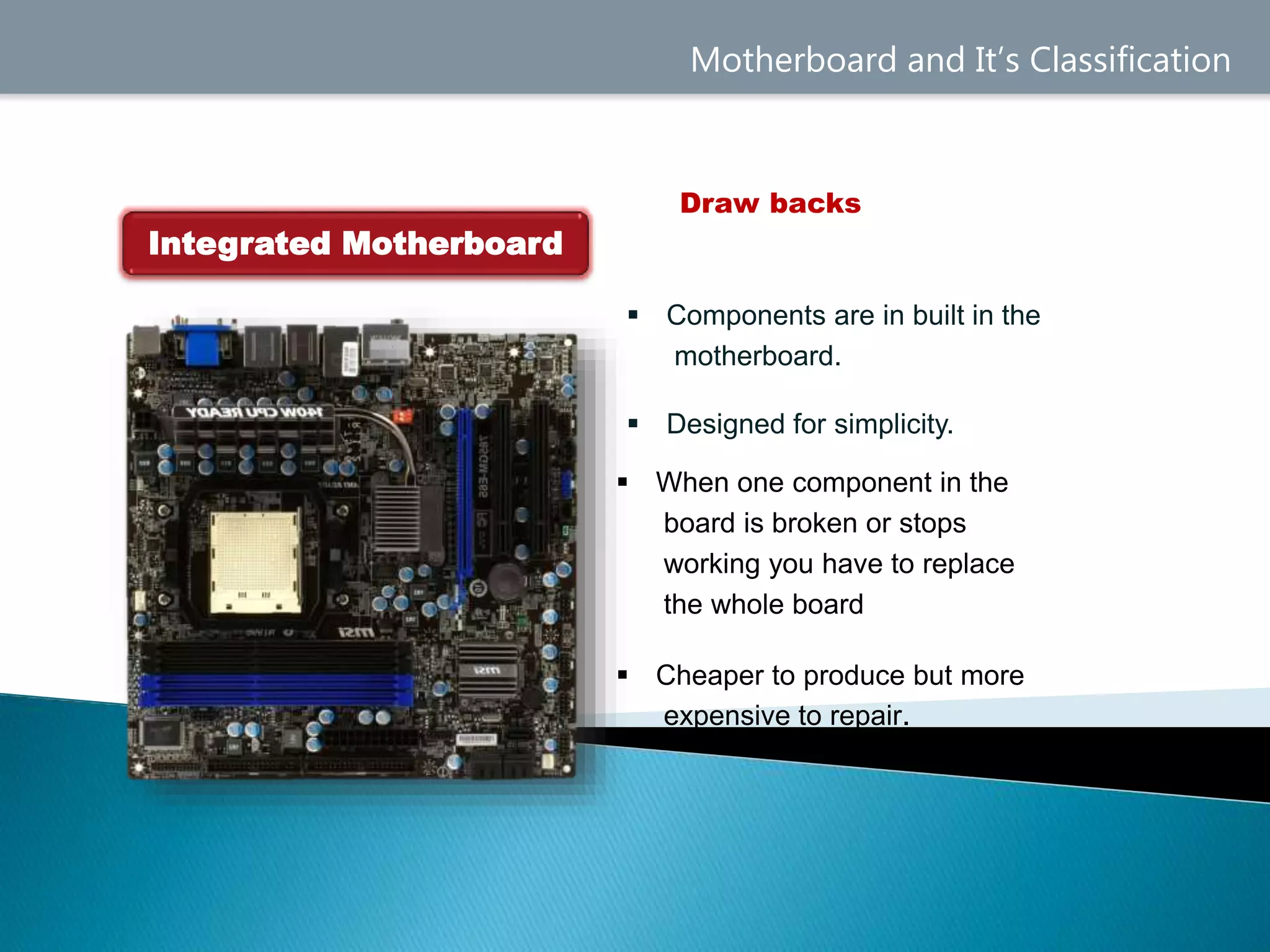
1. A motherboard integrates all the hardware components and allows them to communicate through traces on its circuit boards.
2. Motherboards are classified by their form factor, chipset, and whether components are built-in or require expansion cards.
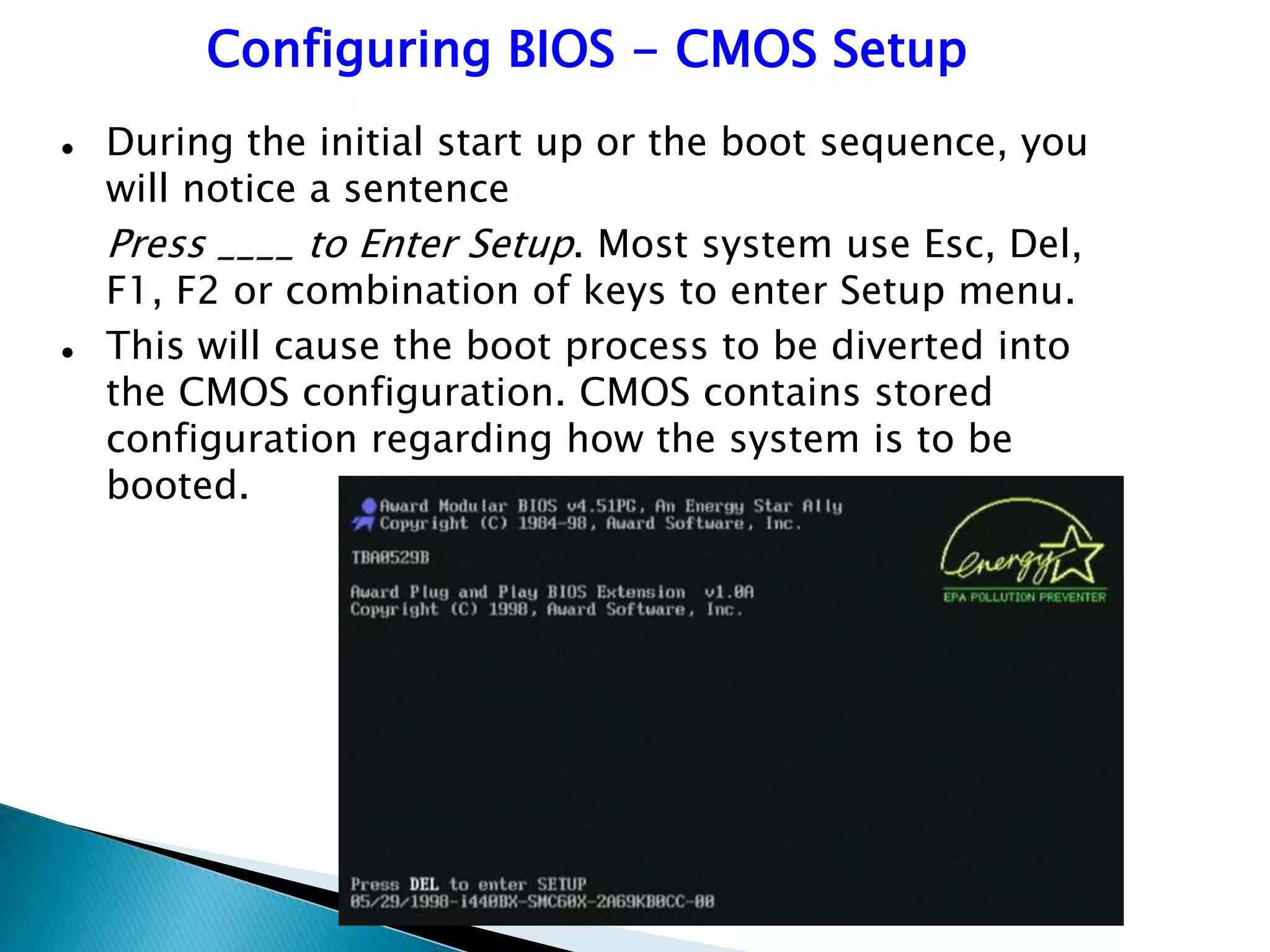
3. When a computer is turned on, the BIOS provides basic instructions to detect hardware and find an operating system to boot from.