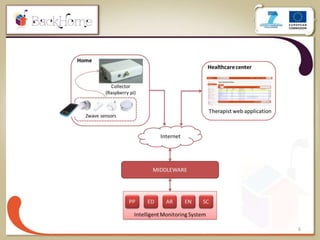
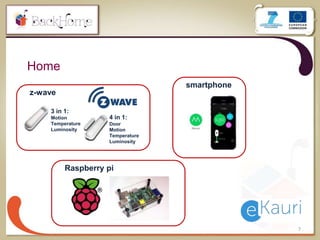
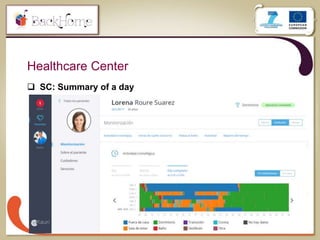
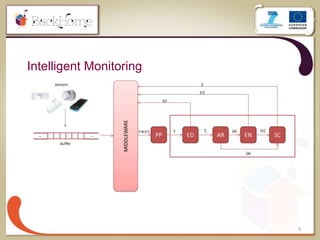
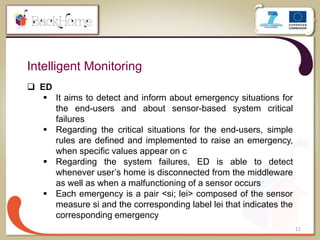
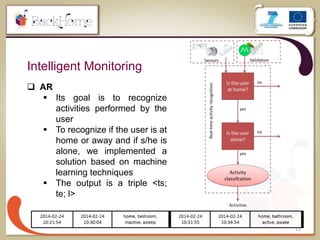
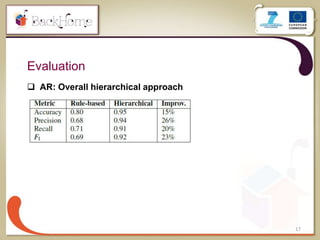
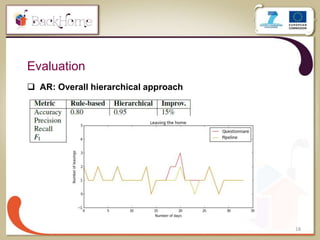
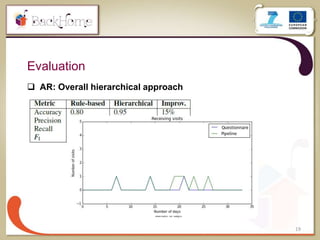
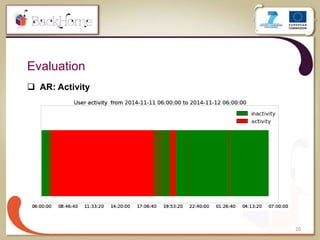
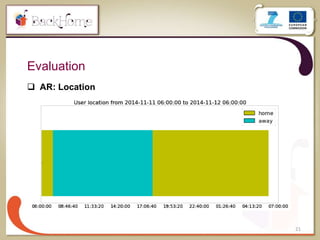
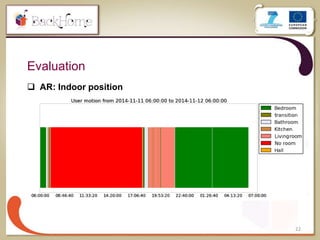
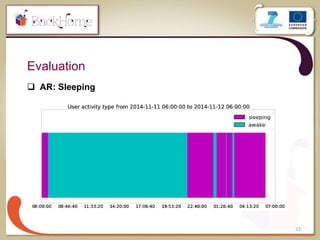
The document discusses a sensor-based telemonitoring system designed to assist elderly and disabled individuals in living independently at home. It outlines the system's capabilities in monitoring health and activity, including emergency detection and quality-of-life assessments, as well as its implementation in two EU projects: Saapho and Backhome. The evaluation results demonstrate the system's effectiveness in enhancing user safety and overall well-being.