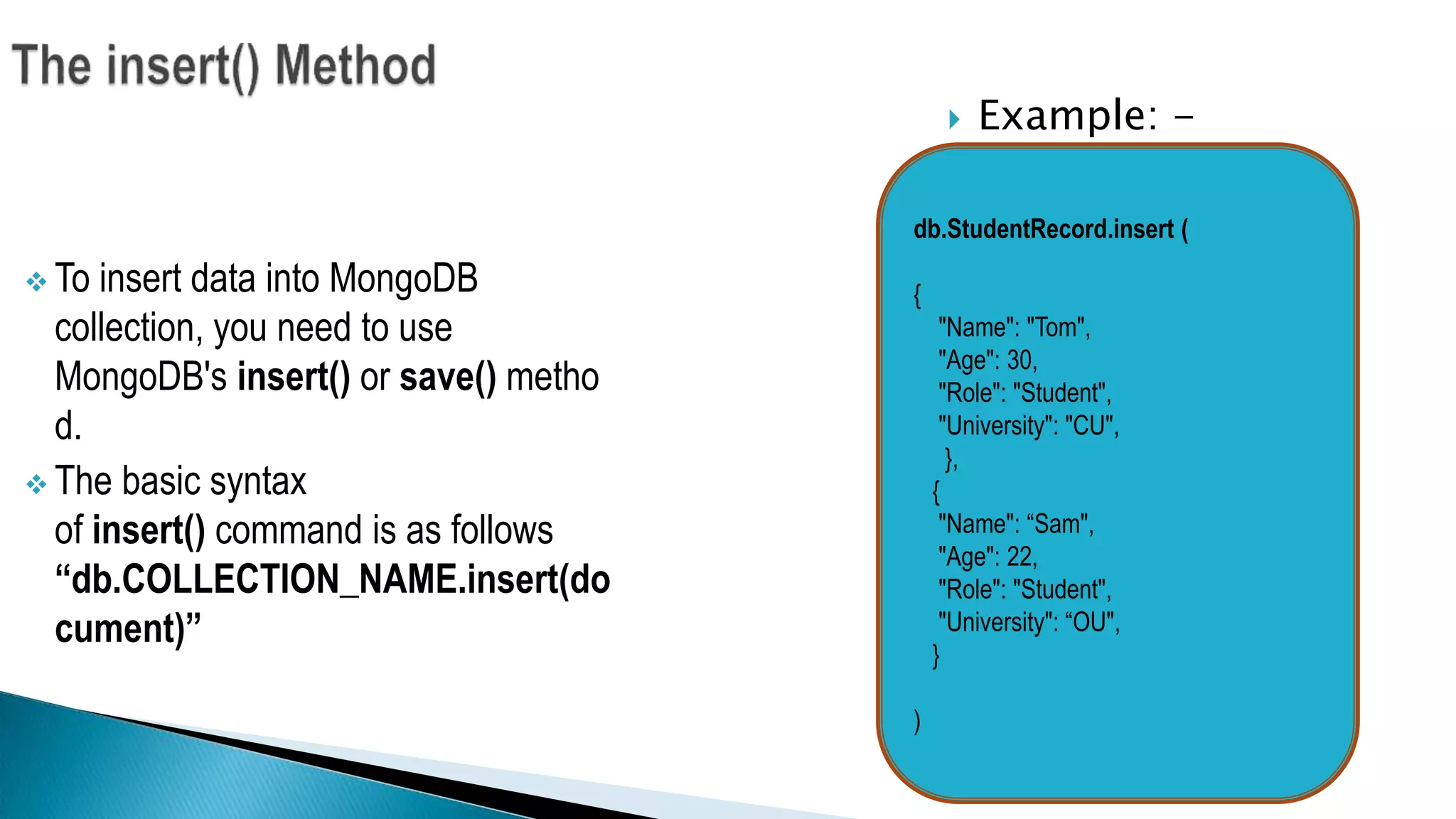
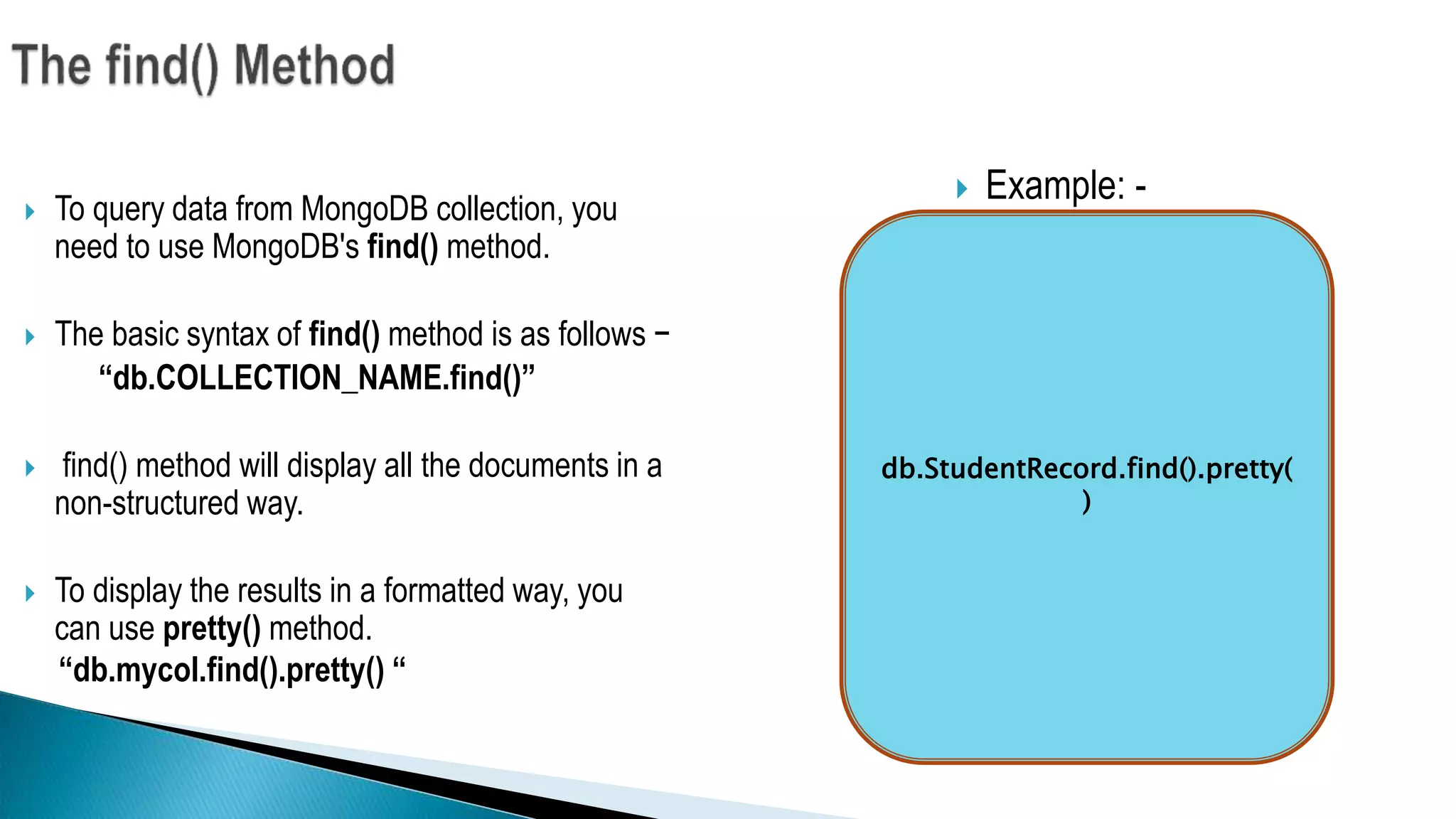
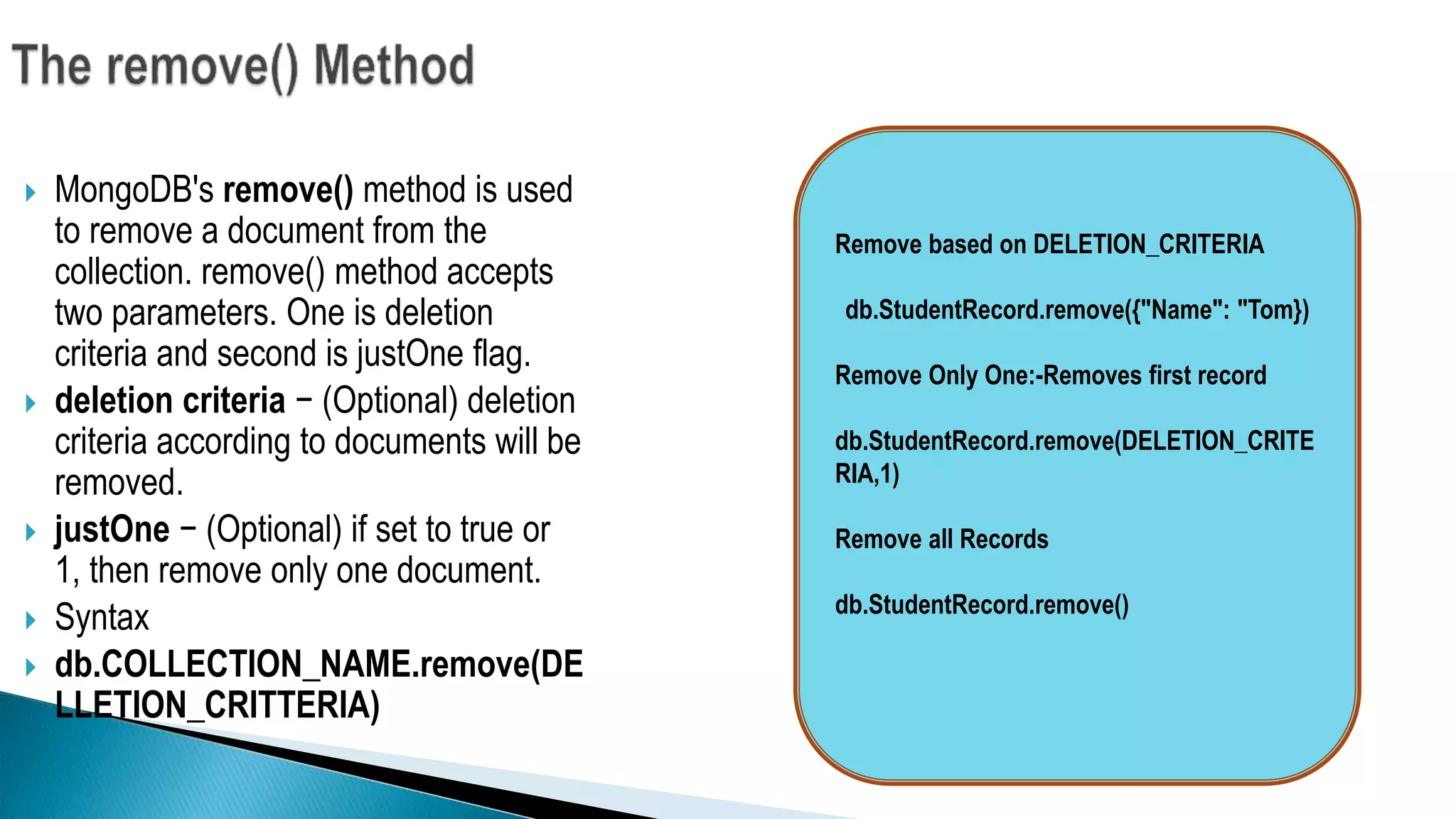
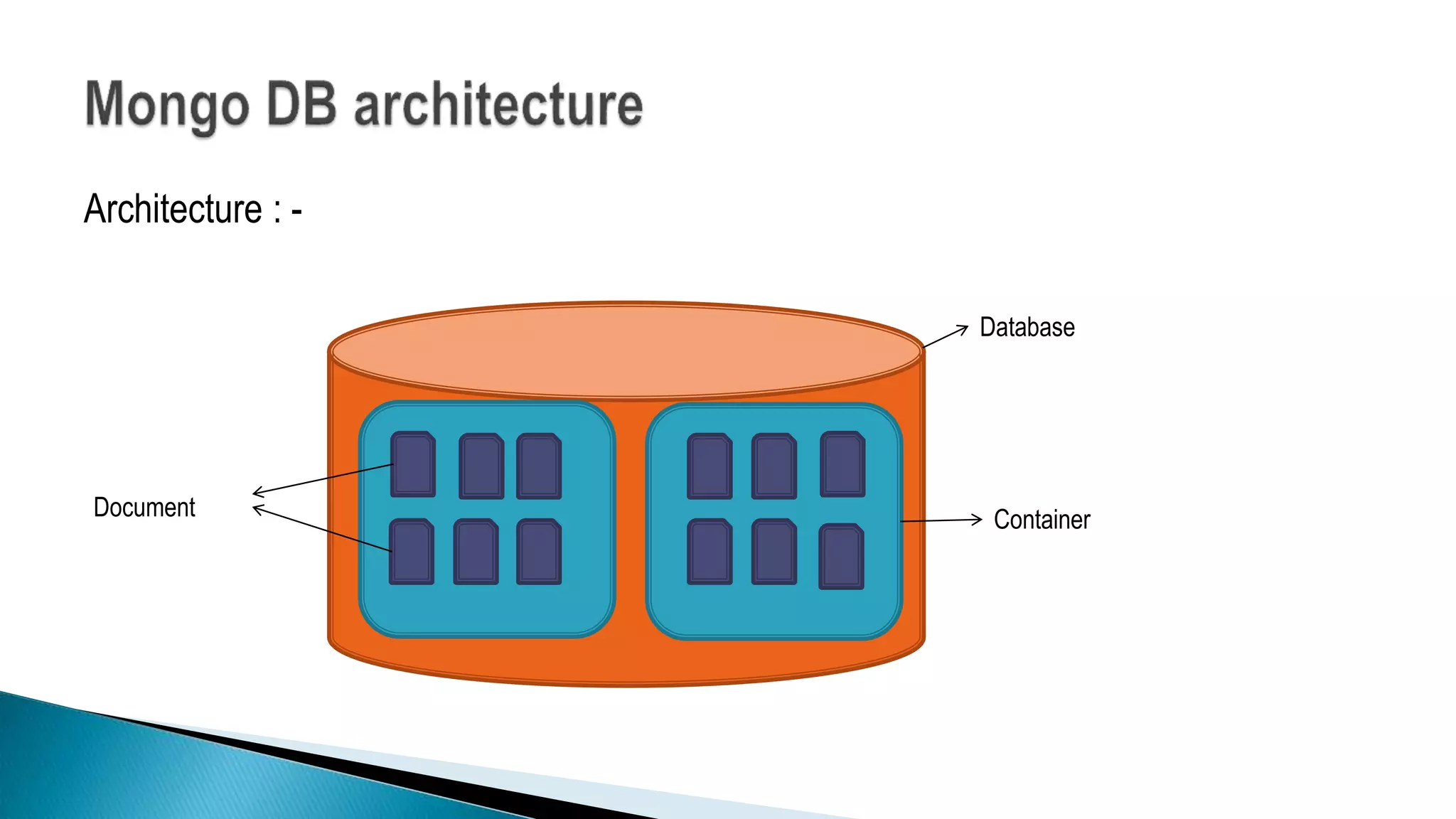
The document discusses NoSQL databases and MongoDB. It defines NoSQL, describes different types of NoSQL databases like key-value, document, graph and column-oriented. It then focuses on MongoDB, explaining its advantages like high performance, flexibility and rich queries. It covers MongoDB concepts like collections and documents. It also discusses JSON structure, MongoDB methods for insertion, querying and removal of documents. Finally, it provides examples of when to use MongoDB, such as for unstructured data, high volume read/writes and changing schemas.

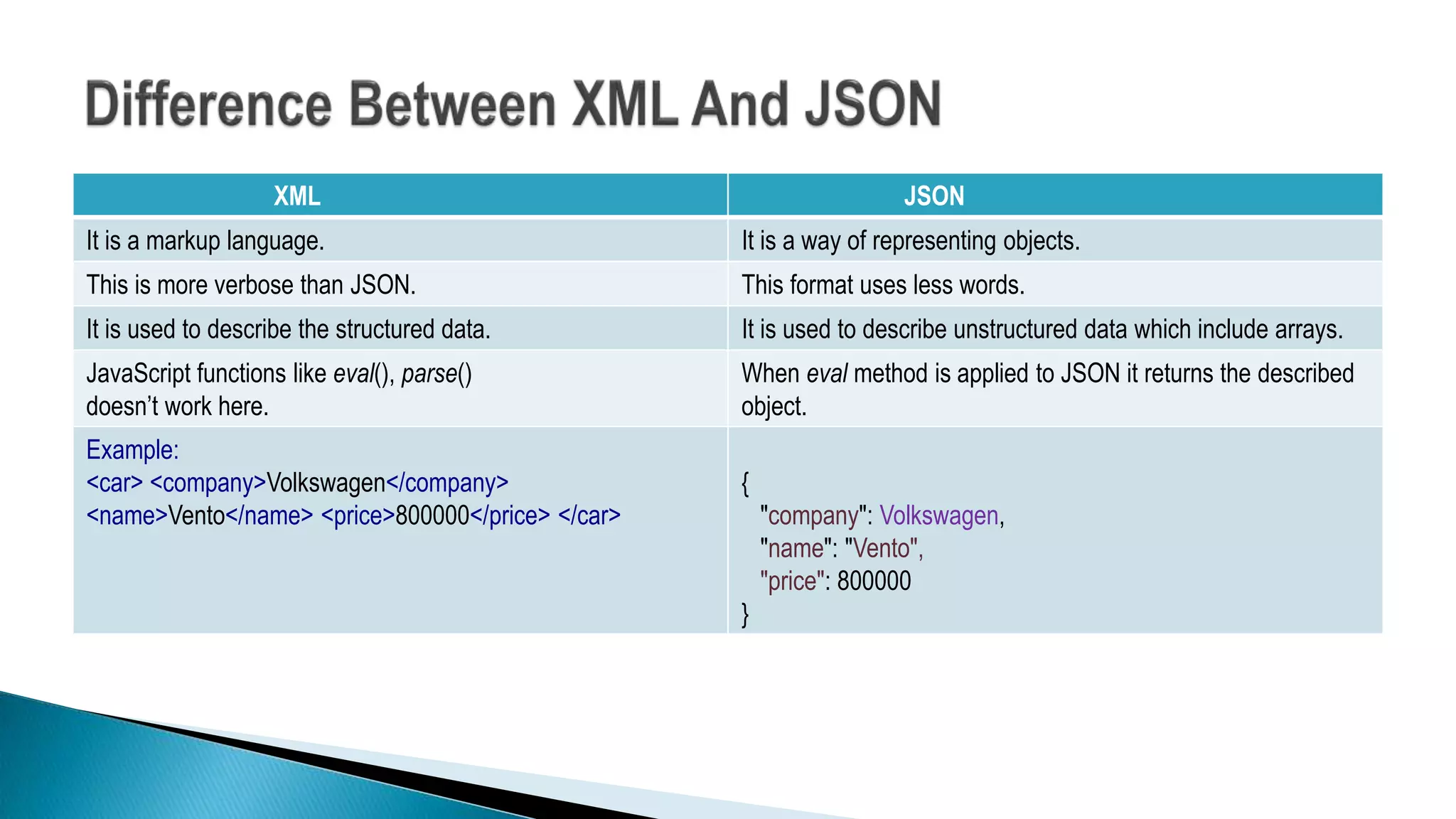
![ Key Value pair
Dynamo DB
Azure Table Storage (ATS )
Graph database
Document Based
Mango Db
AmazonSimple DB
Couch DB
Column Oriented database
(#key,#value)
(Name, Tom)
(Age,25)
(Role,
Student)
(University,
CU)
[
{
"Name": "Tom",
"Age": 30,
"Role": "Student",
"University": "CU",
}
]
Student
Tom
CU
25
Masters
Ottawa Location
• Neo4j
• Infogrid
Row Id Columns
1
Name Tom
Age 25
Role Student
Bigtable(Google)
HBase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-190524095252/75/Mongodb-4-2048.jpg)
![ The document has simple structure and very easy to
understand the content
JSON is smaller, faster and lightweight compared to XML.
For data delivery between servers and browsers, JSON is a
better choice
Easy in parsing, processing, validating in all languages
JSON can be mapped more easily into object oriented
system.
[
{
"Name": "Tom",
"Age": 30,
"Role": "Student",
"University": "CU",
}
{
"Name": “Sam",
"Age": 32,
"Role": "Student",
"University": “OU",
}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-190524095252/75/Mongodb-8-2048.jpg)