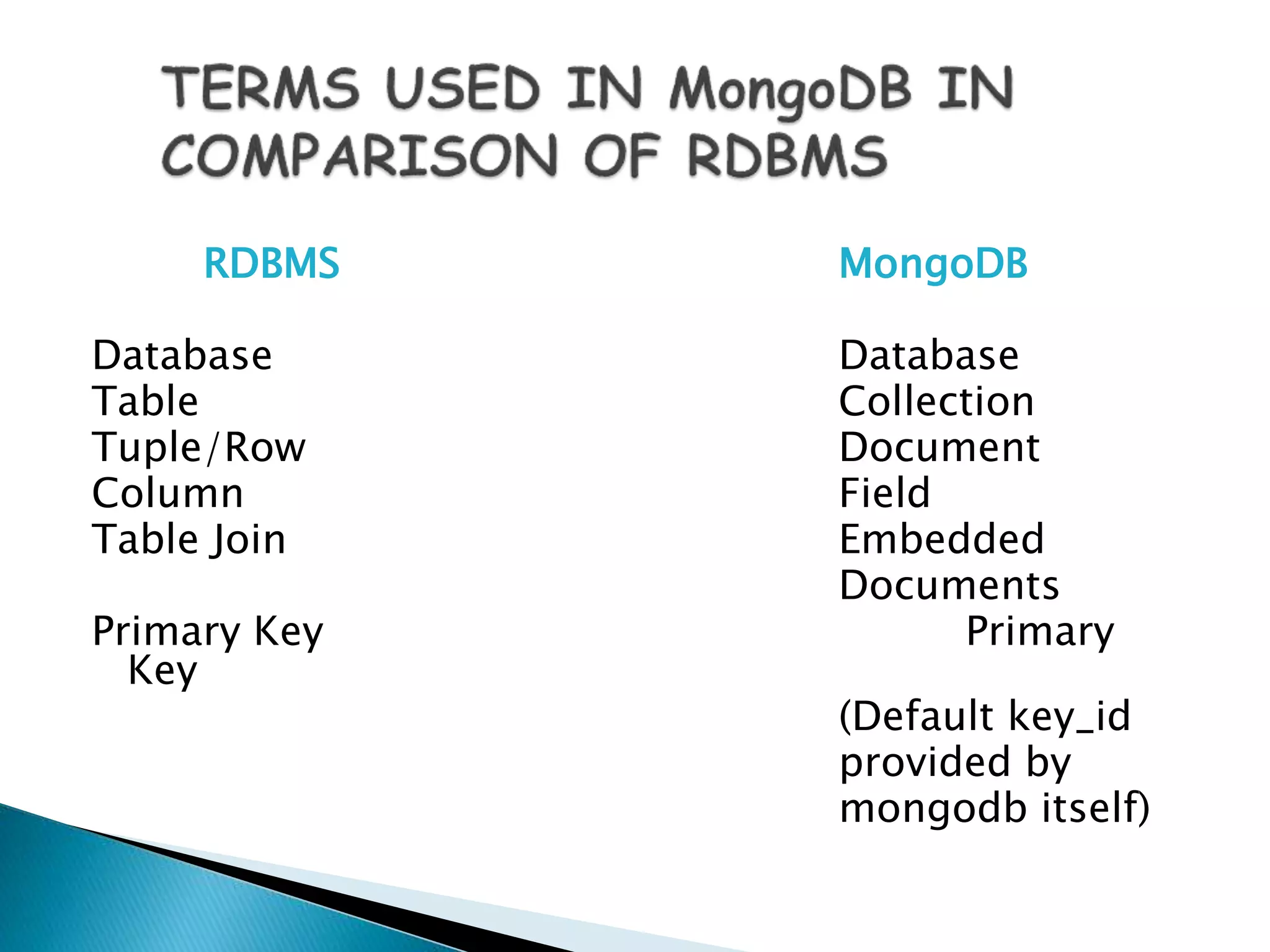
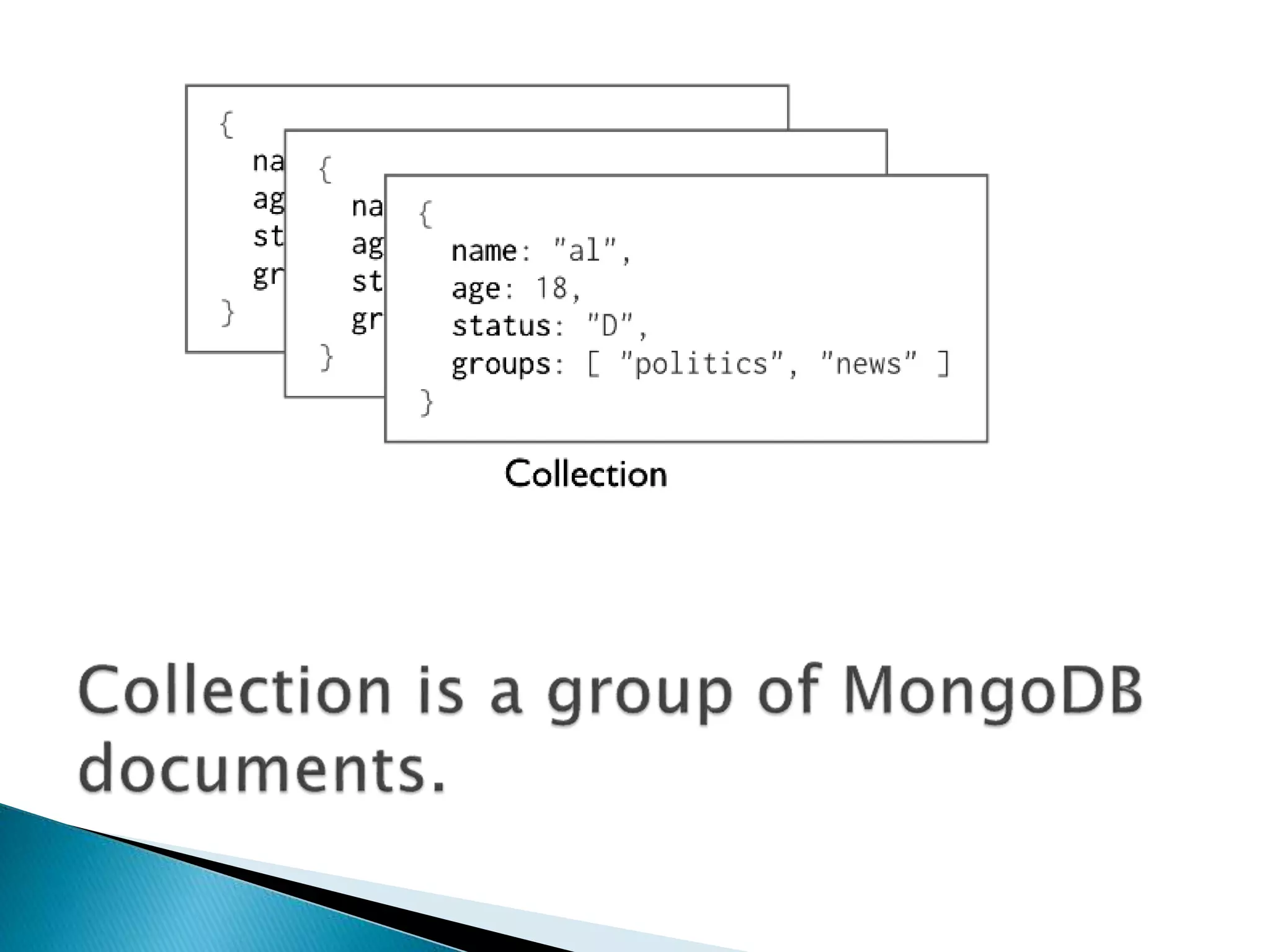
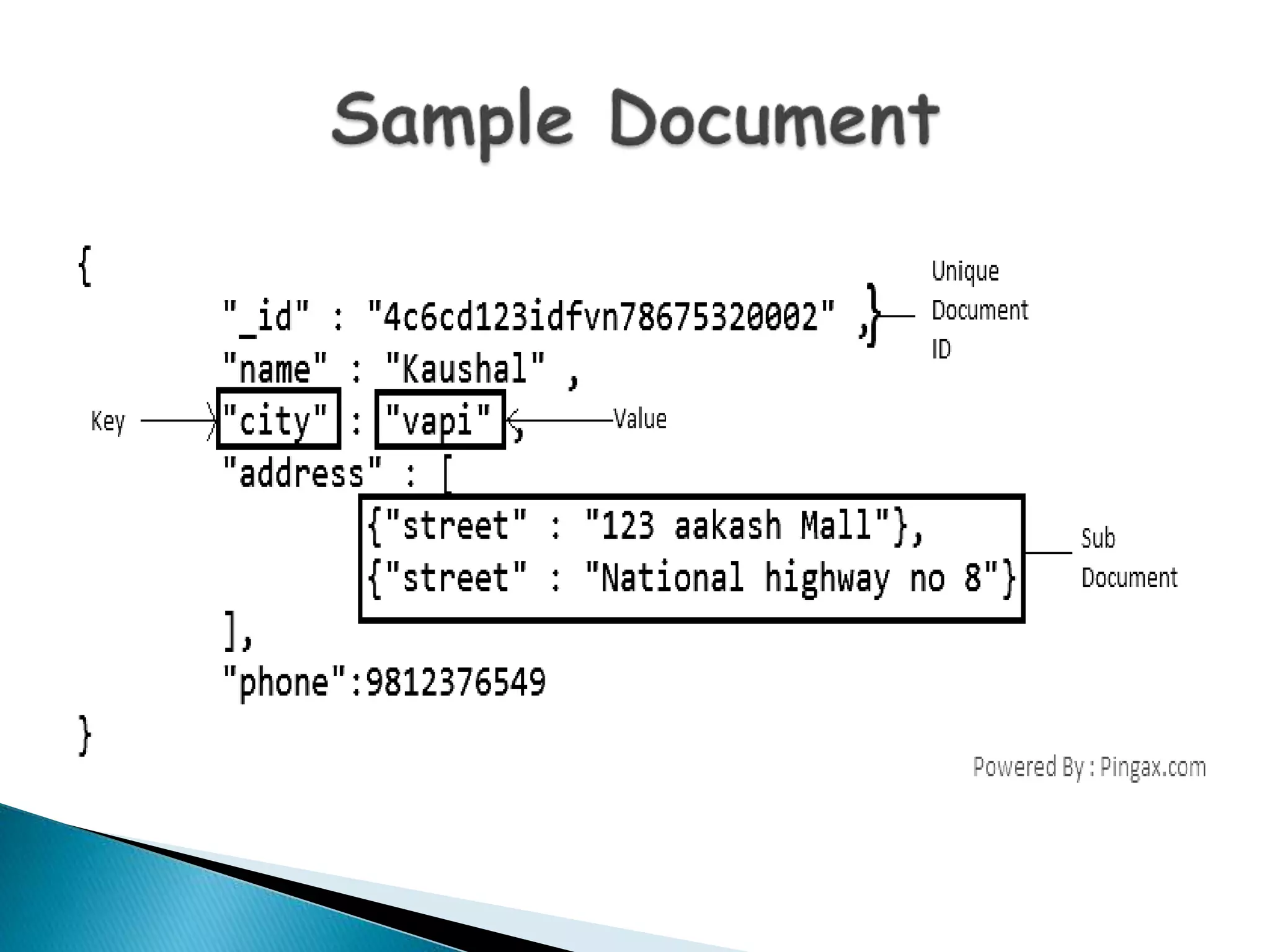
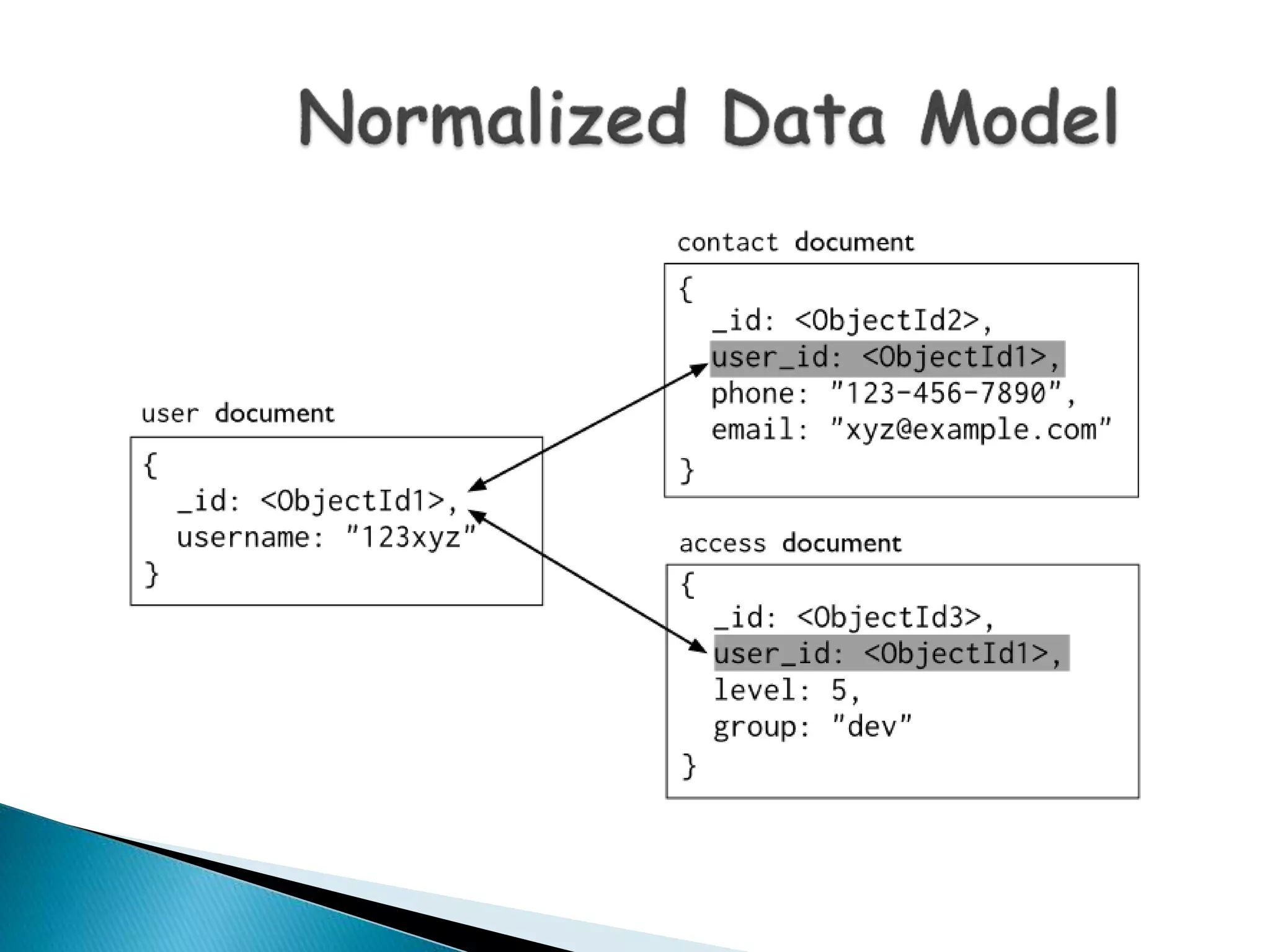
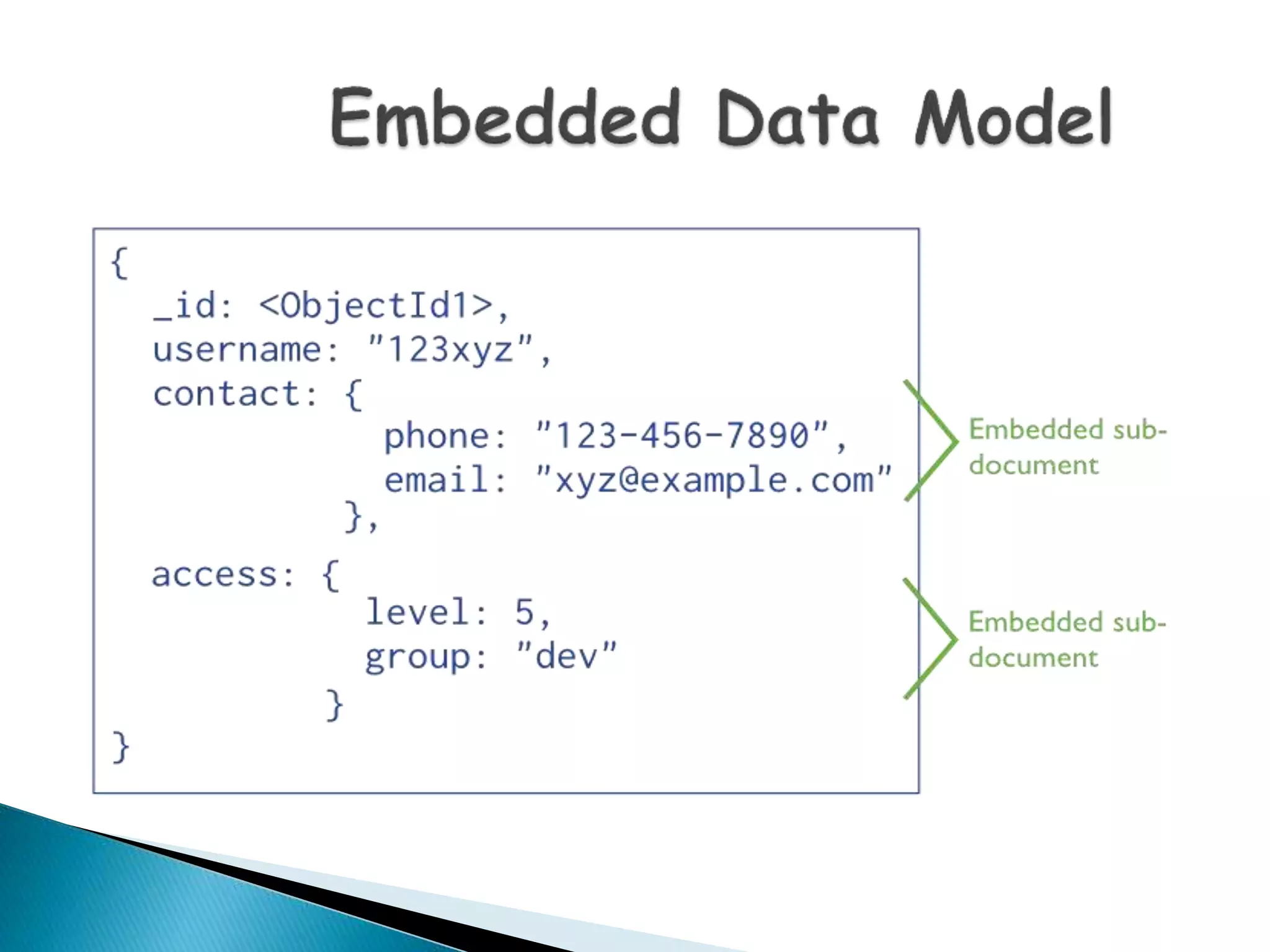
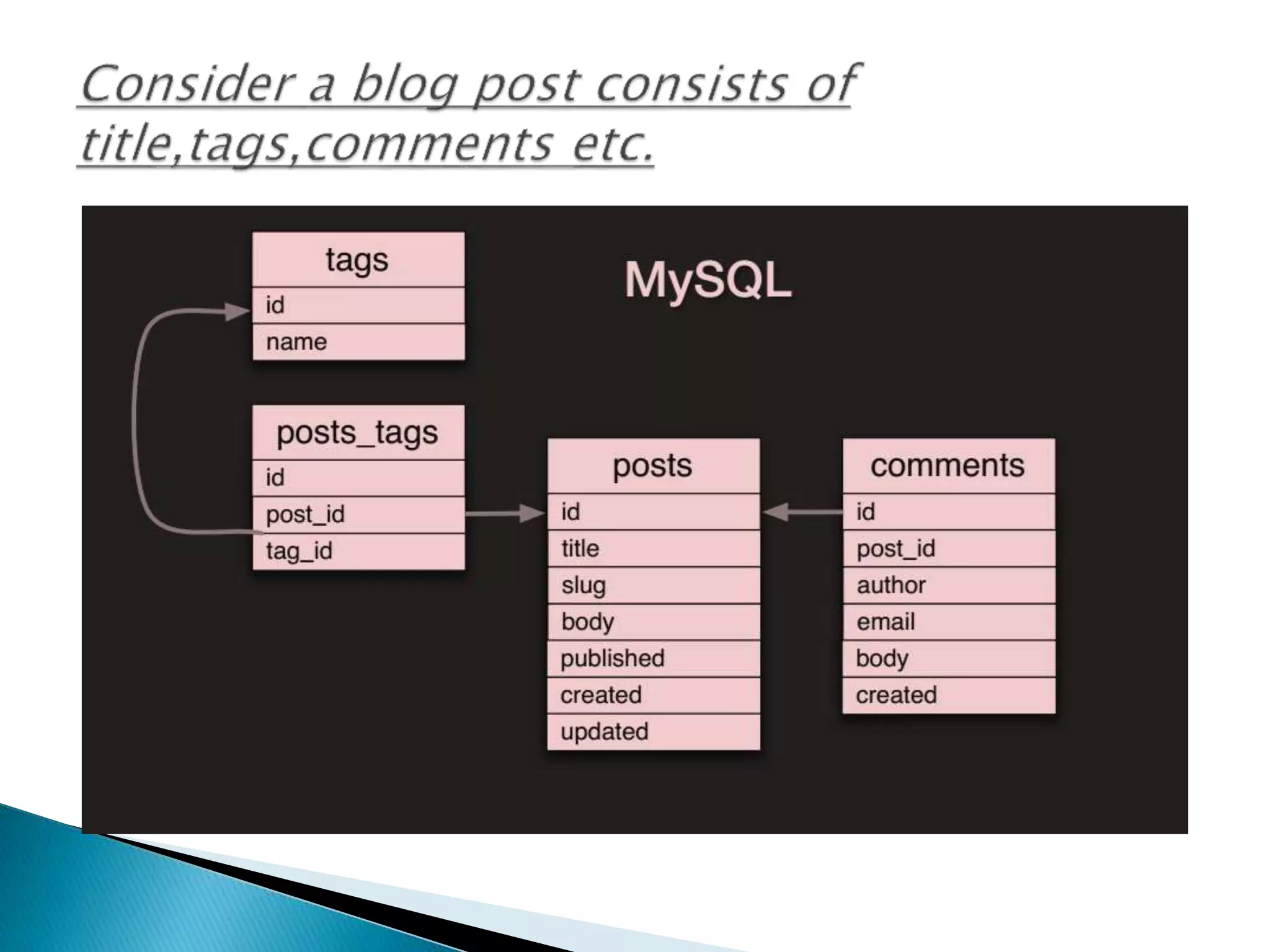
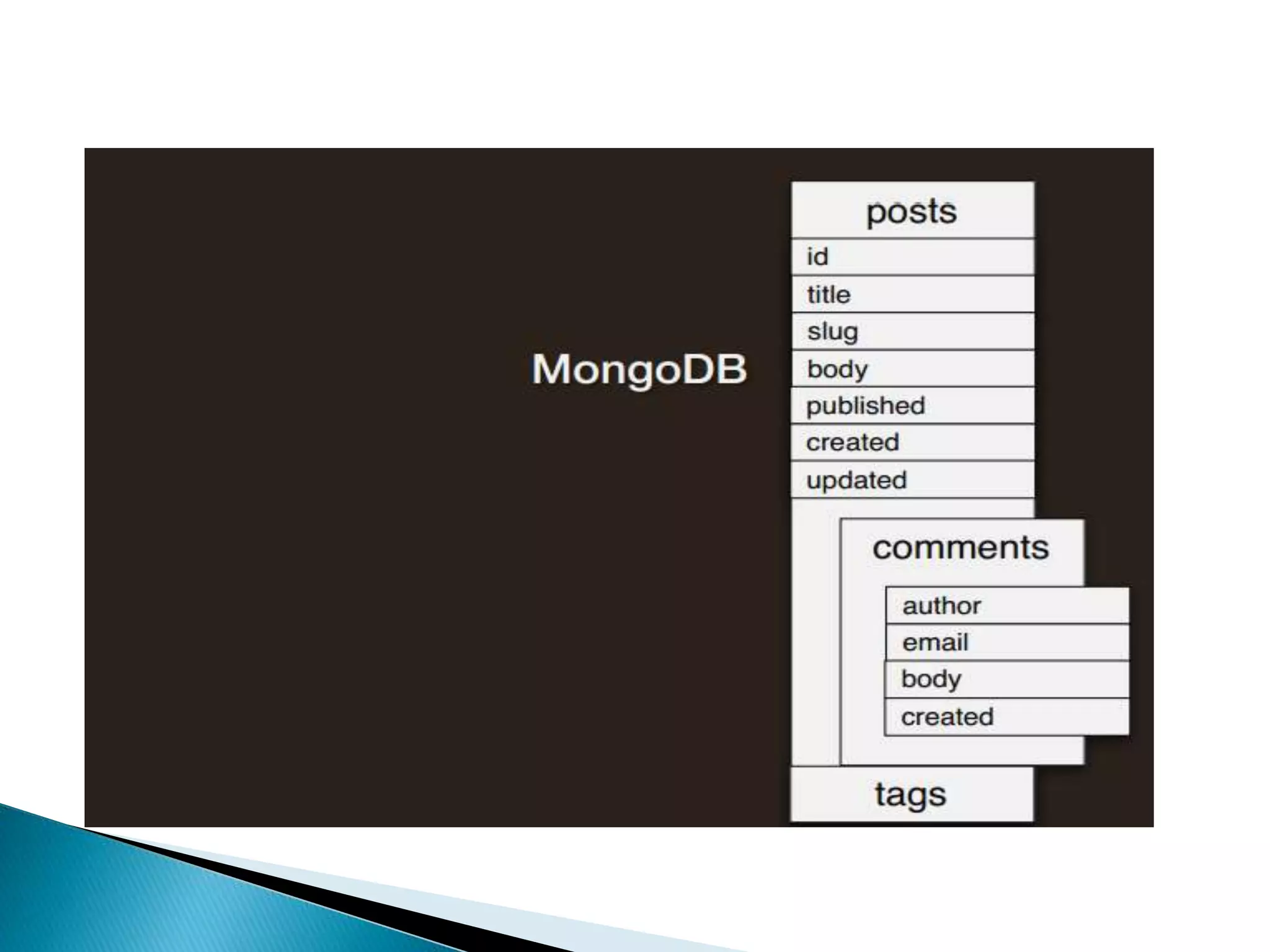
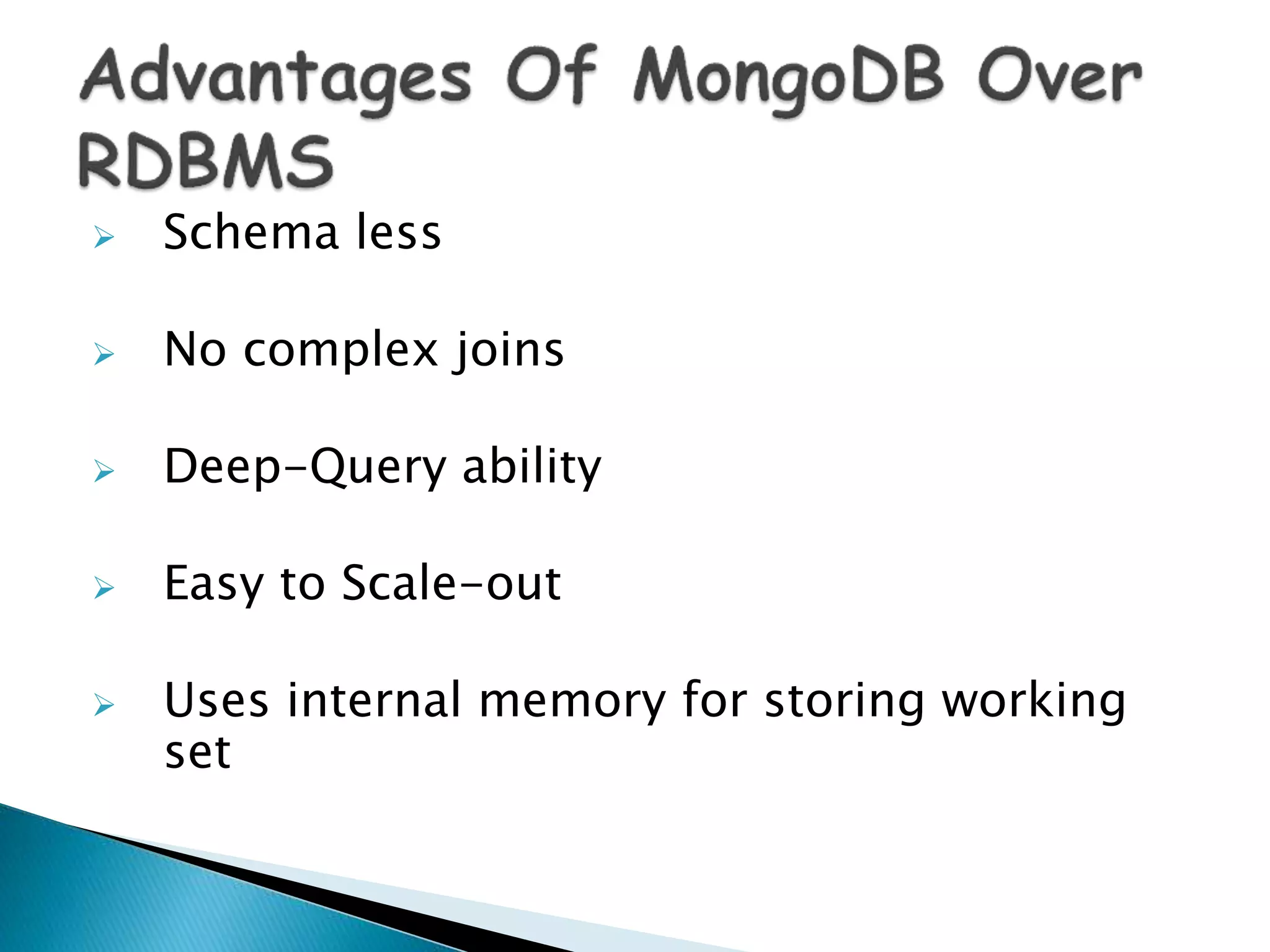
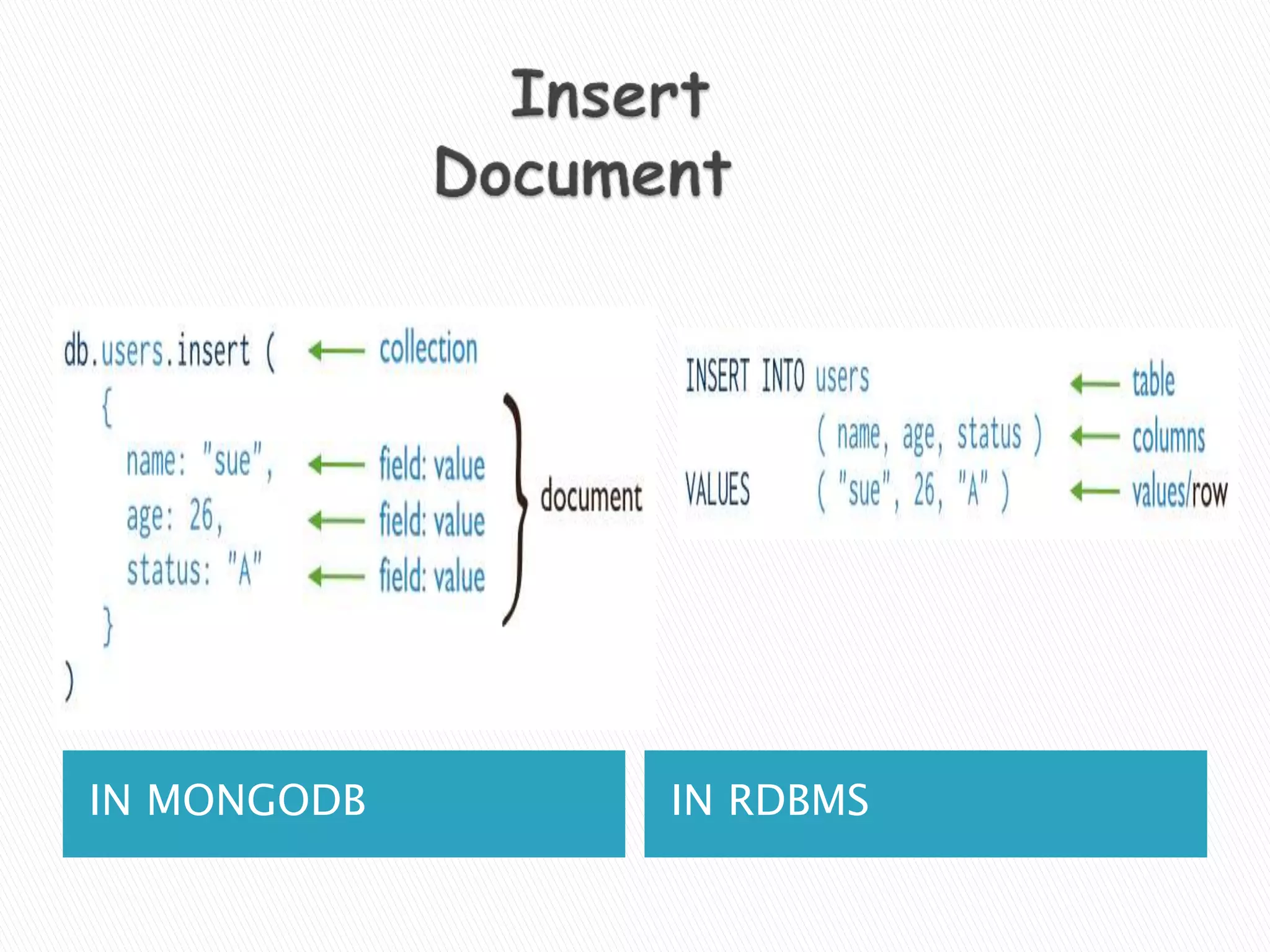
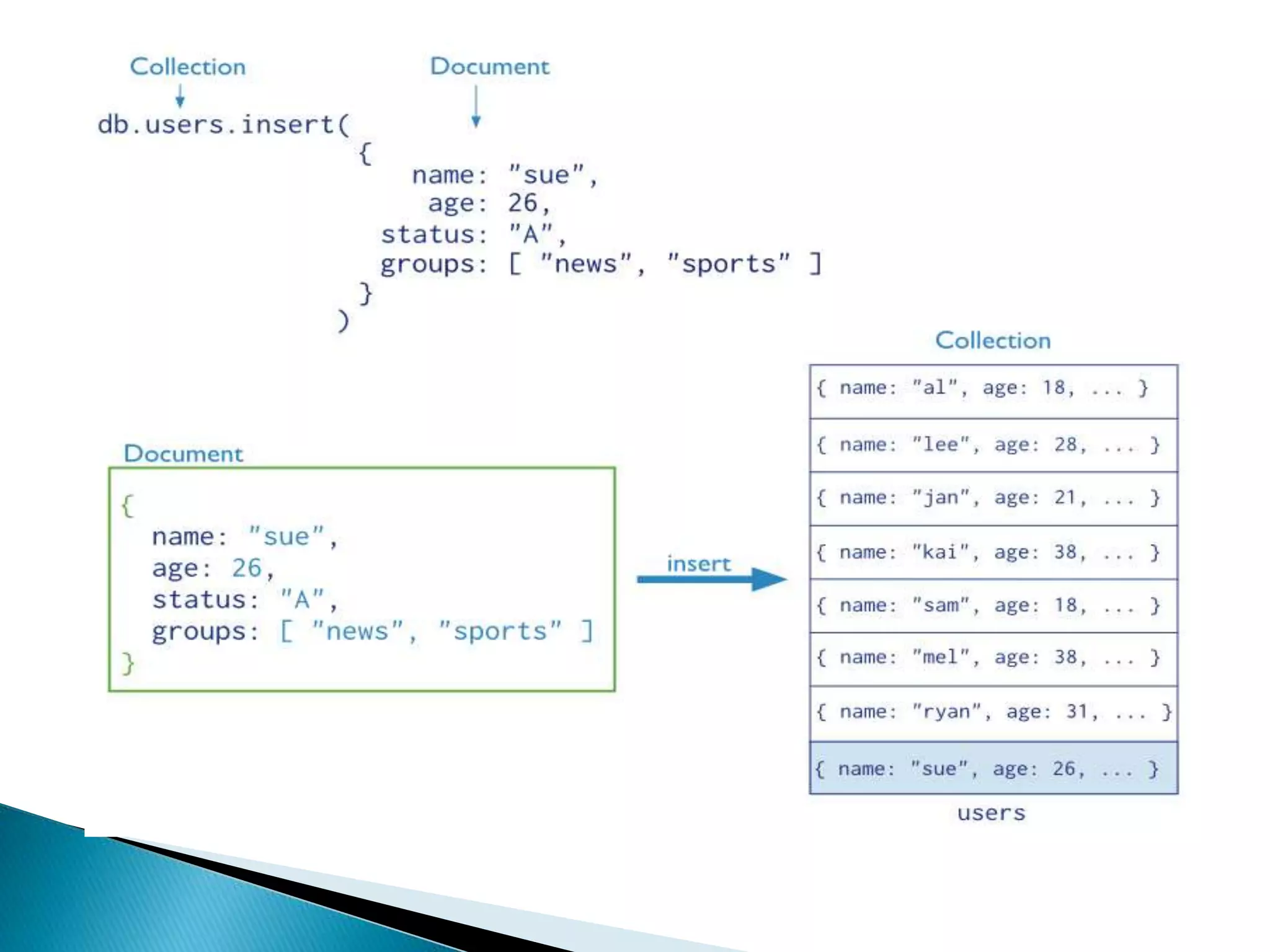
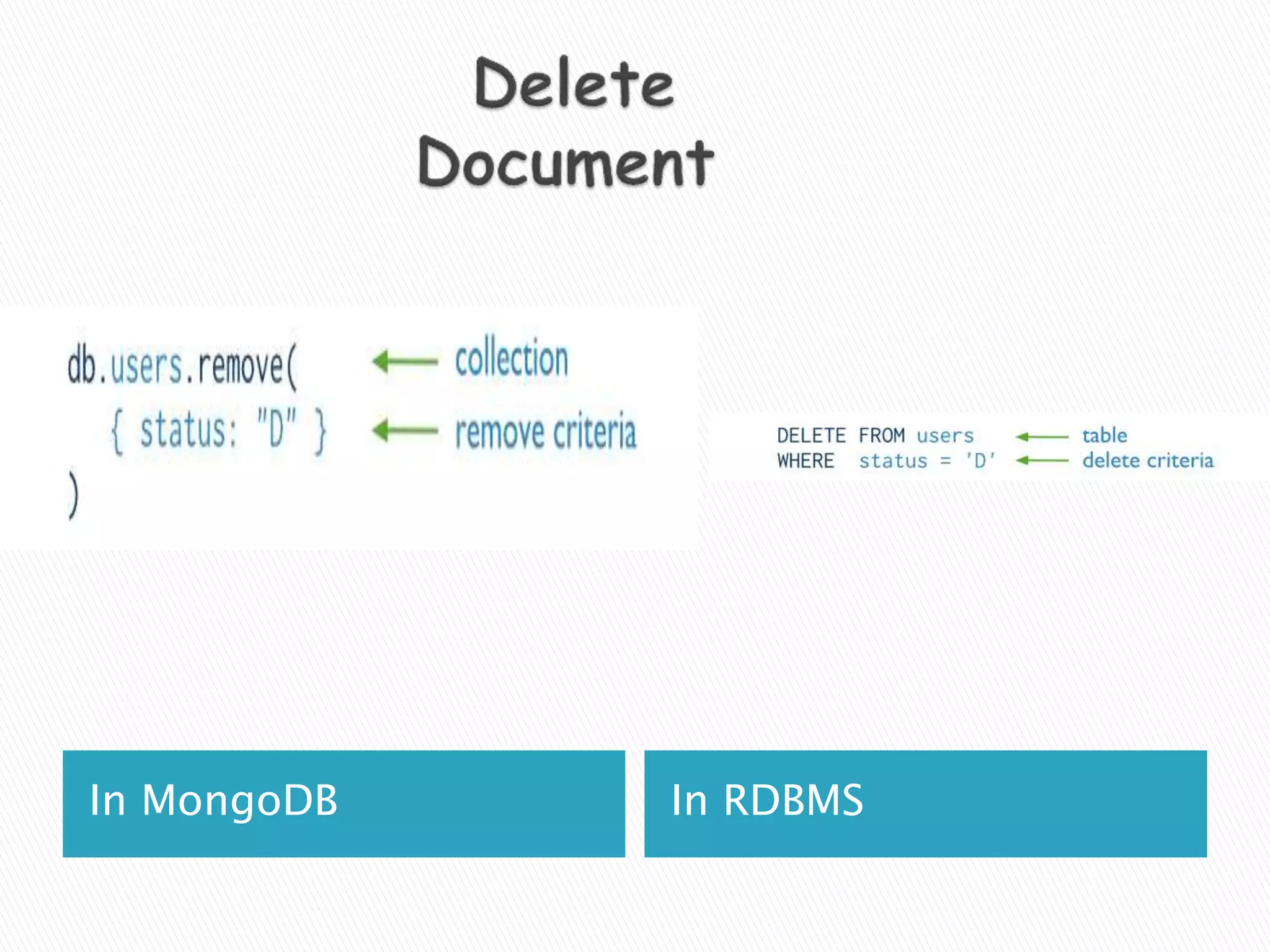
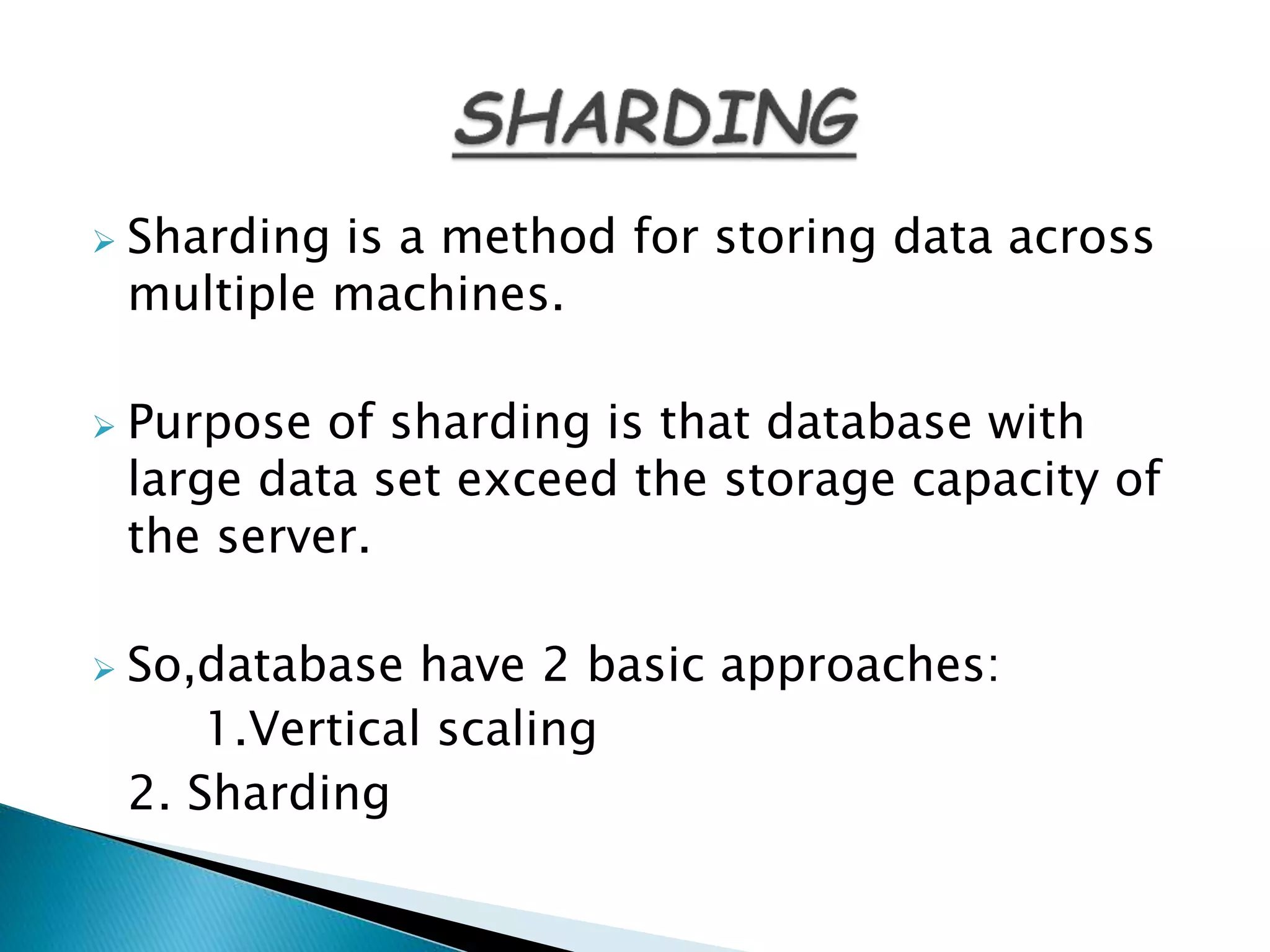
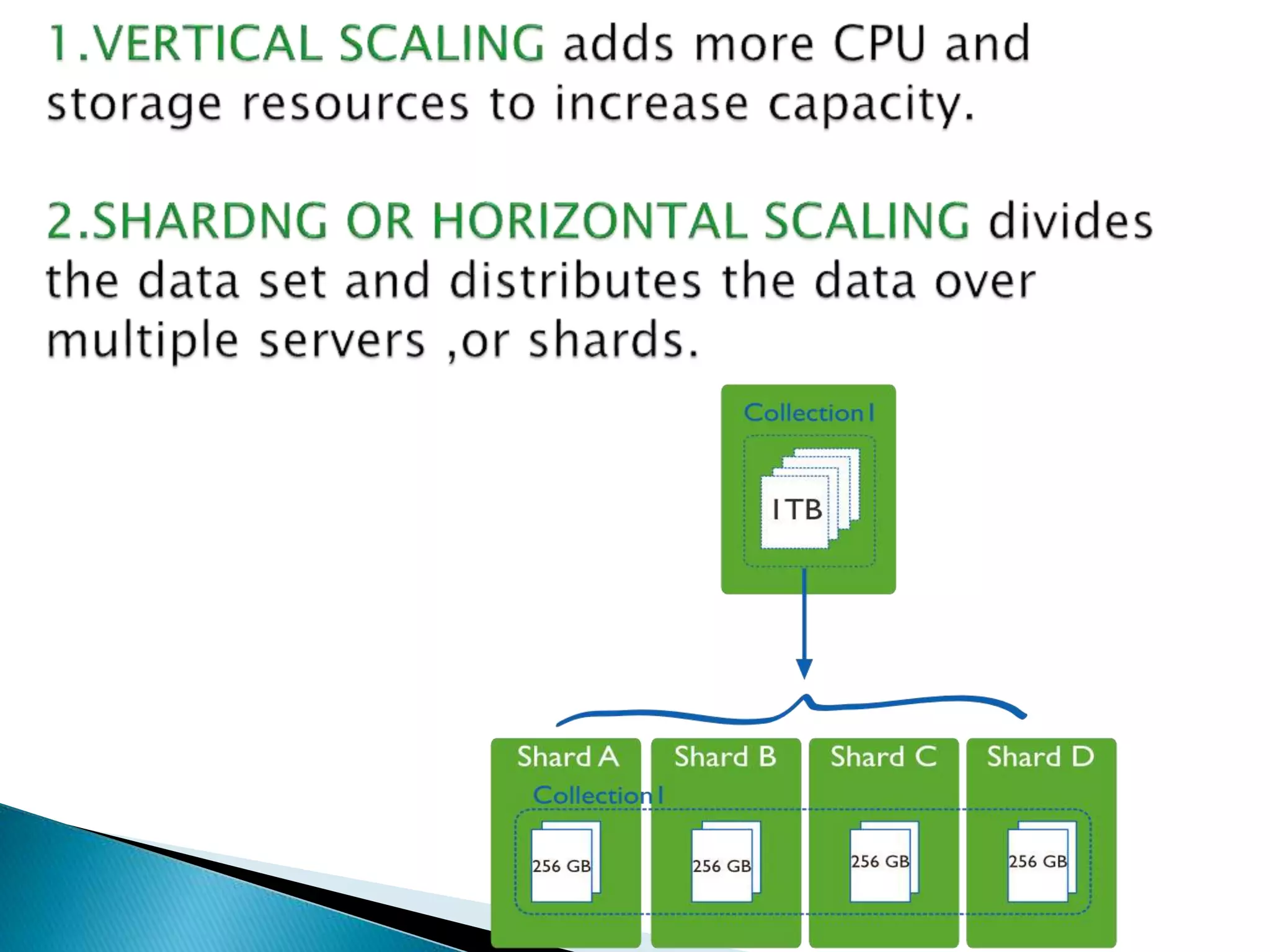
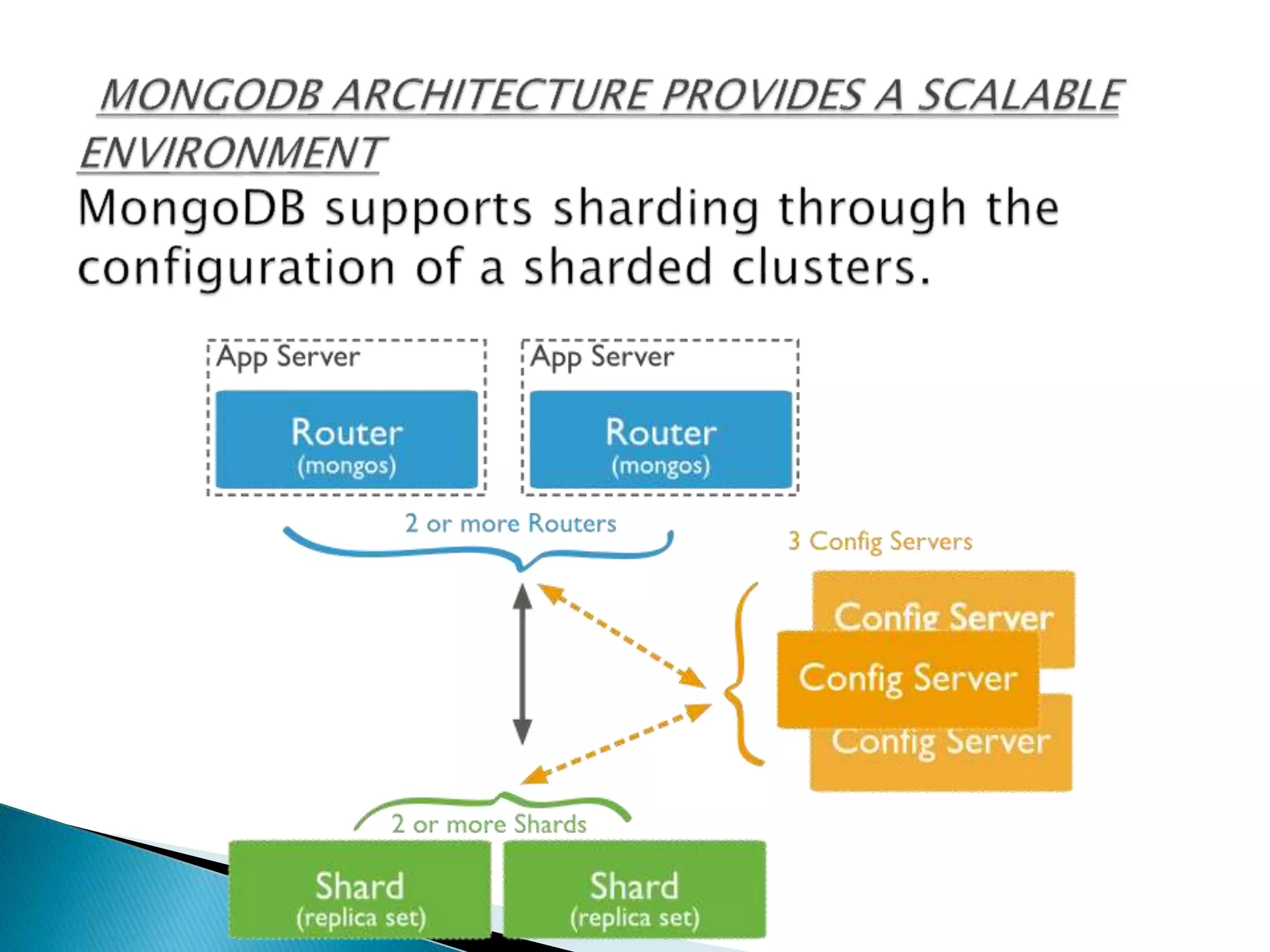
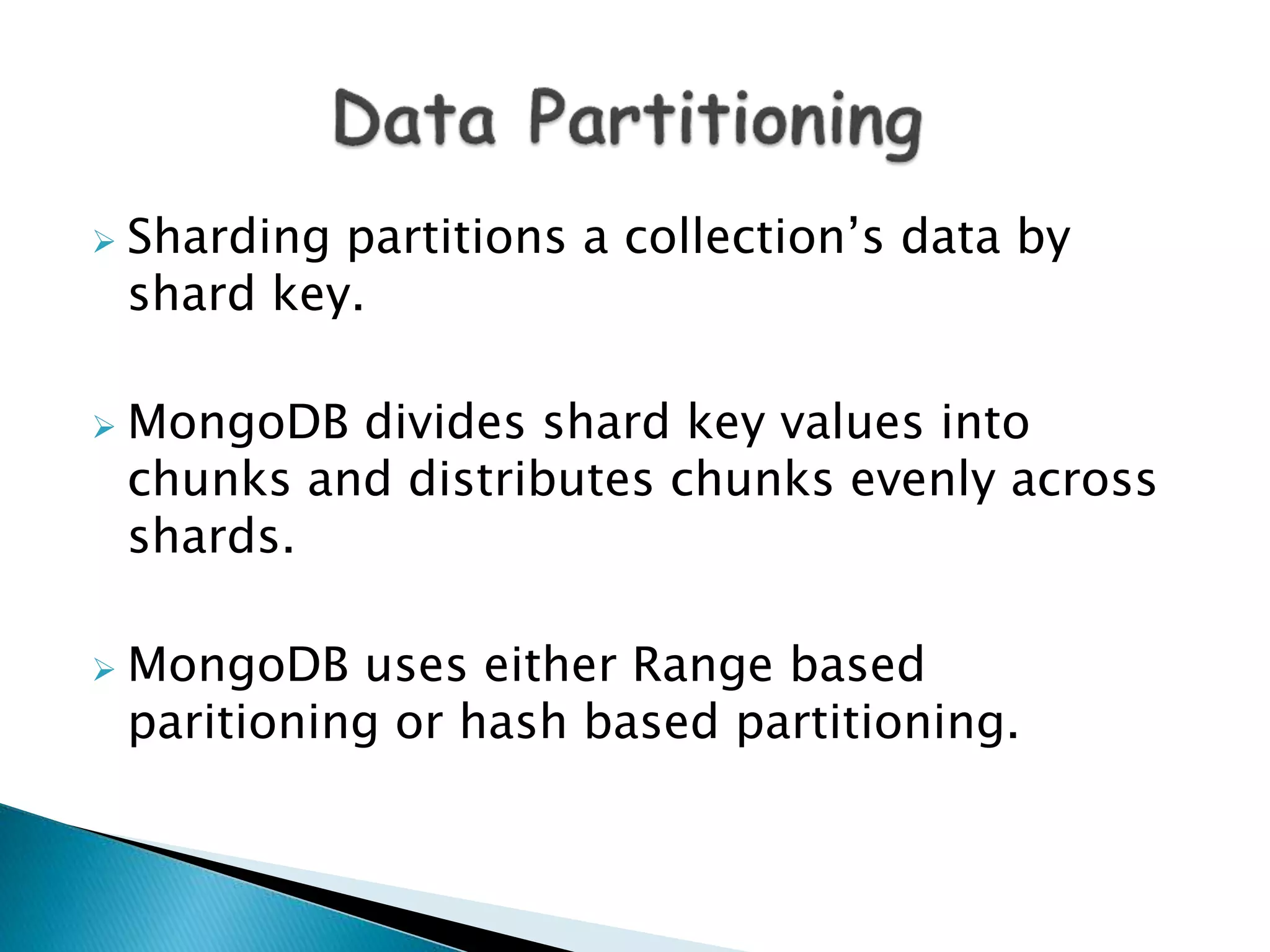
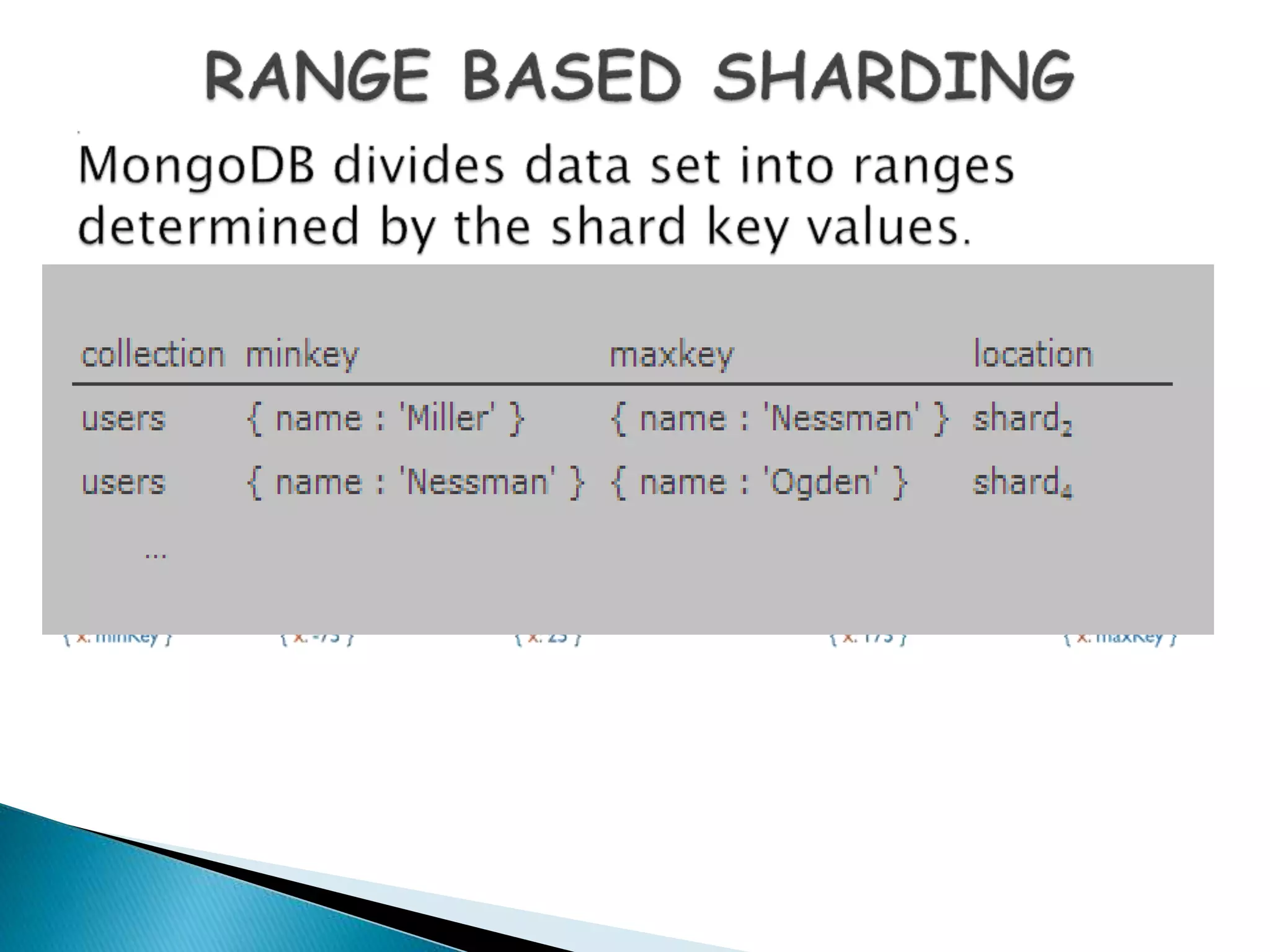
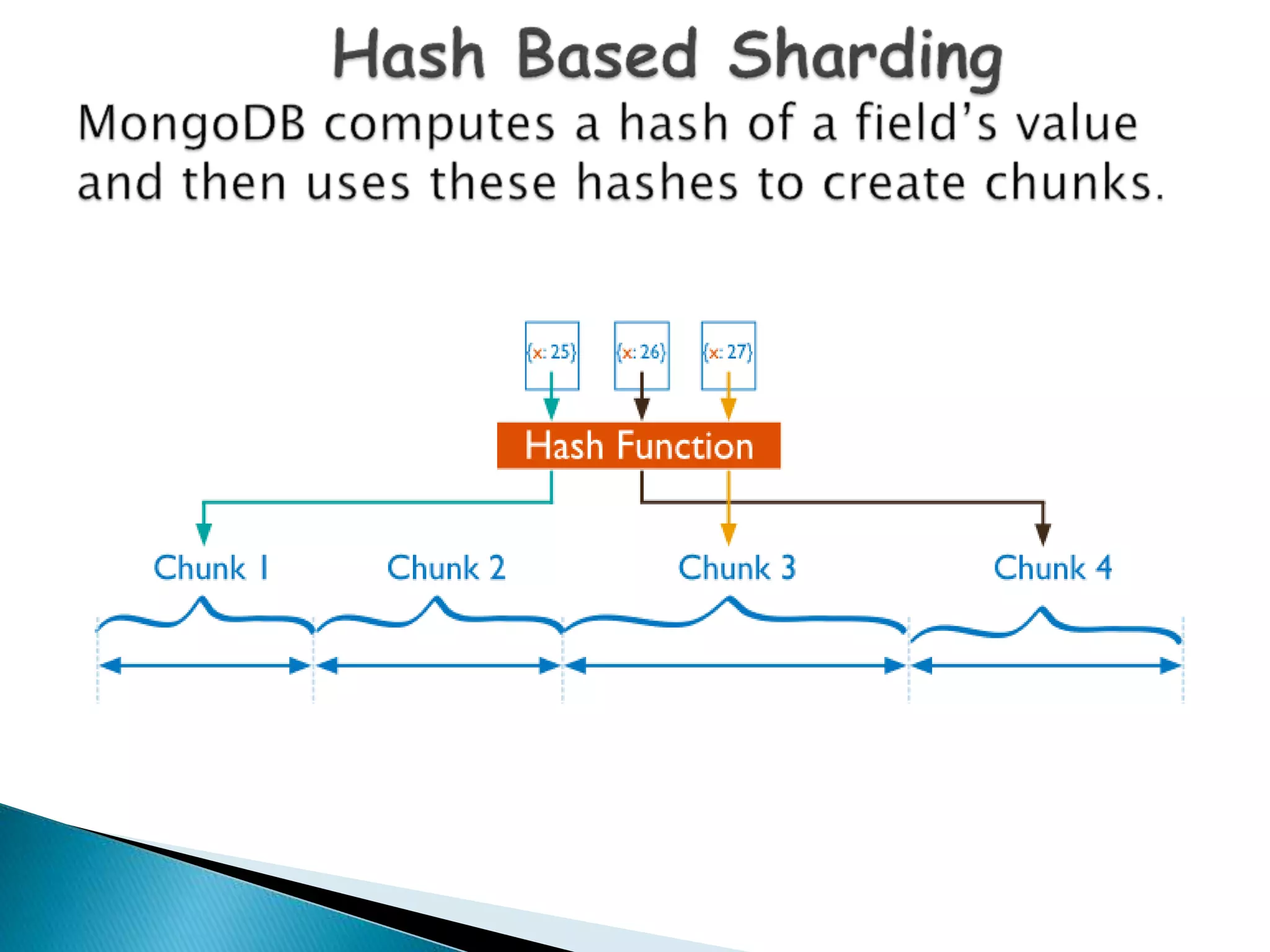
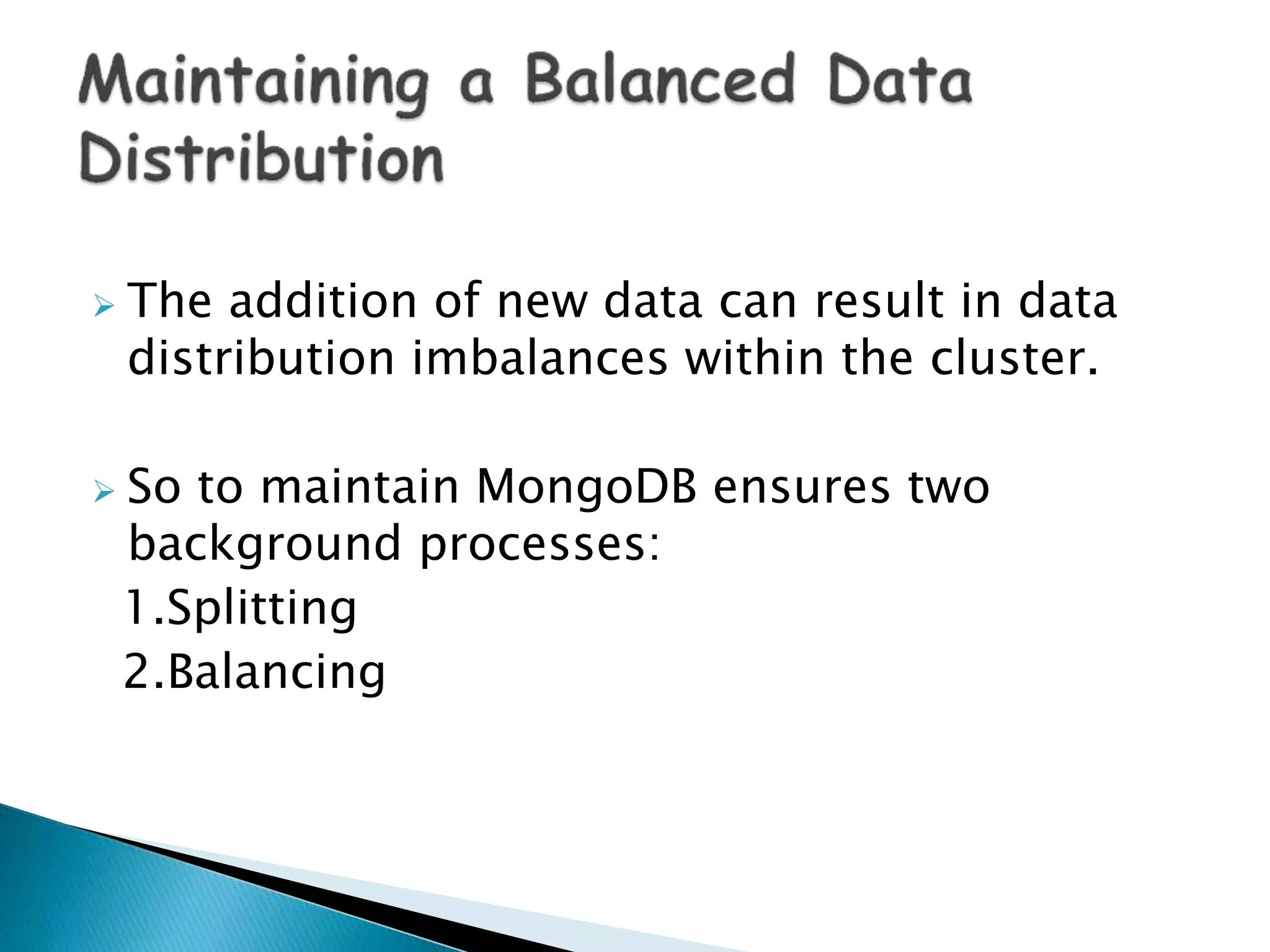
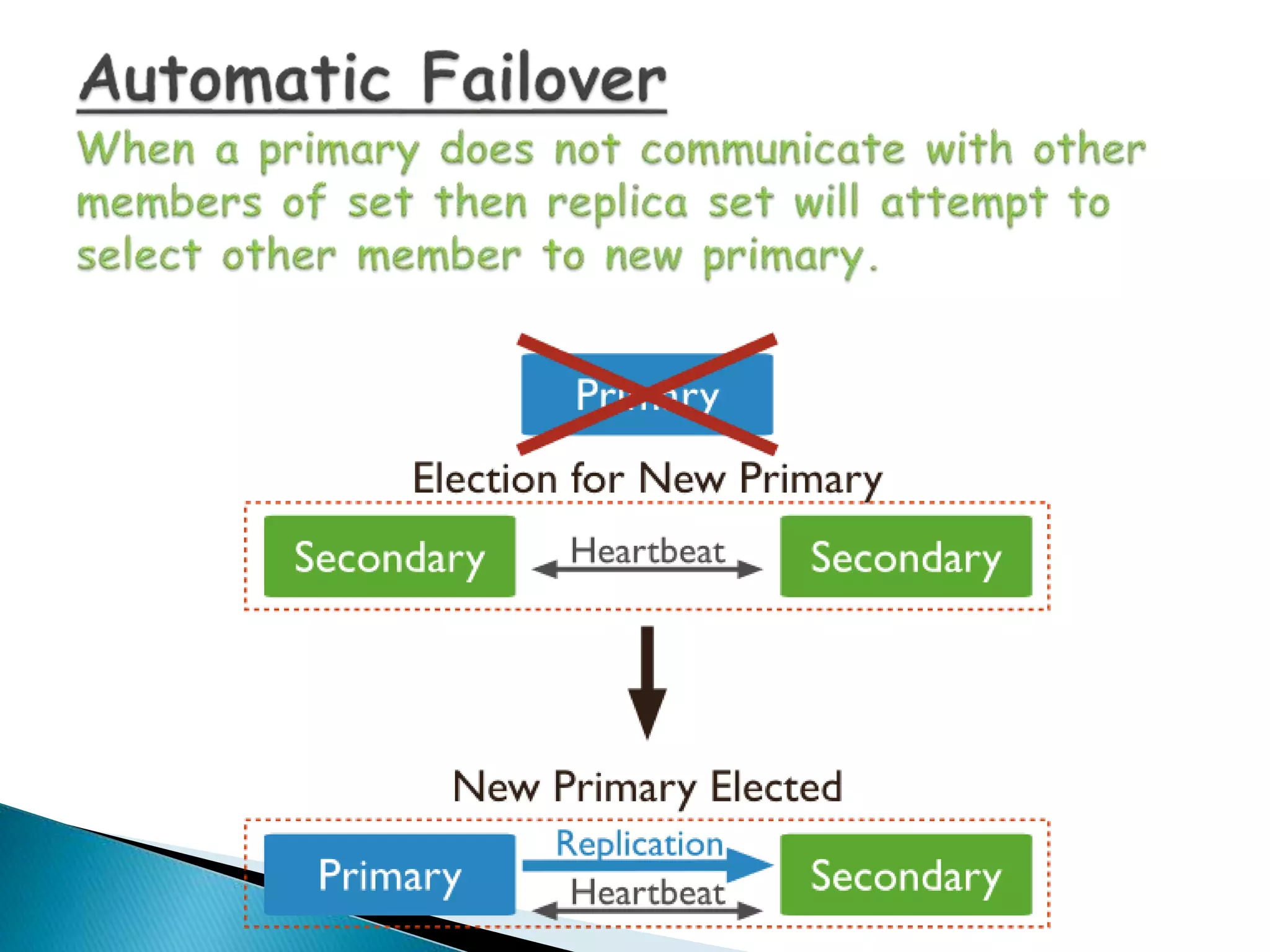
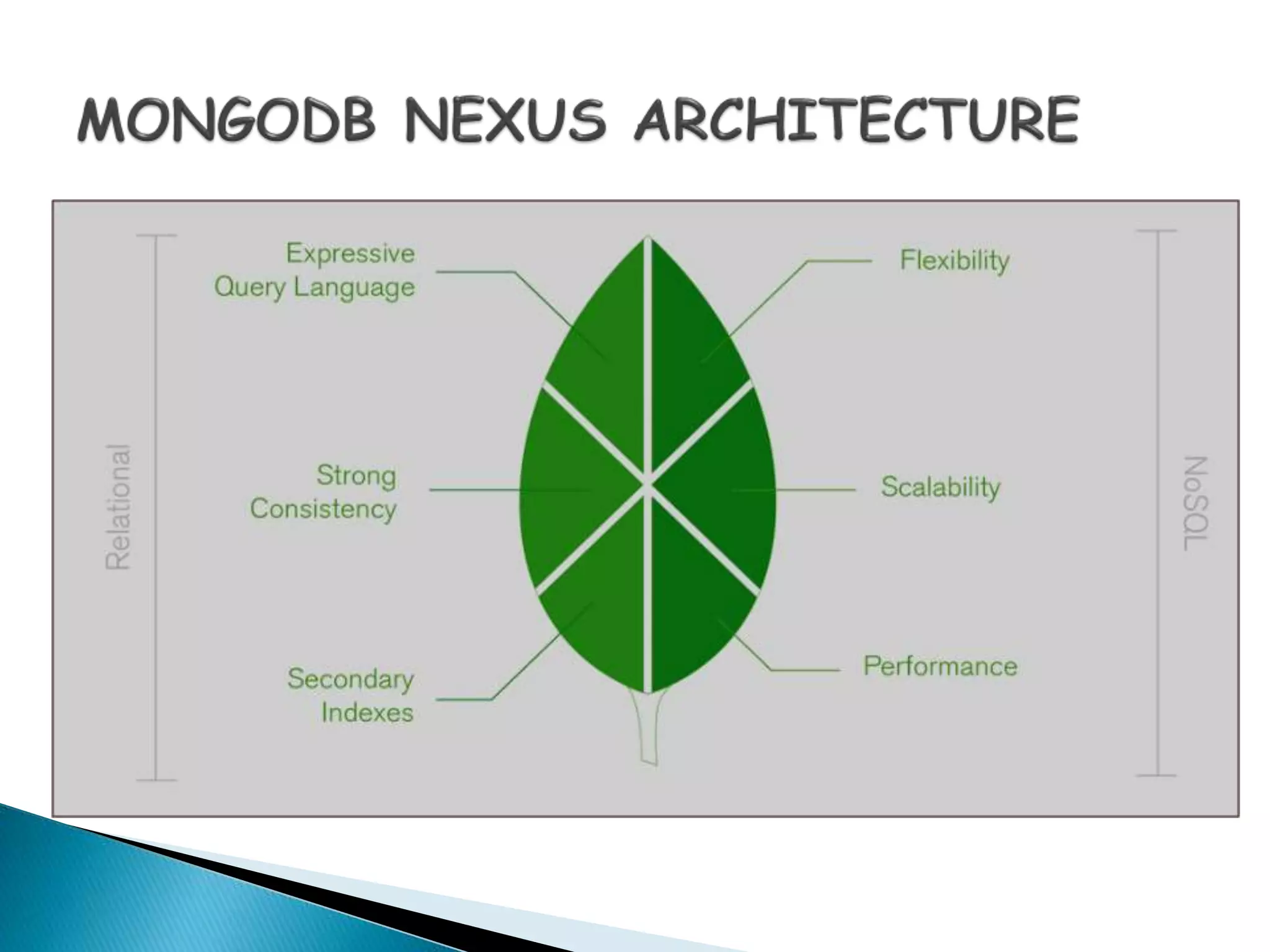
MongoDB, developed by MongoDB Inc. in 2007 and shifted to open source in 2009, is a popular cross-platform, document-oriented database supporting JSON-like documents with dynamic schemas. It offers features like indexing, sharding for horizontal scaling, and replication for redundancy, while avoiding complex joins and supporting deep-query capabilities. Key operations include easy database management commands and automatic balancing to maintain data distribution across shards.