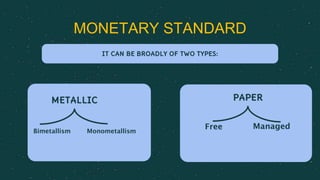
The document discusses monetary standards, which are the officially recognized forms of currency in an economy, detailing their classifications such as silver and gold standards. It outlines the characteristics and historical context of various standards, including monometallism, bimetallism, and indirect gold standards. The document concludes that the gold standard has largely dominated due to its stability, whereas the silver standard was abandoned due to volatility.


![INDEX
INTRODUCTION 5
CLASSIFICATION 6-7
SILVER STANDARD 8
GOLD STANDARD [INDIRECT] 9-12
CONCLUSION 13
BIBLIOGRAPHY 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ritikacbe11-221118093207-f5616e32/85/monetary-standards-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![MONETARY STANDARDS-
MONO METALLISM
[SILVER AND GOLD
STANDARDS]
CBE PRESENTATION BY:
RITIKA SHARMA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ritikacbe11-221118093207-f5616e32/85/monetary-standards-pptx-4-320.jpg)







![GOLD PARITY STANDARD
● Under this system gold is not served as a medium of exchange. The
internal currency consist largely of notes which is not convertible into
gold like other standards.
● This standard is introduced by IMF[international monetary fund]
● The IMF used to calculate the monetary value of each member country.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ritikacbe11-221118093207-f5616e32/85/monetary-standards-pptx-13-320.jpg)

![BIBLIOGRAPHY
● SOURCE:
• https://www.investopedia.com
• http://www.wikipedia.org
• Currency Banking And Exchange [Sahitya Bhawan
Publications].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ritikacbe11-221118093207-f5616e32/85/monetary-standards-pptx-15-320.jpg)
