This document discusses three issues related to developing new scientific models and assessment tools:
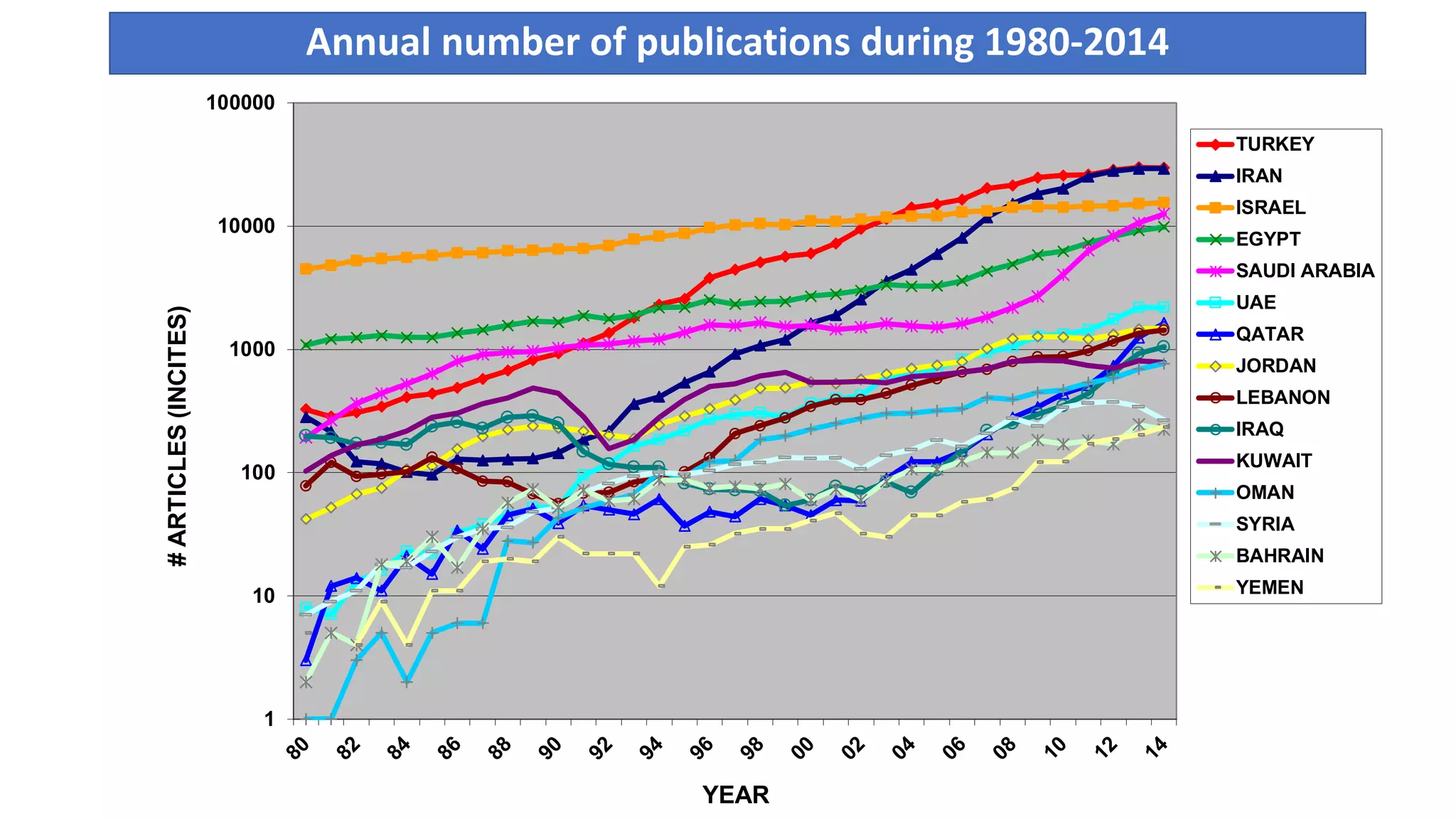
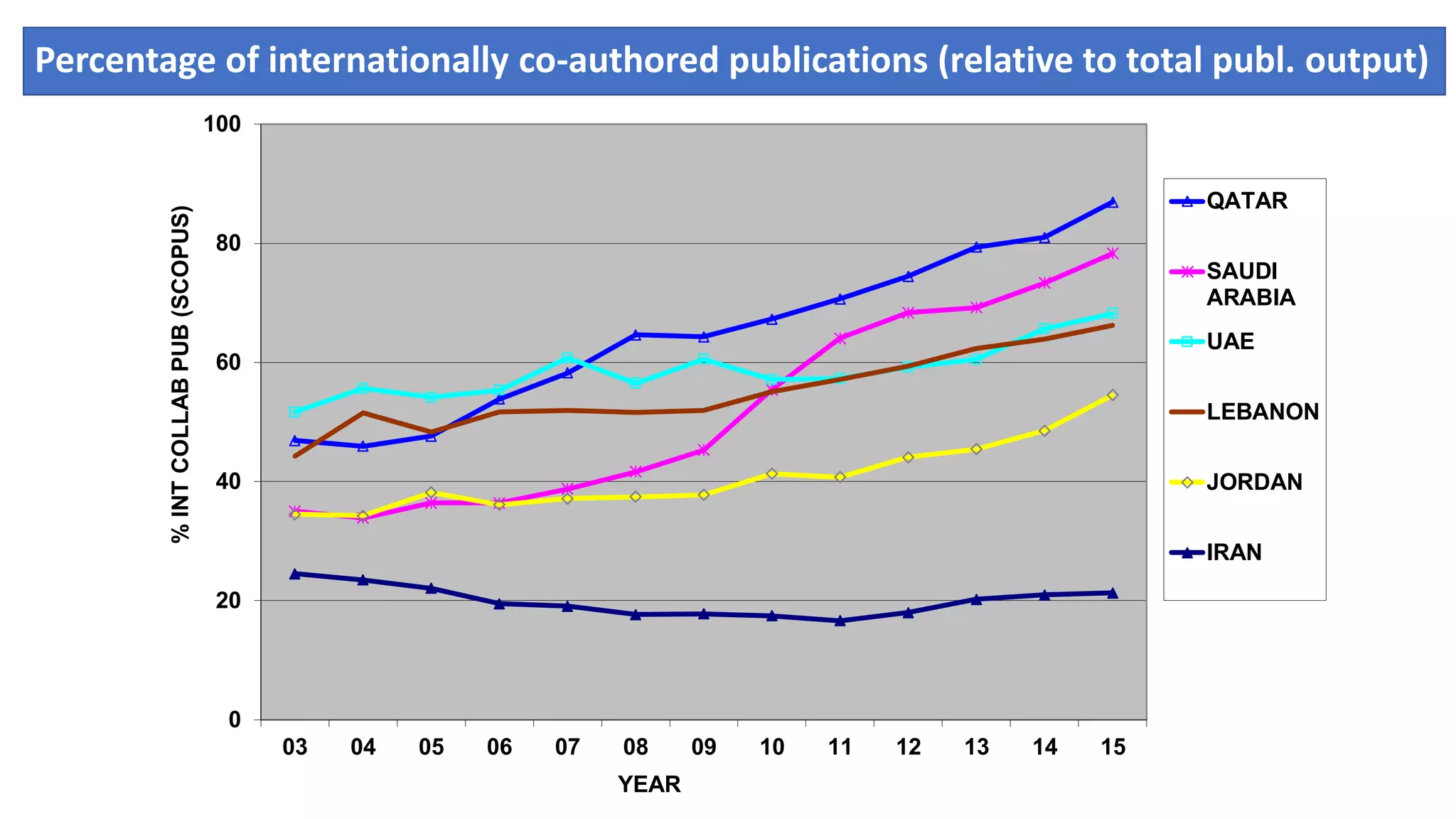
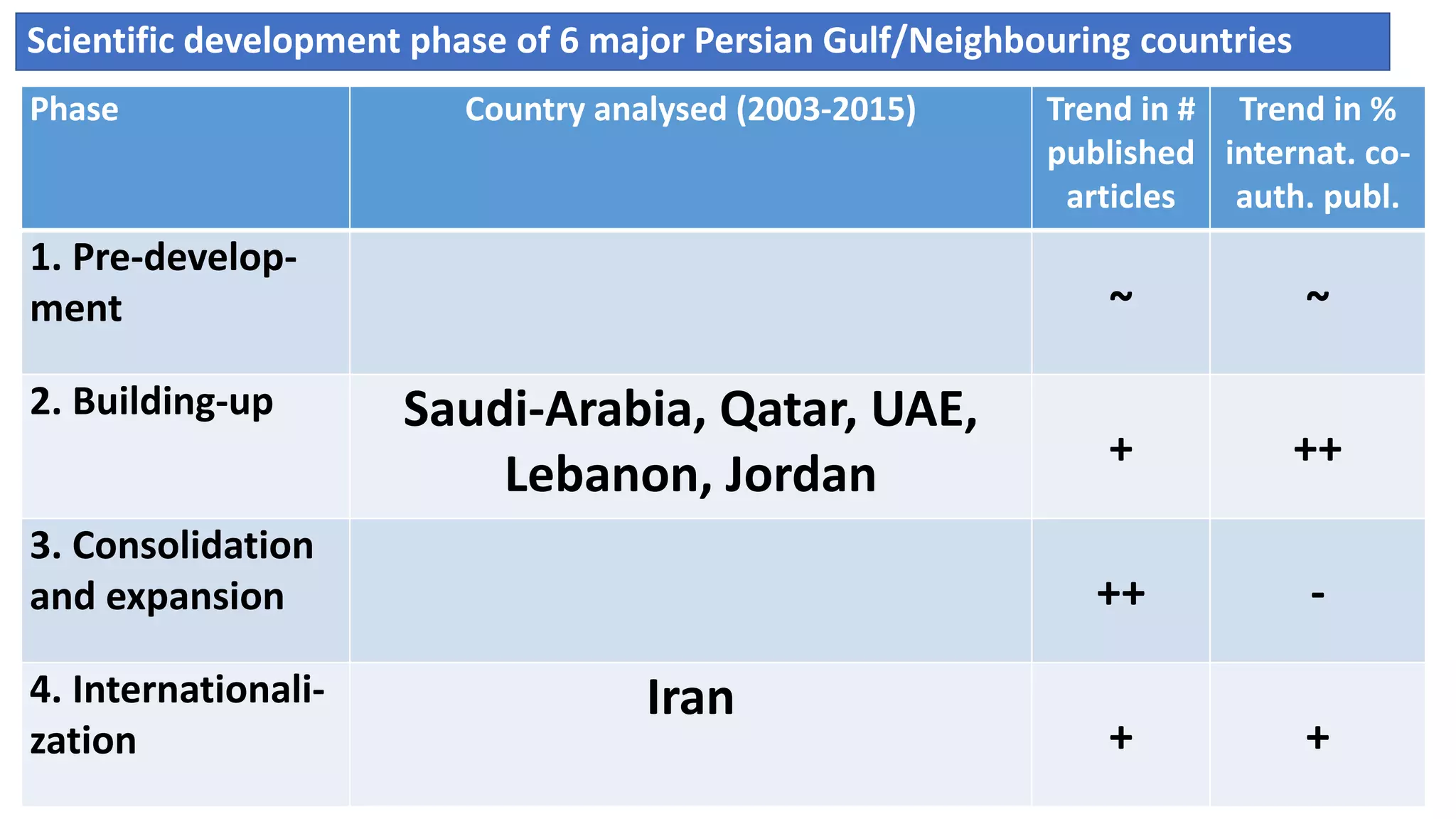
1. Developing a more socially relevant bibliometric model of scientific development that tracks trends in publication output and international collaboration for countries. The model outlines four phases of development.
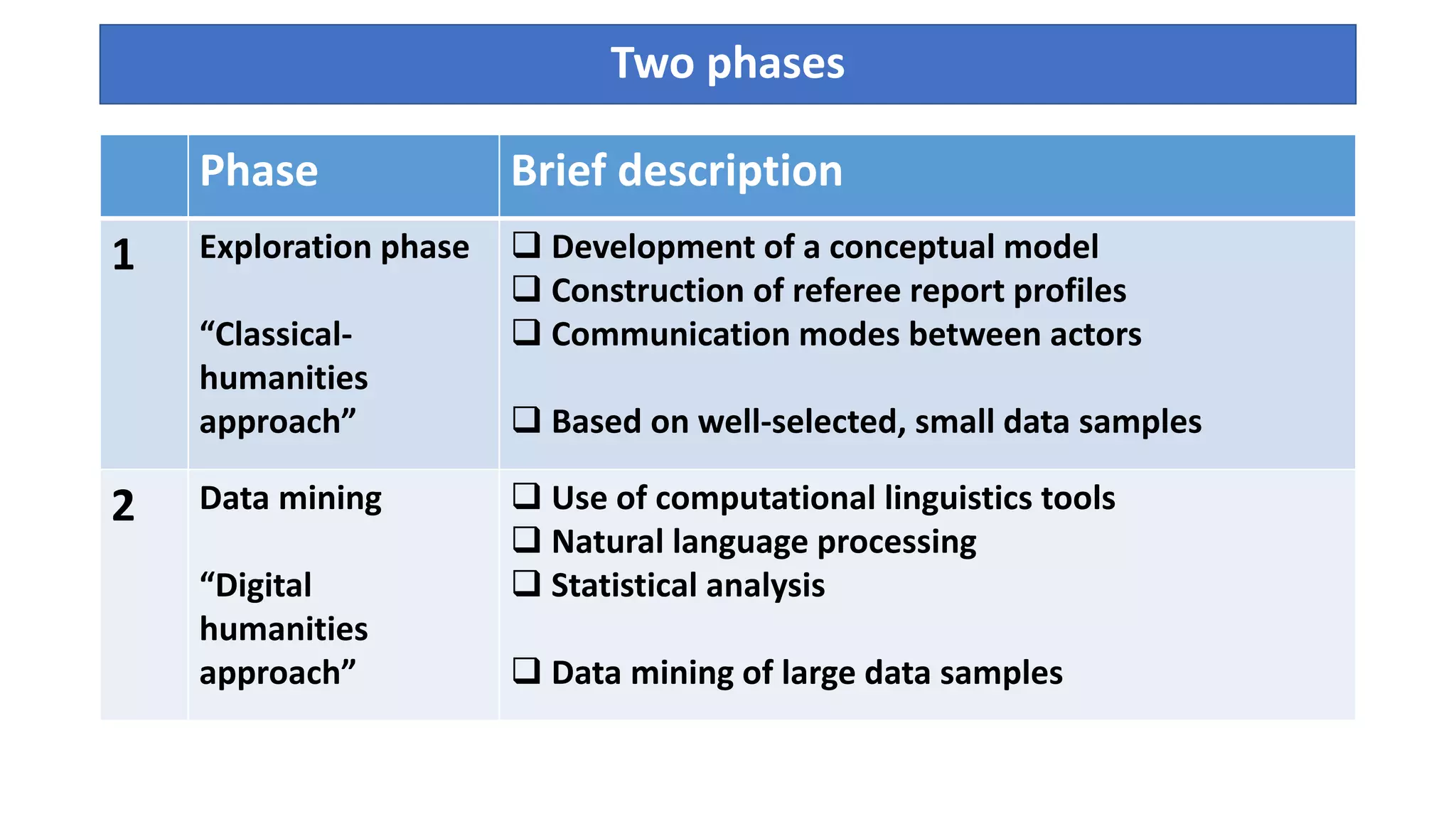
2. Reducing reliance on journal impact factors and developing indicators of the peer review process to provide more transparency and help improve review quality. A two-phase approach is proposed involving exploratory analysis and large-scale data mining.
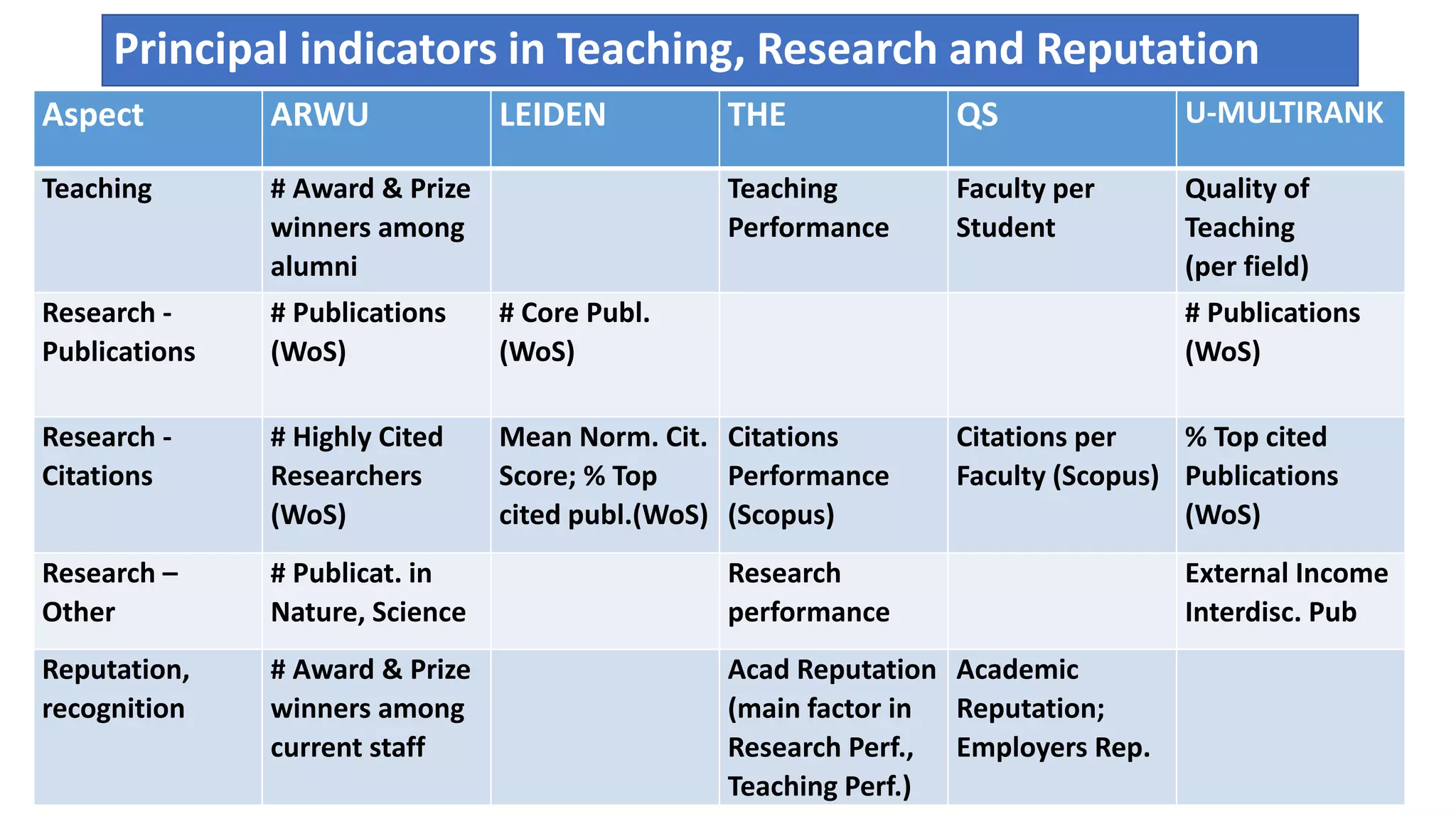
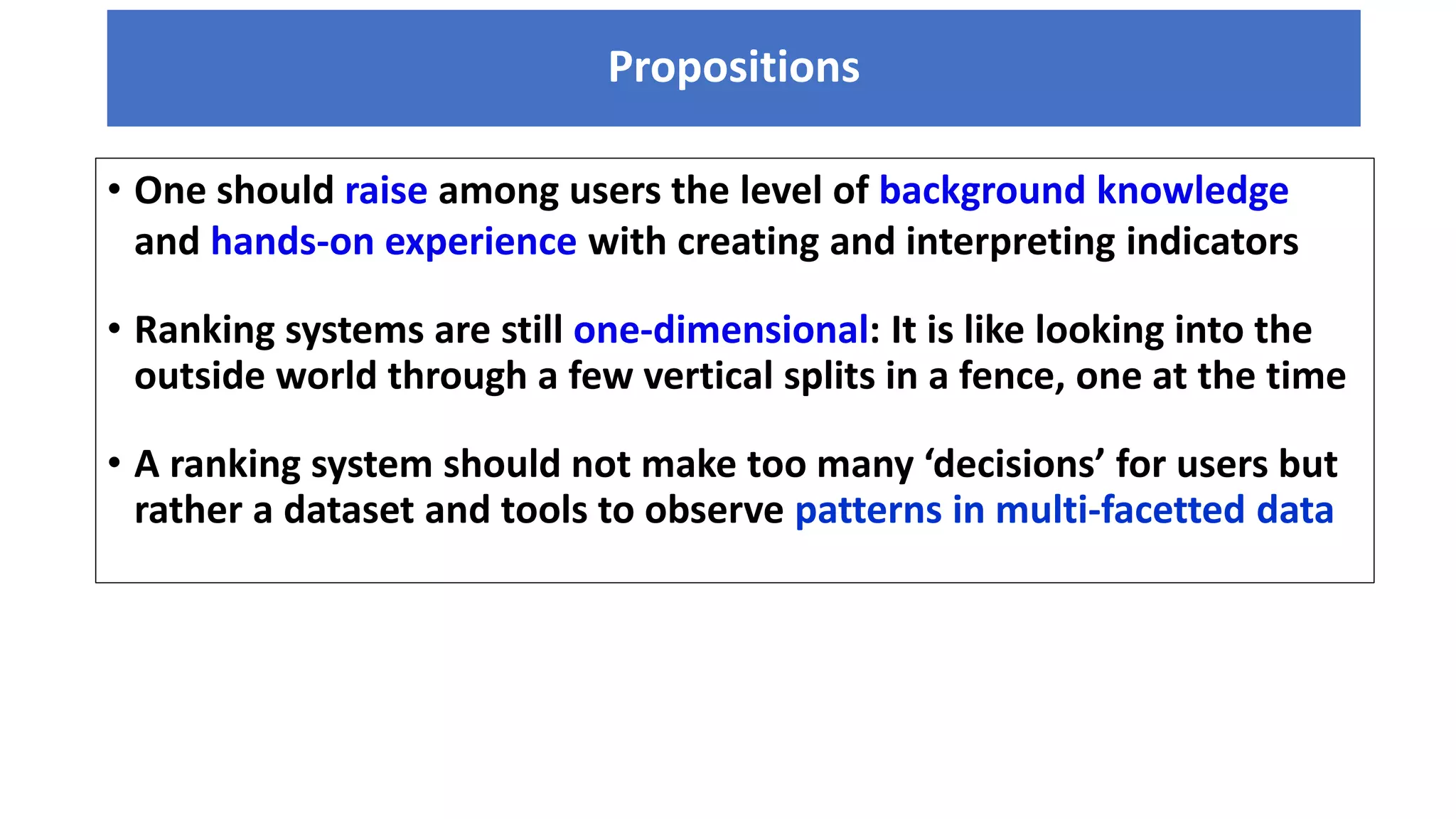
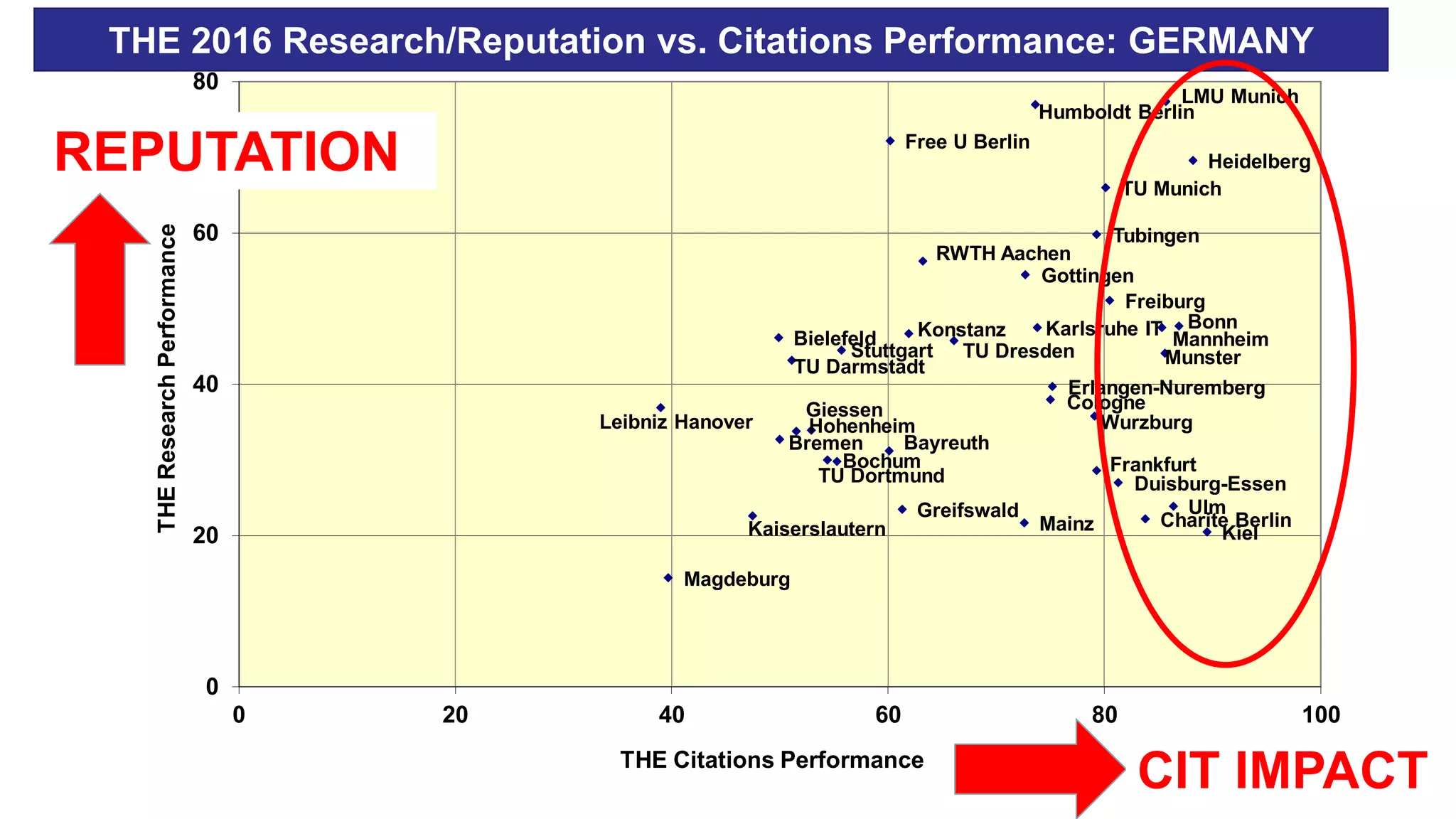
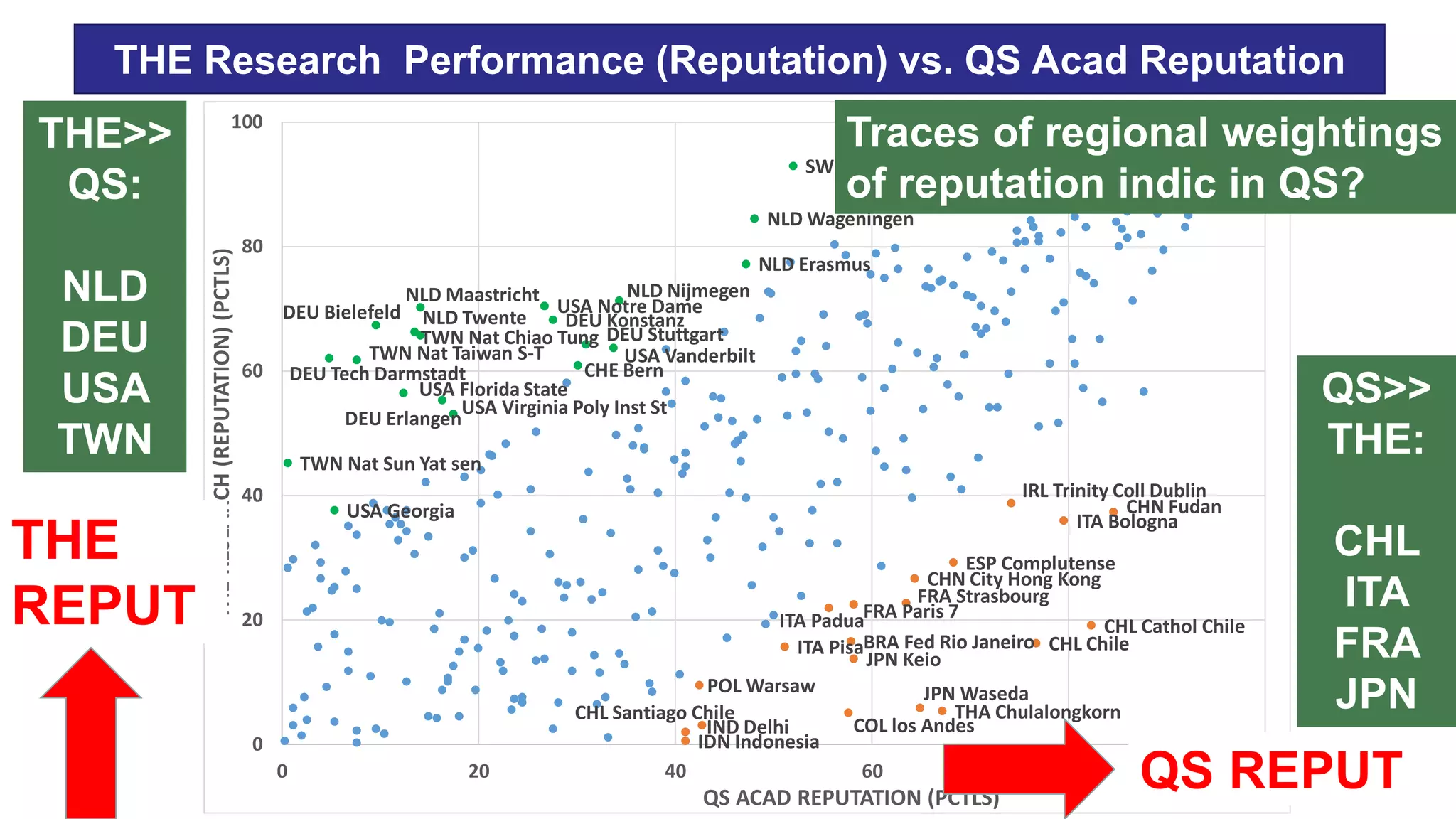
3. Creating a multi-dimensional information system on universities that educates users and provides discovery tools beyond singular rankings. It argues for comparing different ranking systems and allowing users to observe patterns in complex, multi-faceted institutional data.