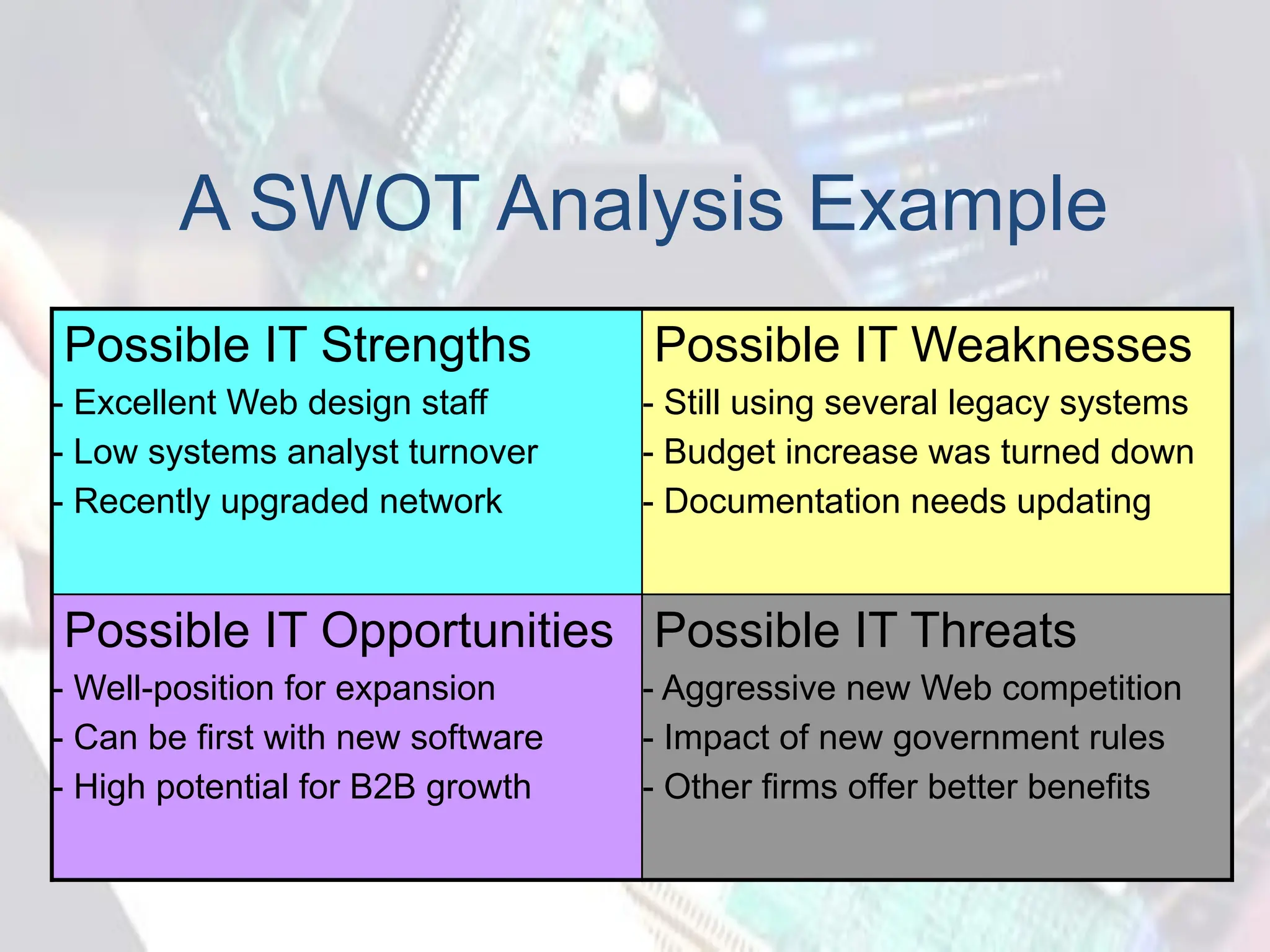
This document provides an overview of systems planning. It discusses strategic planning, including conducting a SWOT analysis and developing a mission statement, goals, and objectives. It also covers factors to consider for information systems projects, such as internal and external influences. The document outlines the steps of a feasibility study, including assessing operational, technical, economic, and schedule feasibility. Finally, it discusses the preliminary investigation process for planning an information systems project, which involves understanding the problem, defining scope and constraints, fact-finding, feasibility evaluation, estimating time and costs, and presenting results to management.