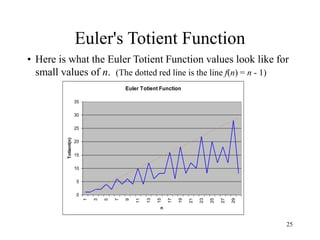
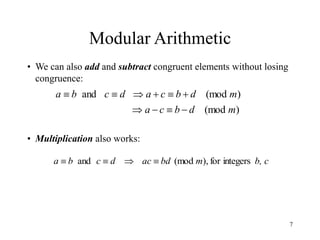
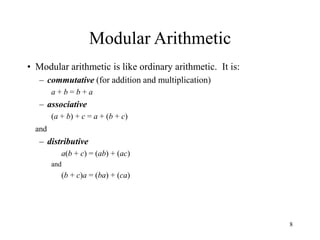
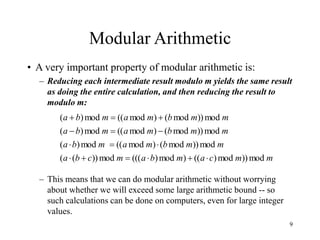
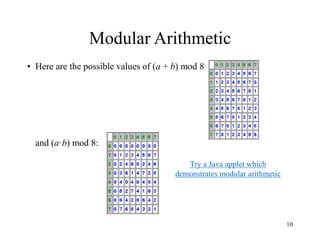
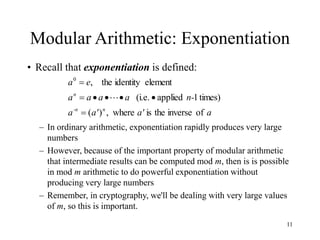
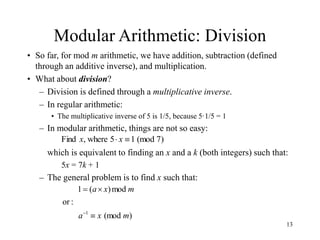
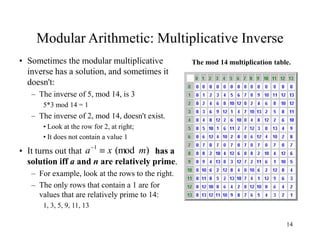
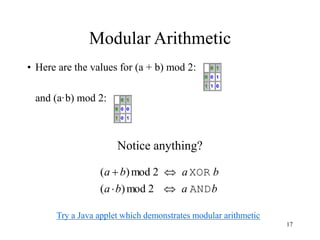
This document discusses modular arithmetic and its applications in cryptography. Modular arithmetic involves dividing integers and taking the remainder, known as the residue, and exploring properties when doing arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication on these residues. Finite fields, where the set of integers is modulo a prime number, are important for cryptography. Fermat's Little Theorem and Euler's Totient function, which counts numbers relatively prime to n, also relate to modular arithmetic.











![24
Euler's Totient Function
• Assume we have two distinct prime numbers, p and q, and an
integer n = pq
– Then:
– The set of residues in Zn i s{0,1,...,(pq - 1)}
– The residues that are not relatively prime to n are:
• The set {p, 2p, ... ,(q - 1)p}, the set {q, 2q, ... ,(p - 1)q}, and 0
– So:
)
1
(
)
1
(
)
(
φ
)
(
φ
)
(
φ
)
(
φ
q
p
q
p
pq
n
)
(
φ
)
(
φ
)
1
(
)
1
(
1
)
(
]
1
)
1
(
)
1
[(
)
(
φ
q
p
q
p
q
p
pq
p
q
pq
n
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulararithmetic-240414025526-4f64df65/85/Modular-Arithmetic-concept-in-mathematics-24-320.jpg)