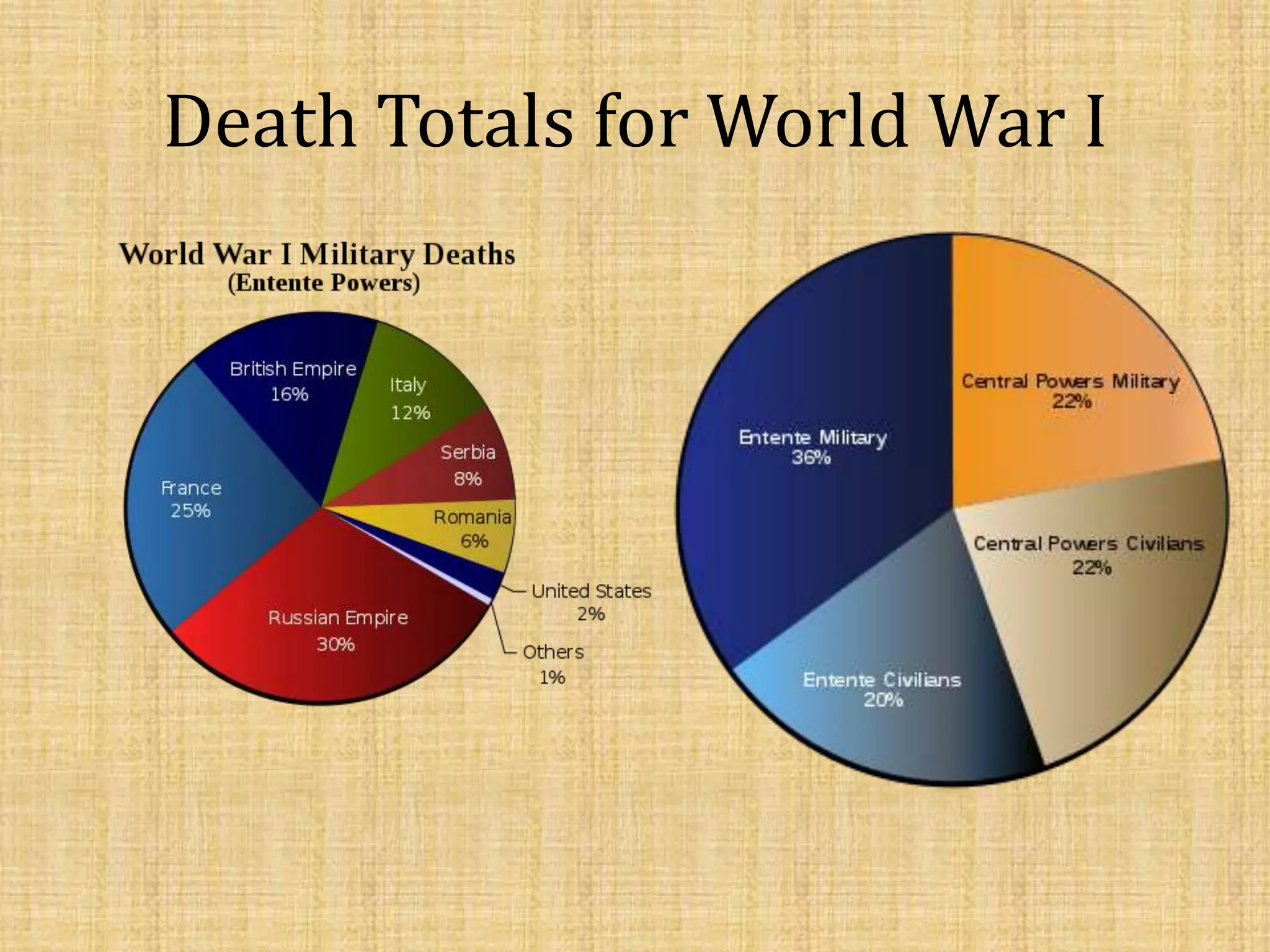
The document provides an overview of major events from 1900-1945, including World War I and II, the rise of modernism, and key modernist writers and works. Some of the main events discussed are the start of WWI due to the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, Germany's surrender in 1918, the Treaty of Versailles, the stock market crash of 1929 beginning the Great Depression, and the US dropping atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945. The document also summarizes features of modernism such as its pessimistic viewpoint and focus on language and style over content or morality in art.