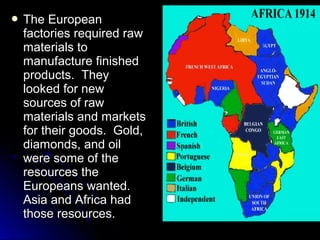
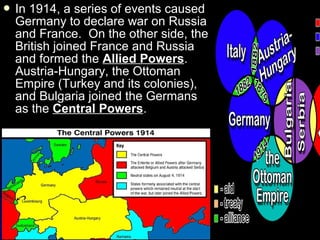
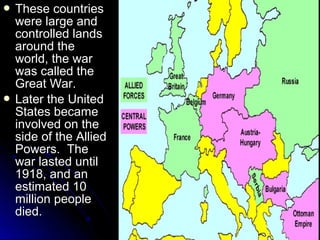
The document provides background information on the origins and events of World War I and World War II in Europe. It discusses how imperialism and nationalism in European countries led to the colonization of Africa and Asia in the late 19th century. Tensions escalated after the Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh terms on Germany after WWI. The rise of totalitarian regimes in Germany, Italy and the USSR weakened countries and paved the way for WWII. The war began in 1939 and involved two main theaters - Europe and the Pacific. Major events discussed include the Holocaust and the turning point Battle of Stalingrad.