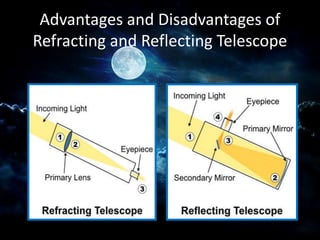
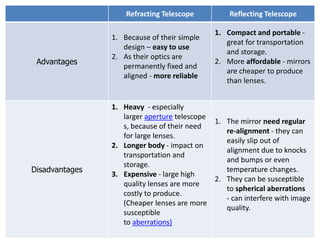
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation like visible light. There are two main types - refracting telescopes which use lenses, and reflecting telescopes which use mirrors. The first working telescope was created in 1608 by Hans Lippershey and consisted of convex and concave lenses in a tube. Galileo then improved on this design and was the first to observe astronomical objects like the moons of Jupiter. Reflecting telescopes later became more widely used as advances allowed for larger, more stable mirrors to be crafted. Modern telescopes can see distant galaxies and observe the evolution of the universe over billions of years.