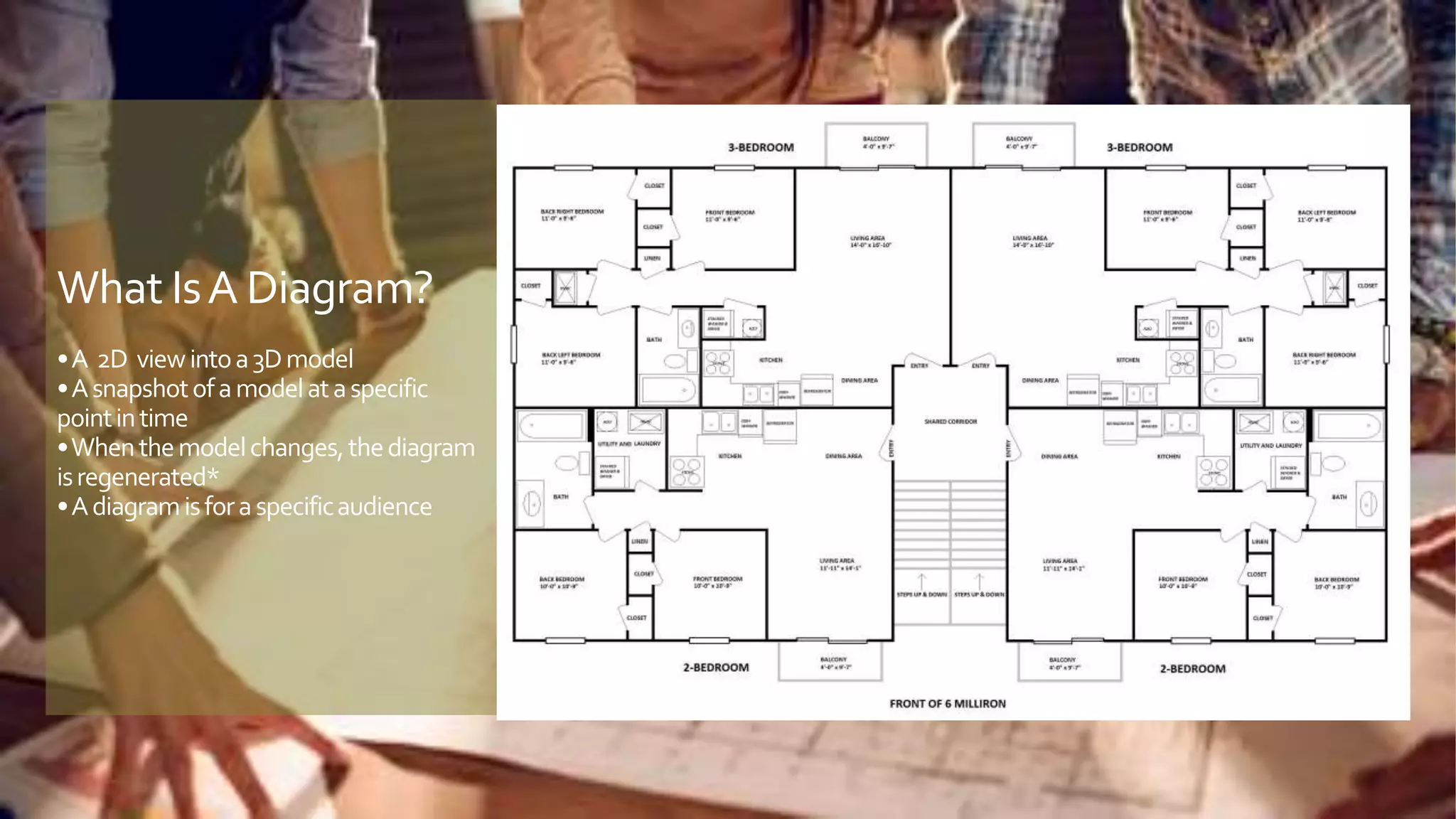
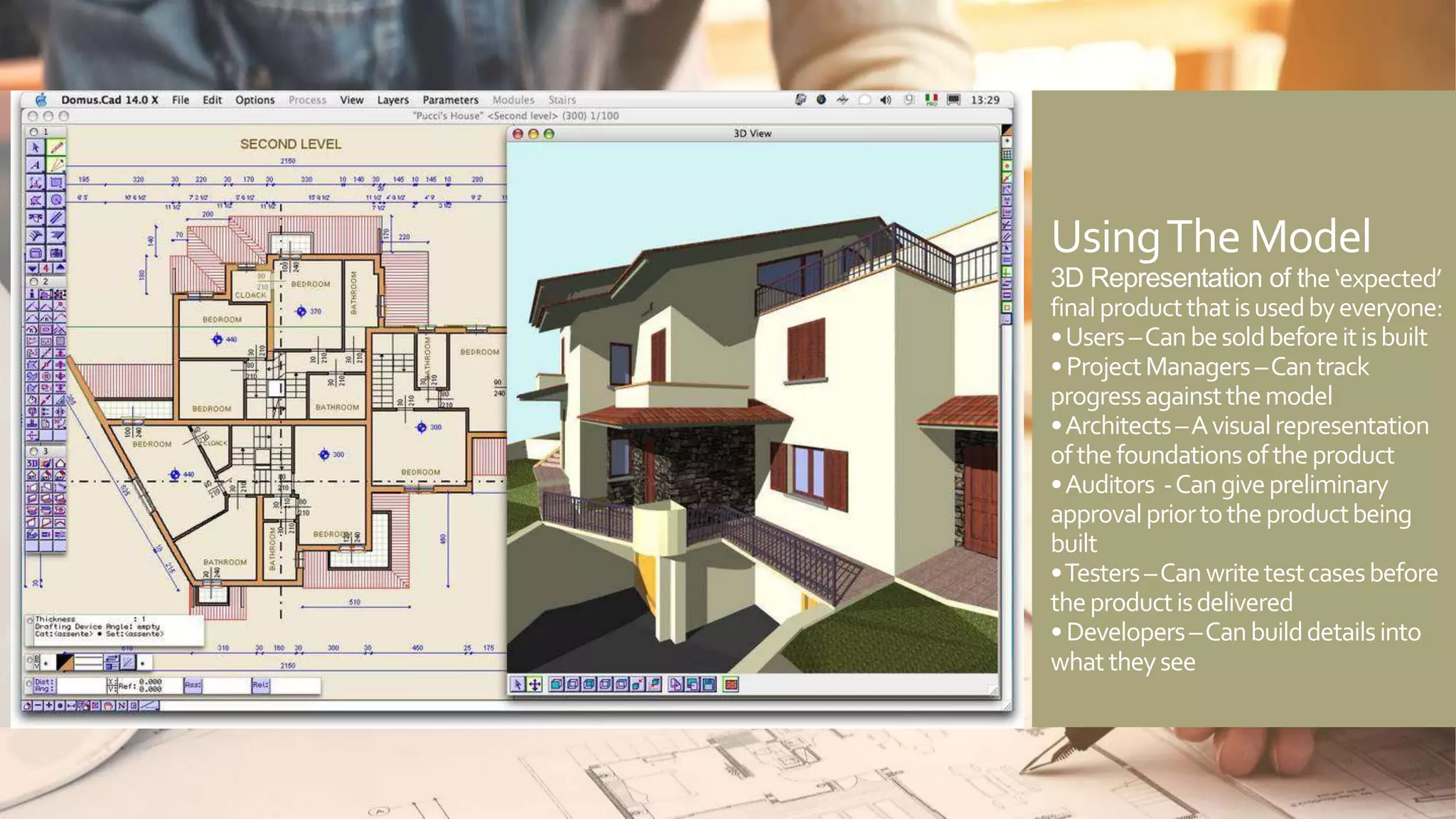
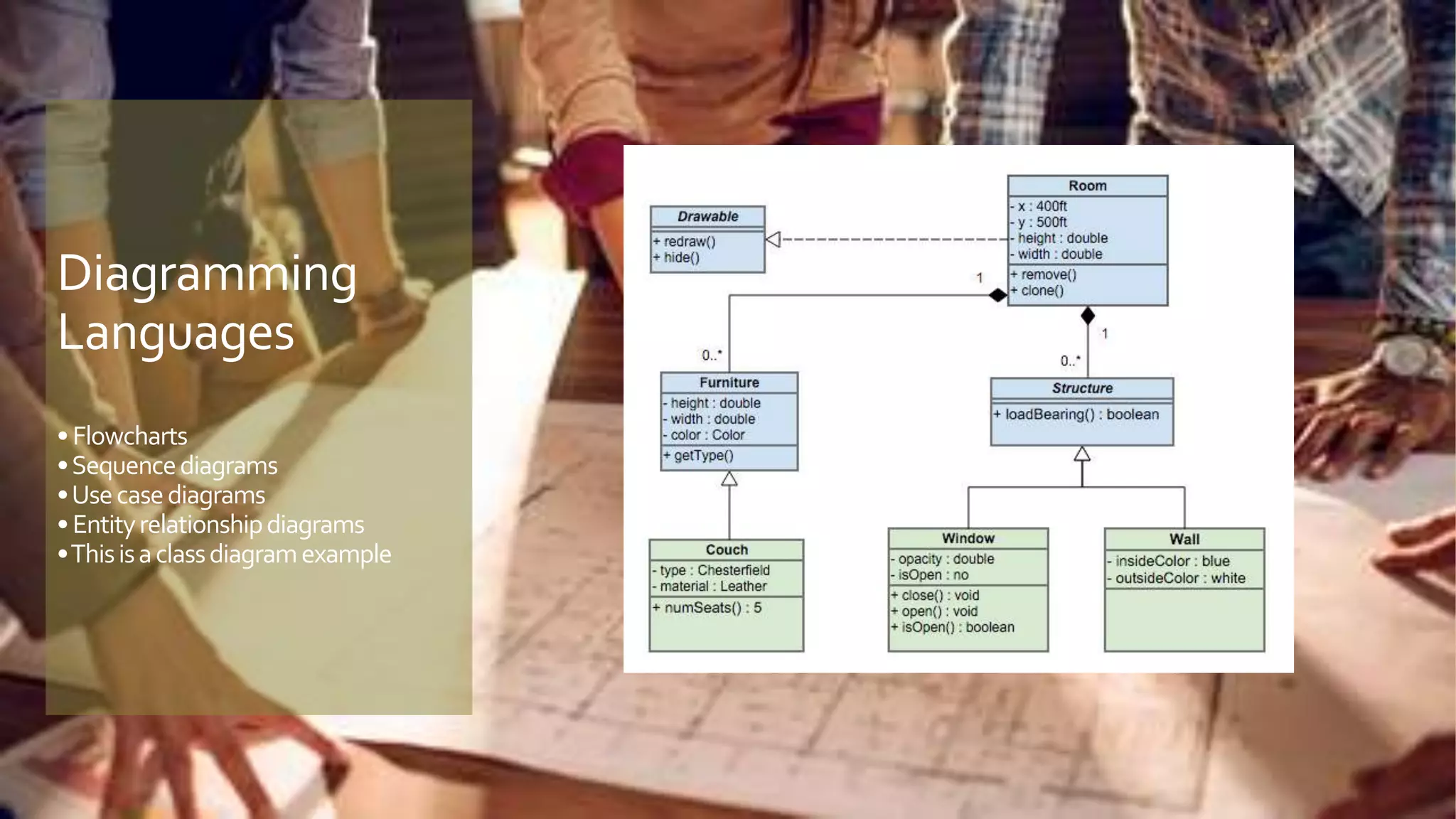
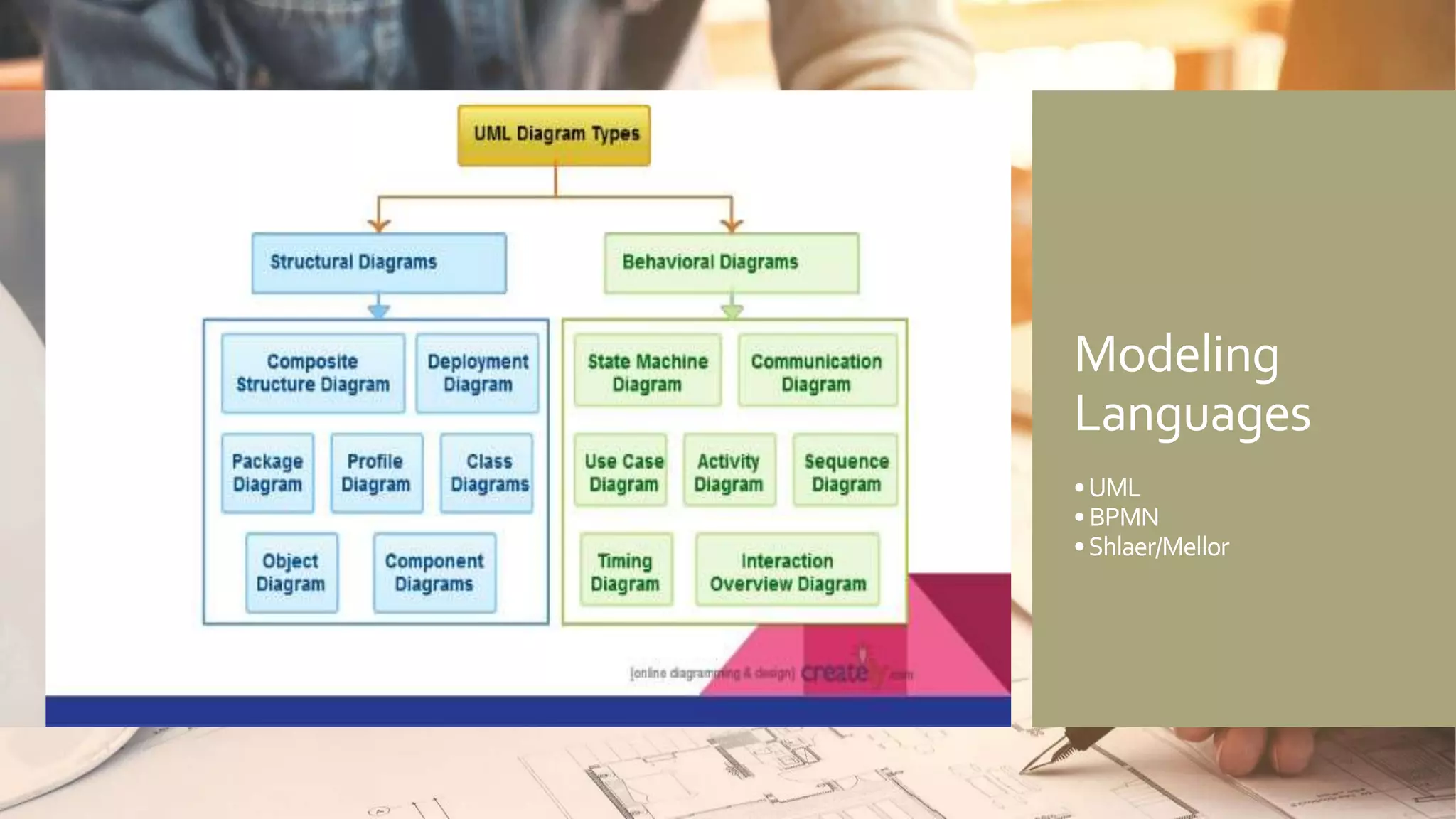
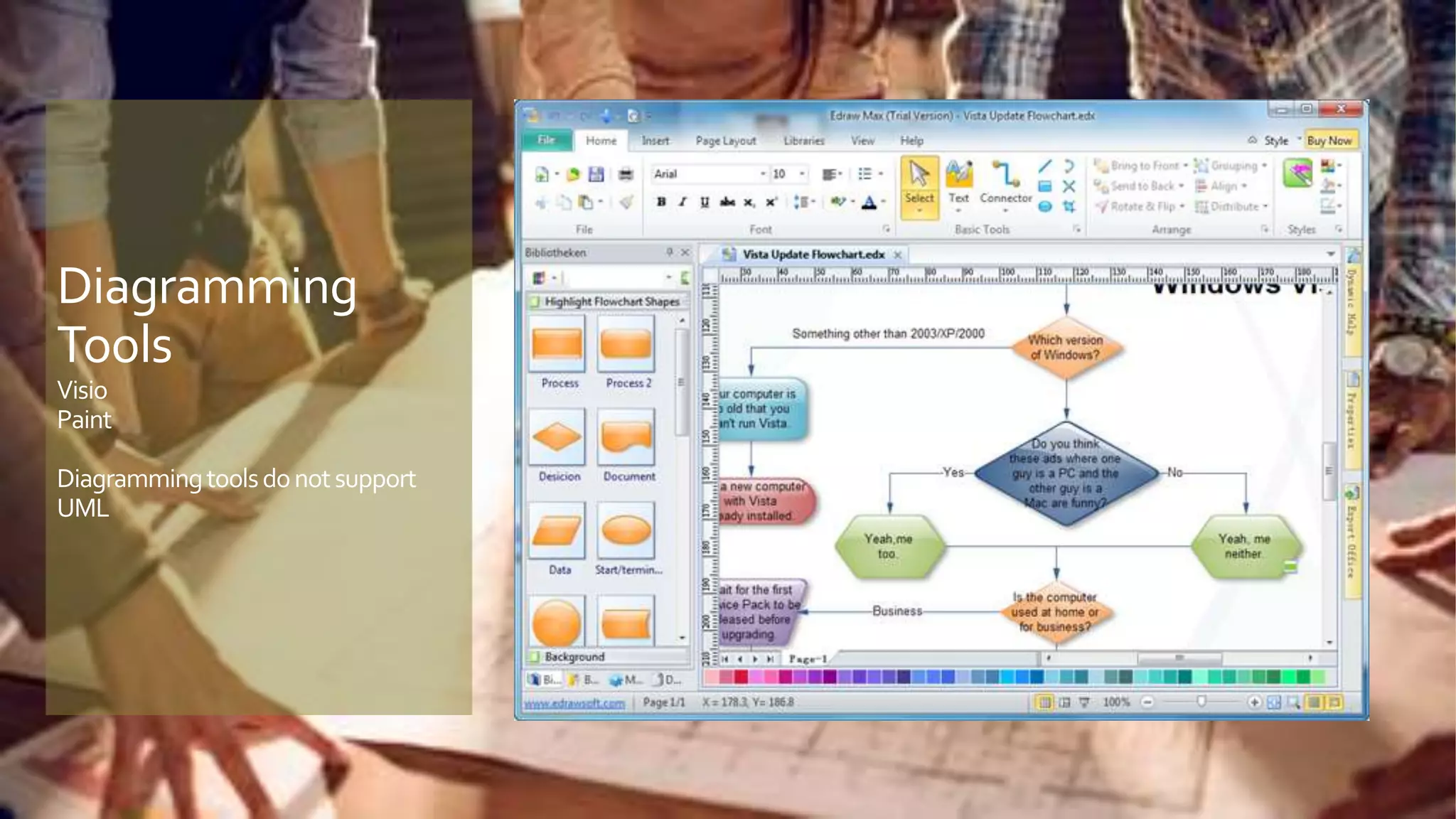
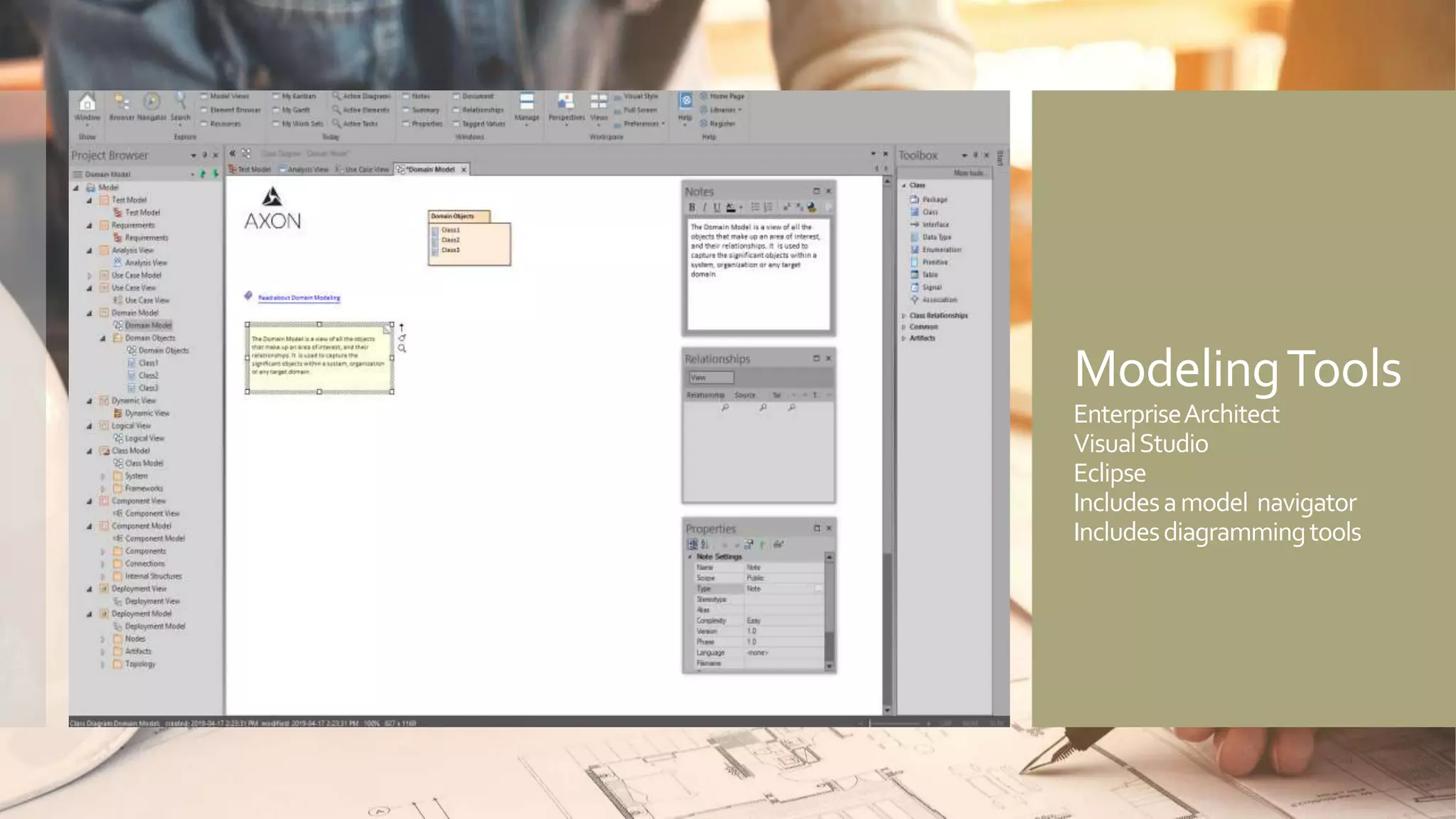
A model is an abstract representation of a system that is created before and maintained during construction, while a diagram is a 2D view of a model at a specific point in time. Models are used by various roles to visualize, plan, and develop a product before it is built. Diagramming tools like Visio create static diagrams, while modeling tools like Enterprise Architect allow editing models and synchronizing changes across multiple dynamic diagrams. UML is a modeling language that defines not just diagramming notation but also modeling elements, rules, interfaces, and functionality.