This document provides an overview of marketing management concepts from a textbook. It covers:
1. The main topics in marketing management including identifying opportunities, developing strategies, and implementing marketing programs.
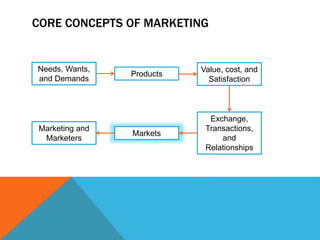
2. Core marketing concepts such as needs, products, value, exchange, markets, and marketers.
3. Guiding marketing concepts including the production concept, product concept, sales concept, and marketing concept.
4. Key aspects of the marketing concept like target markets, understanding customer needs, coordinated marketing, and profitability.