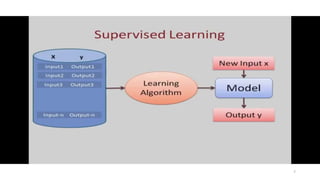
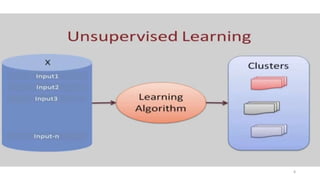
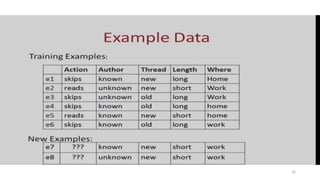
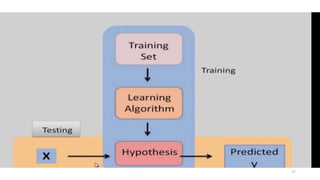
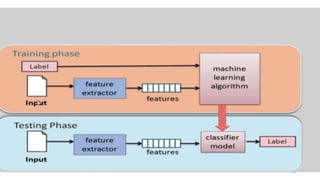
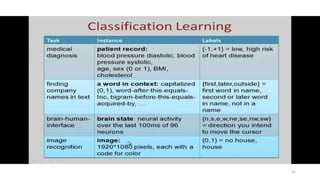
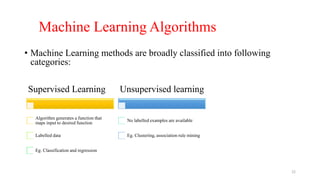
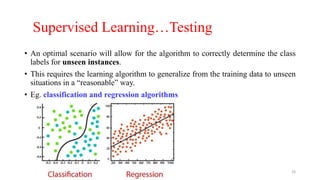
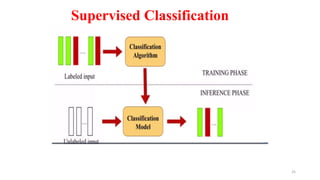
The document explores various types of machine learning, including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning. It emphasizes that supervised learning involves analyzing labeled training data to generate a function for classifying new instances, while unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data to discover hidden structures. Key applications and distinctions between these learning types, such as classification and regression in supervised learning and clustering in unsupervised learning, are also highlighted.