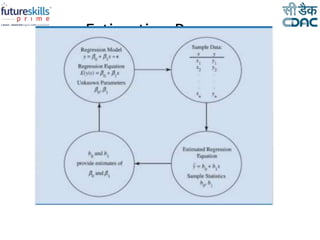
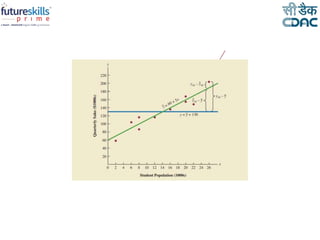
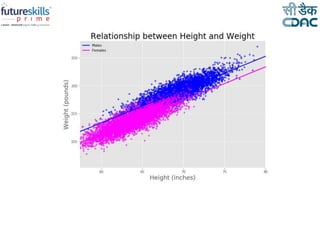
Linear regression is a machine learning technique used to model relationships between variables. It can be used to predict the value of a dependent variable based on the value of one or more independent variables. Simple linear regression uses one independent variable to predict the dependent variable, while multiple linear regression uses two or more independent variables. The linear regression equation is estimated using the least squares method to minimize error. Linear regression has various applications including predictive analytics and assessing risk.