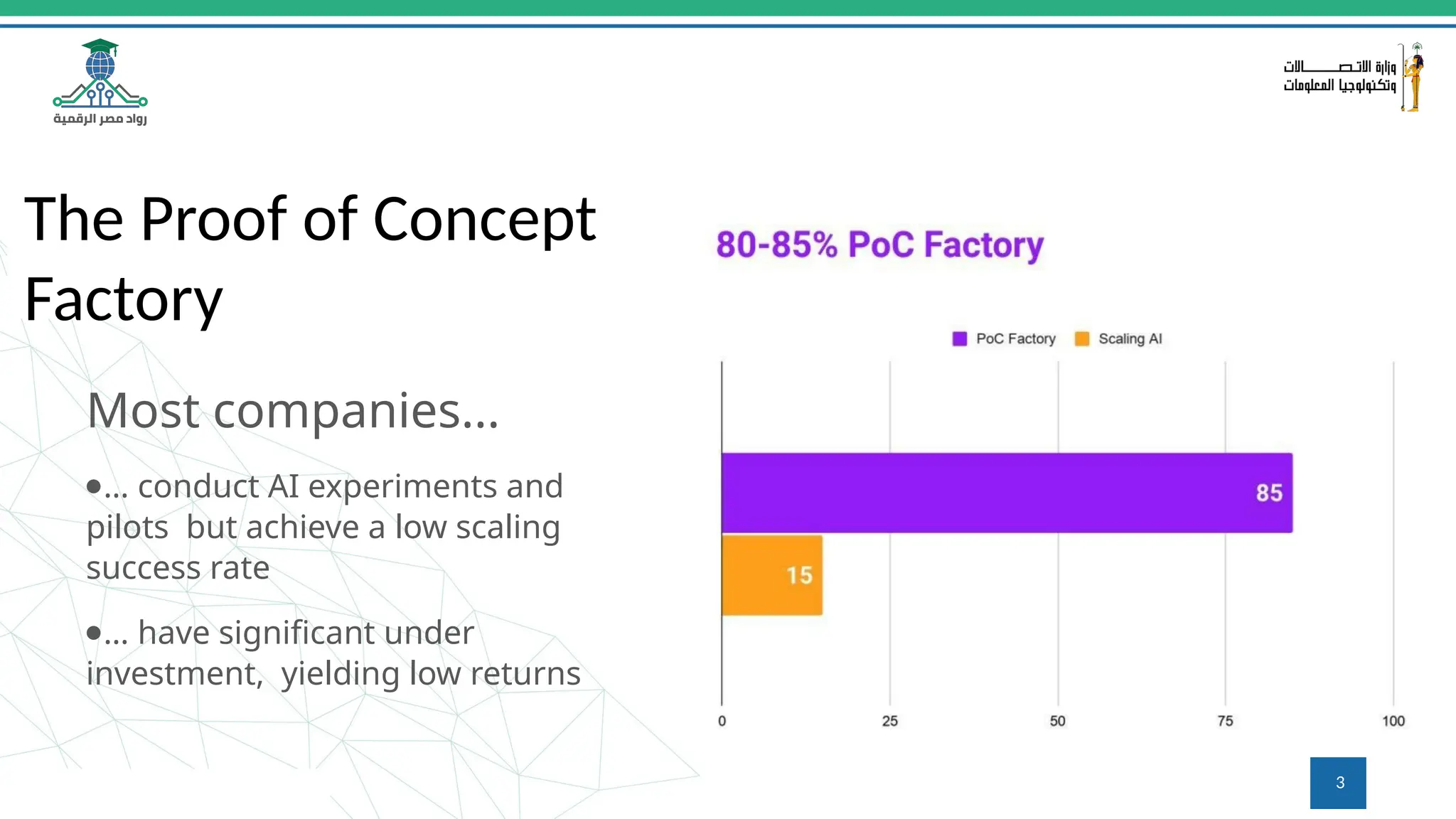
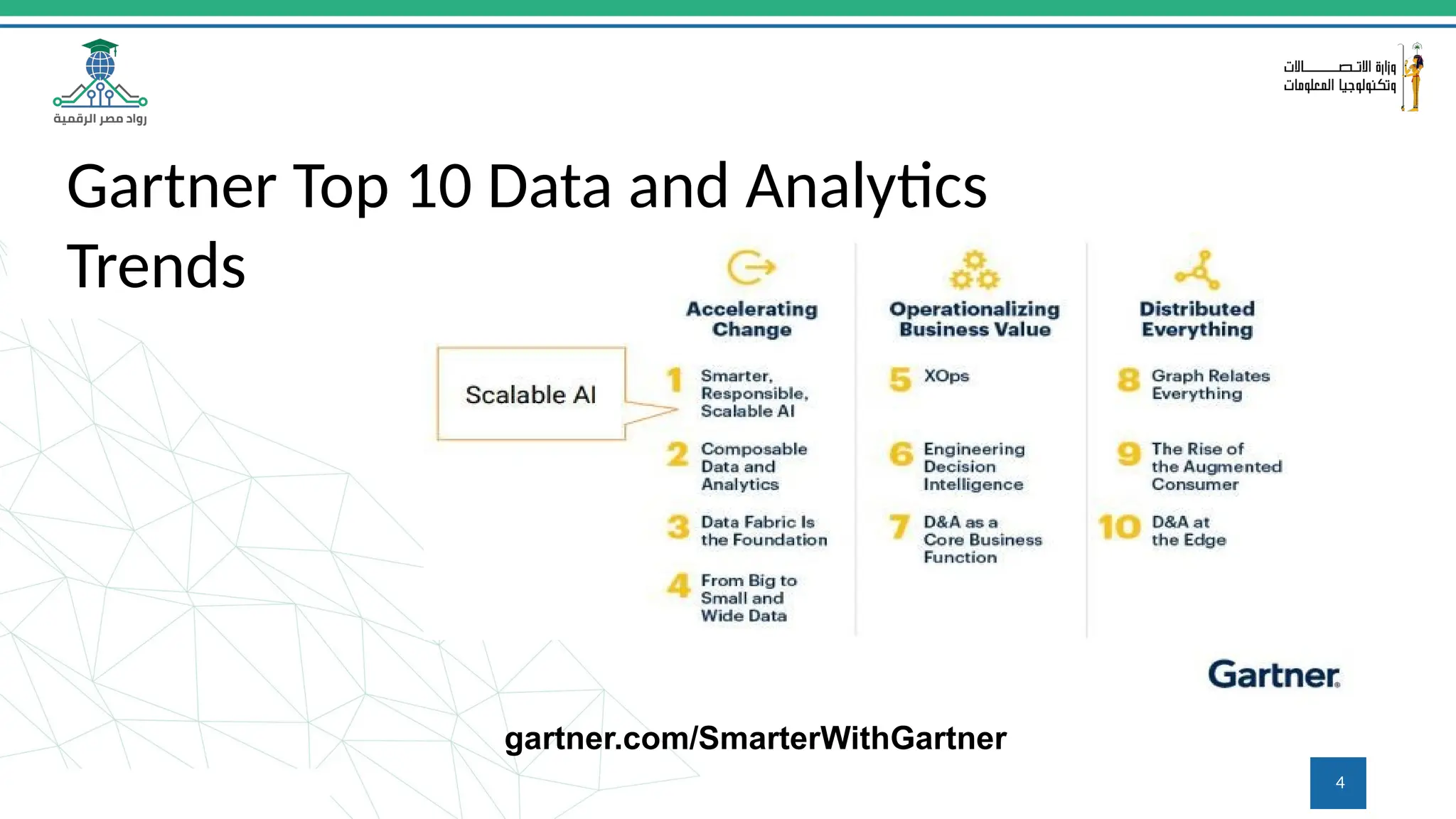
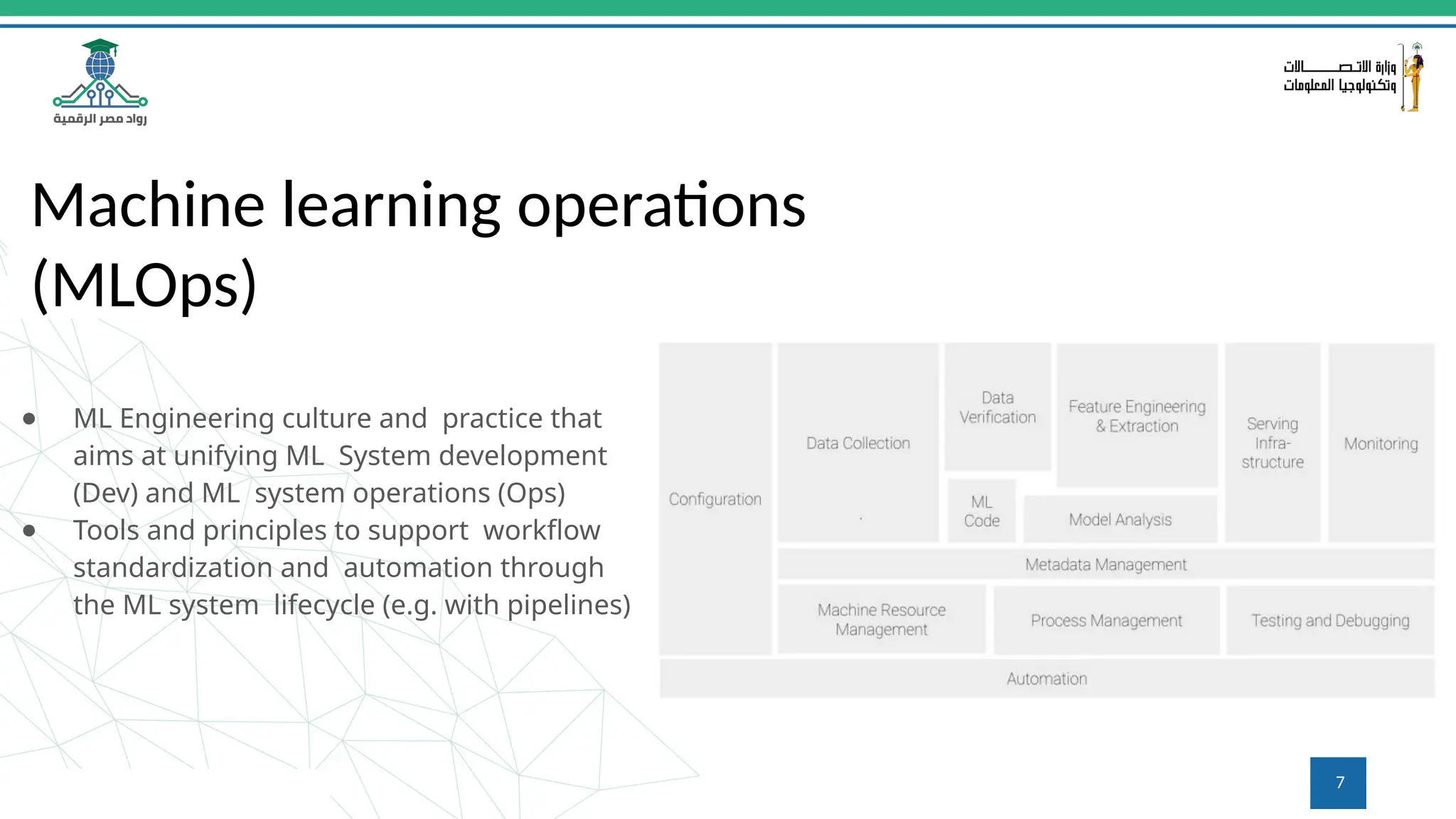
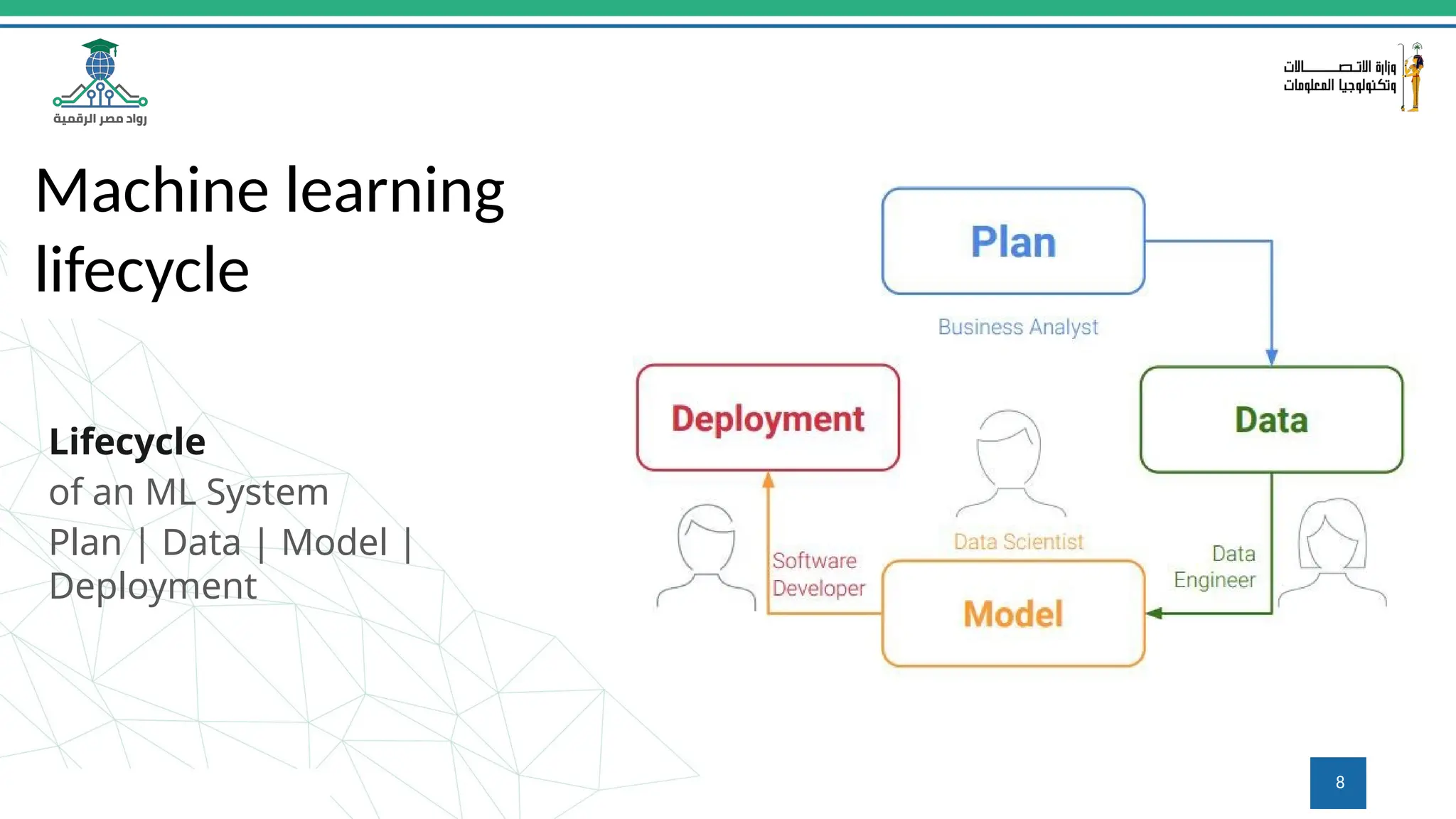
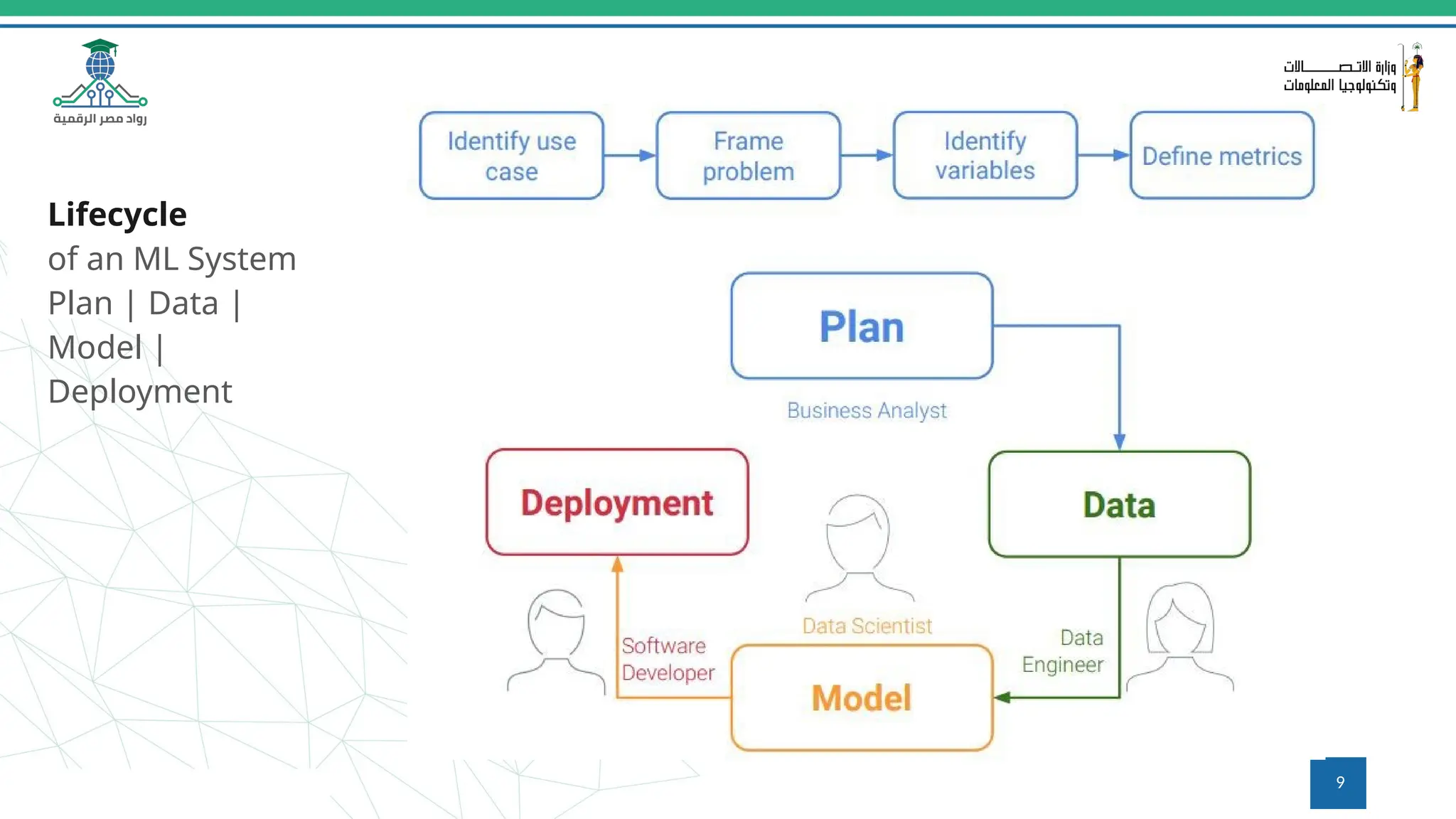
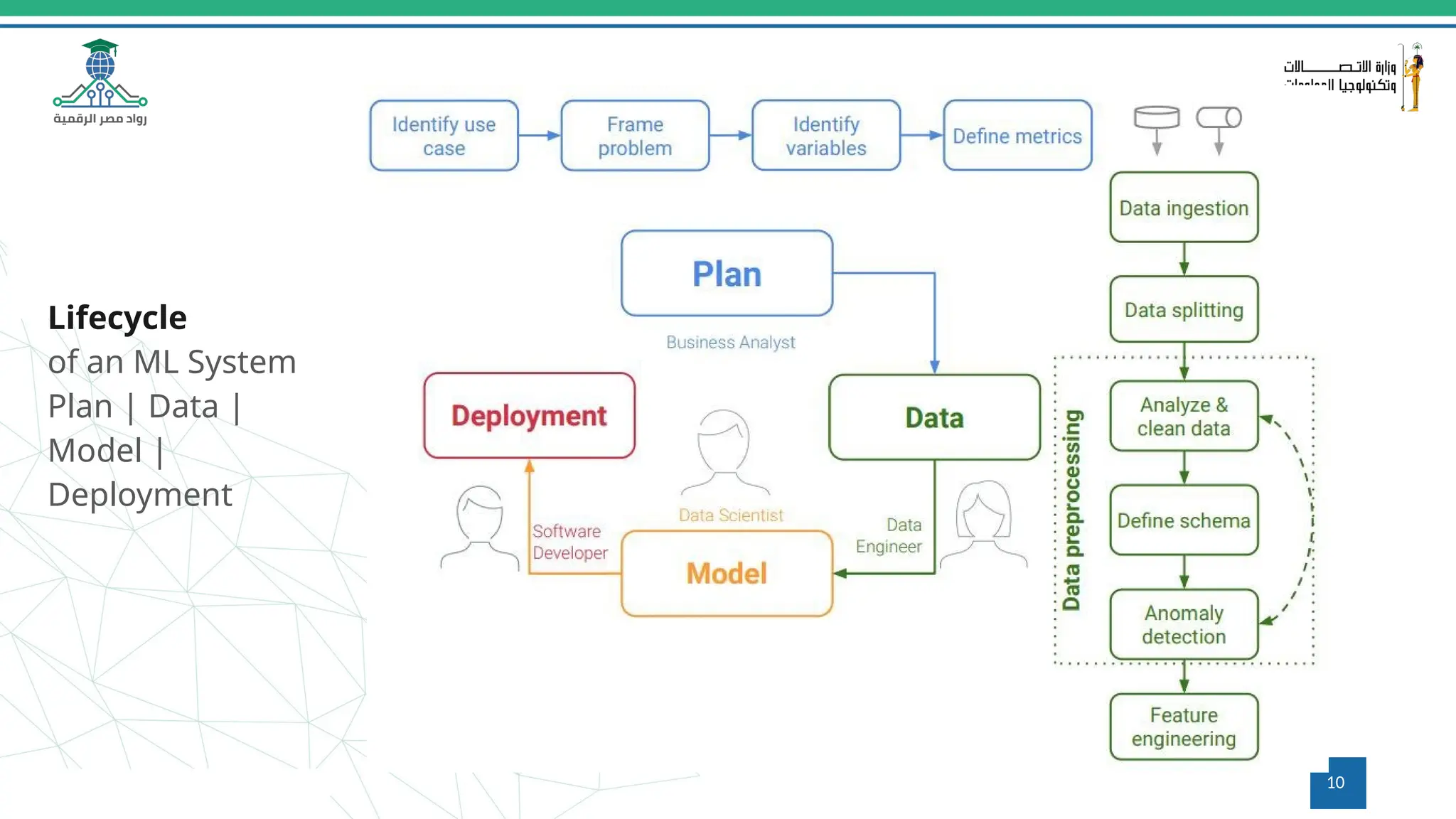
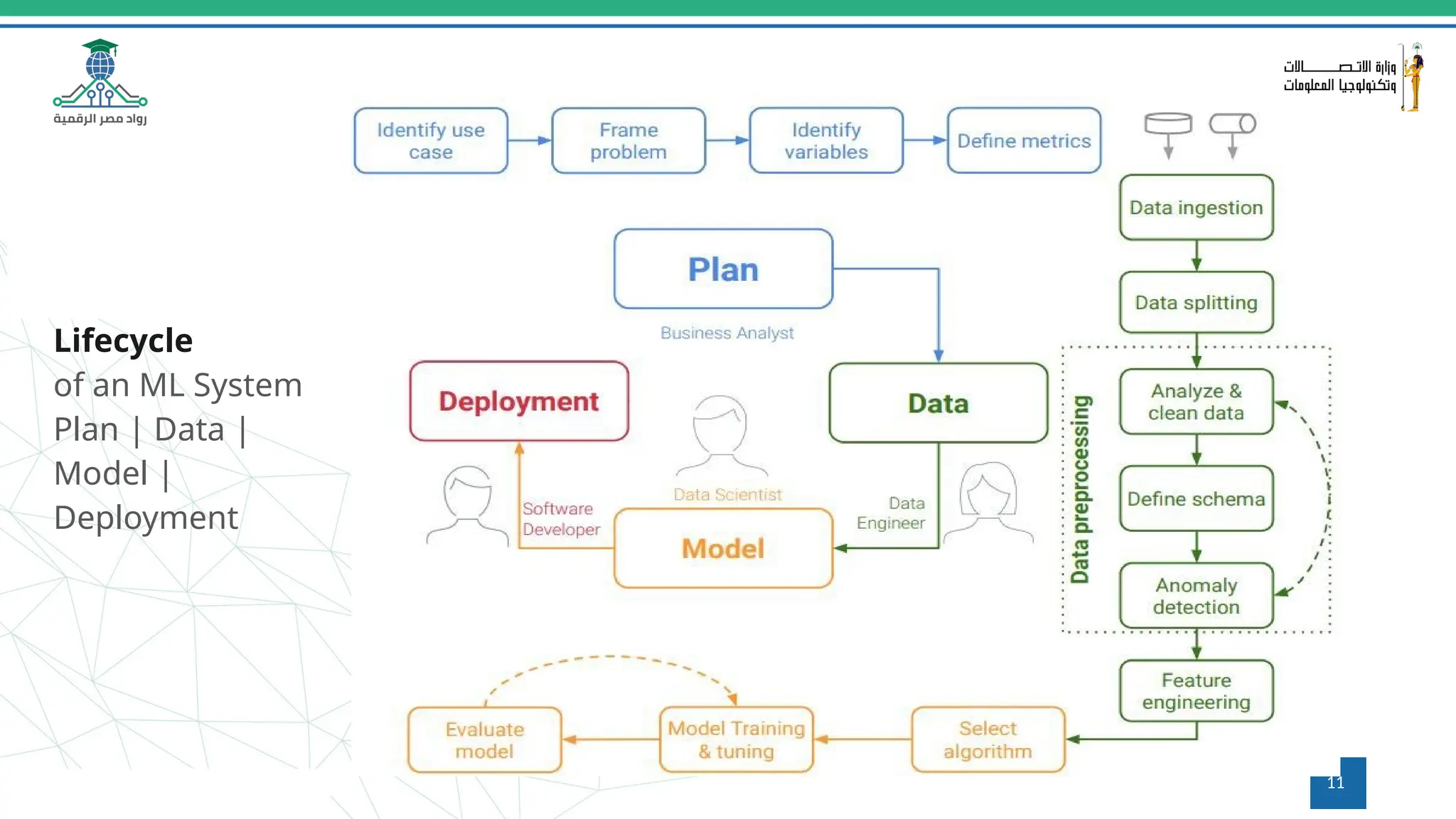
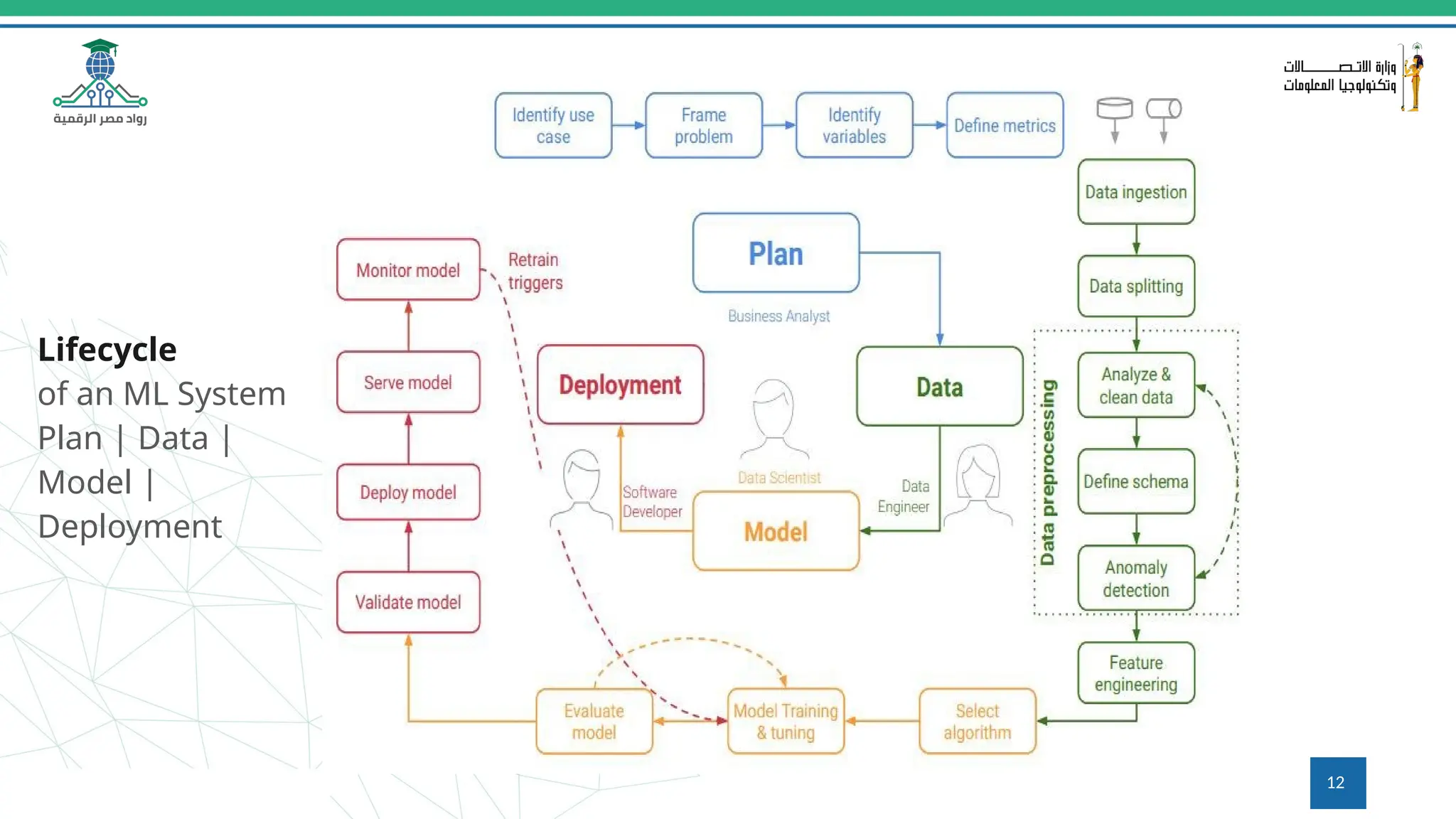
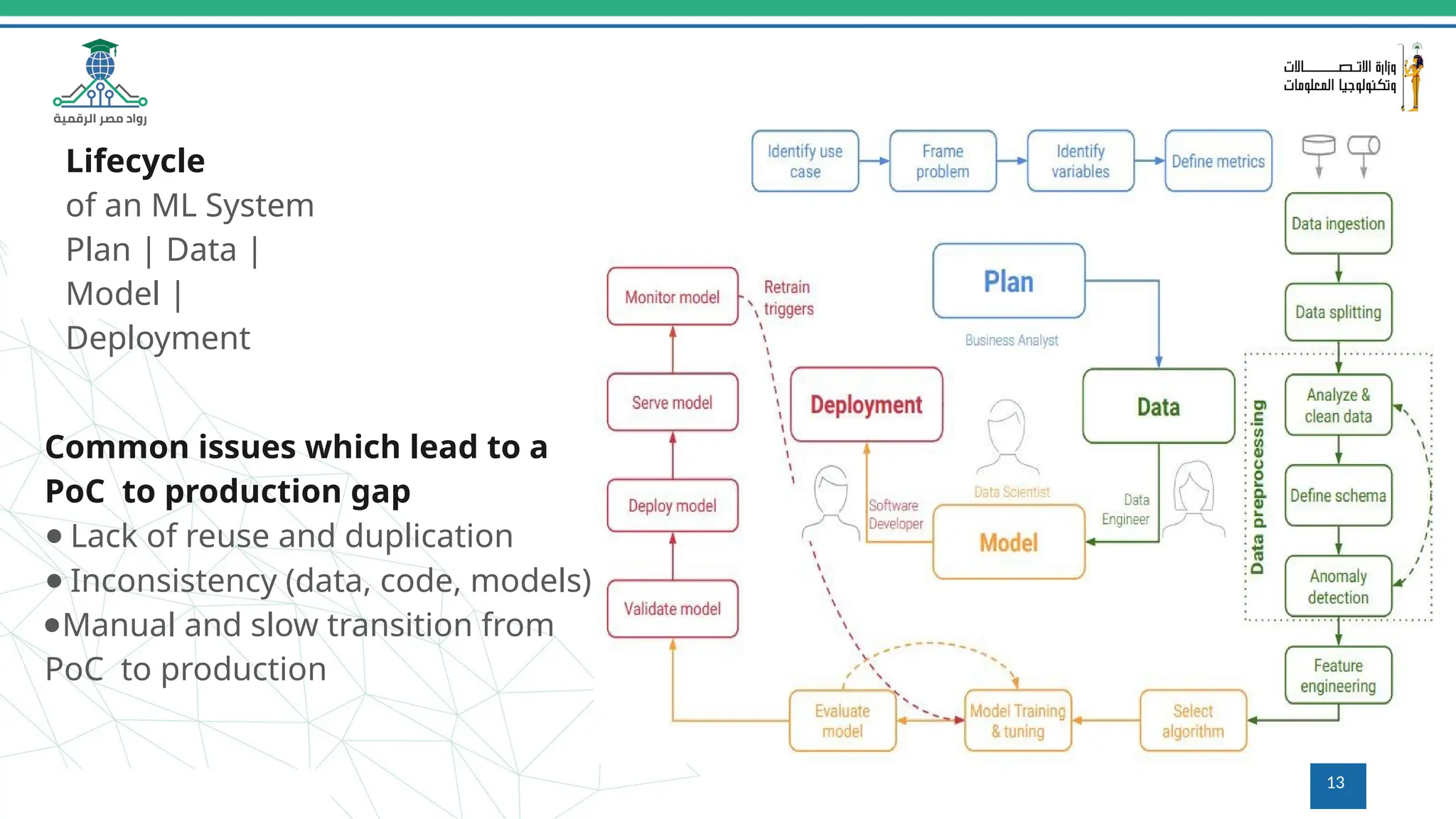
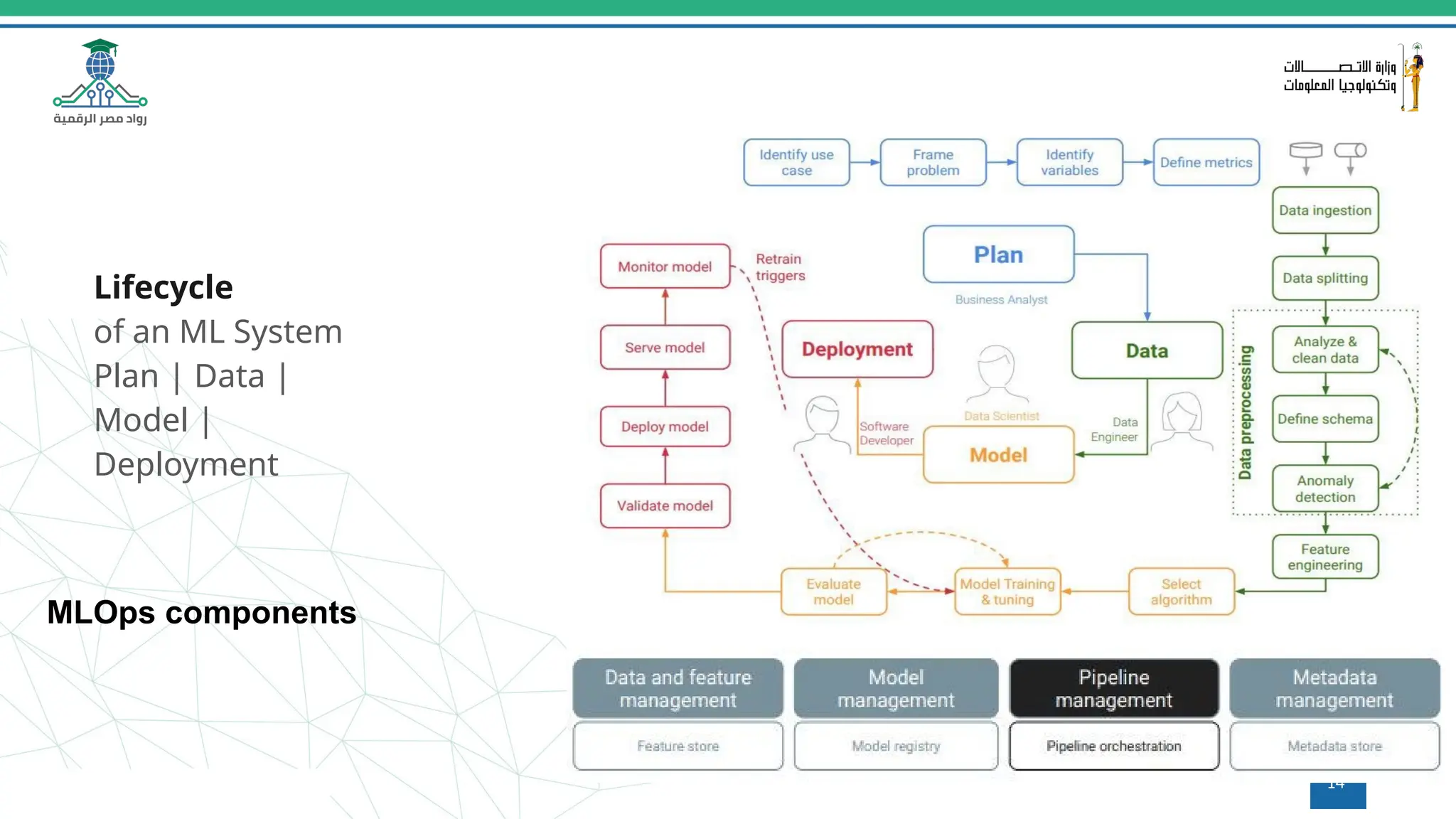
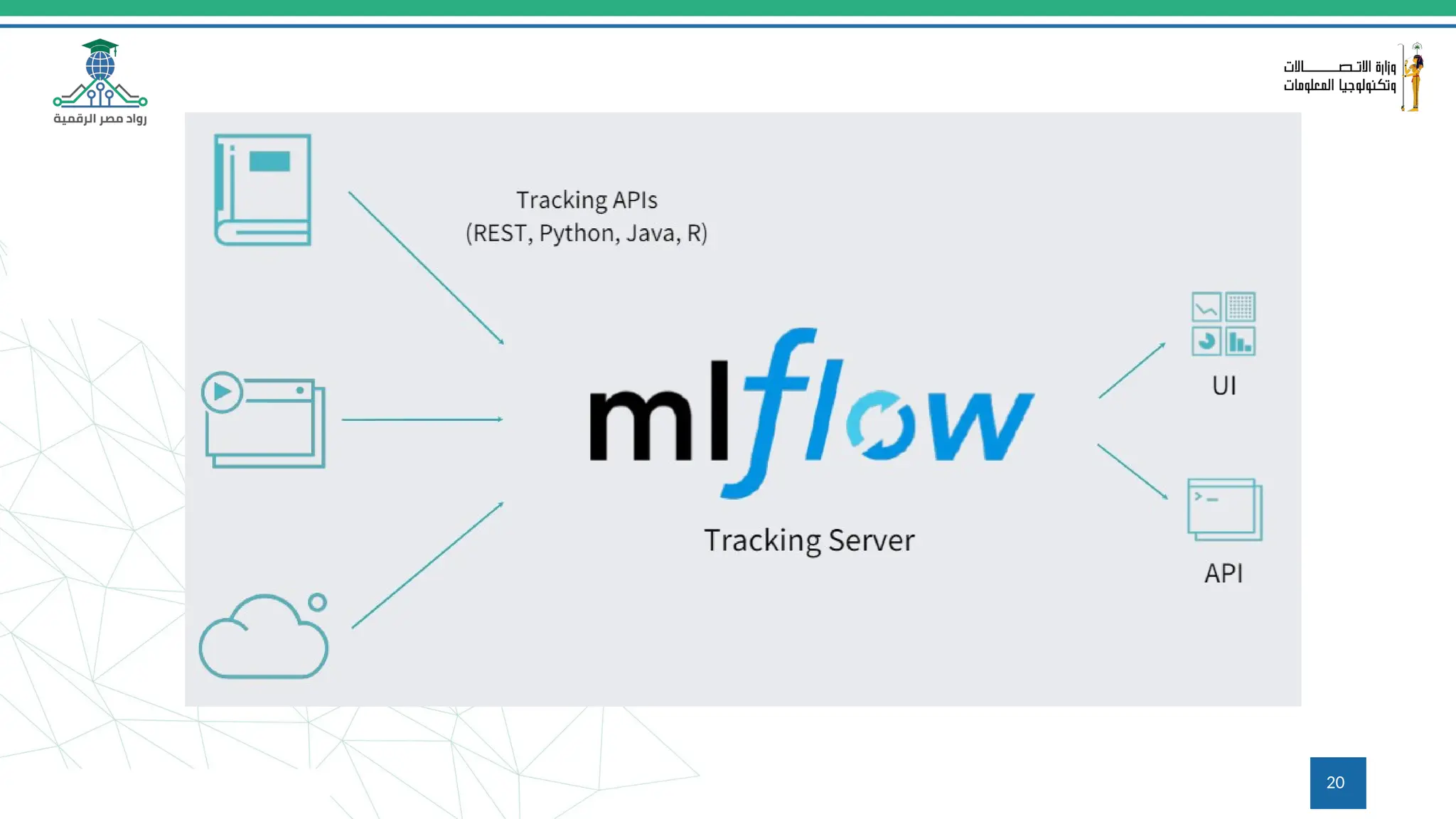
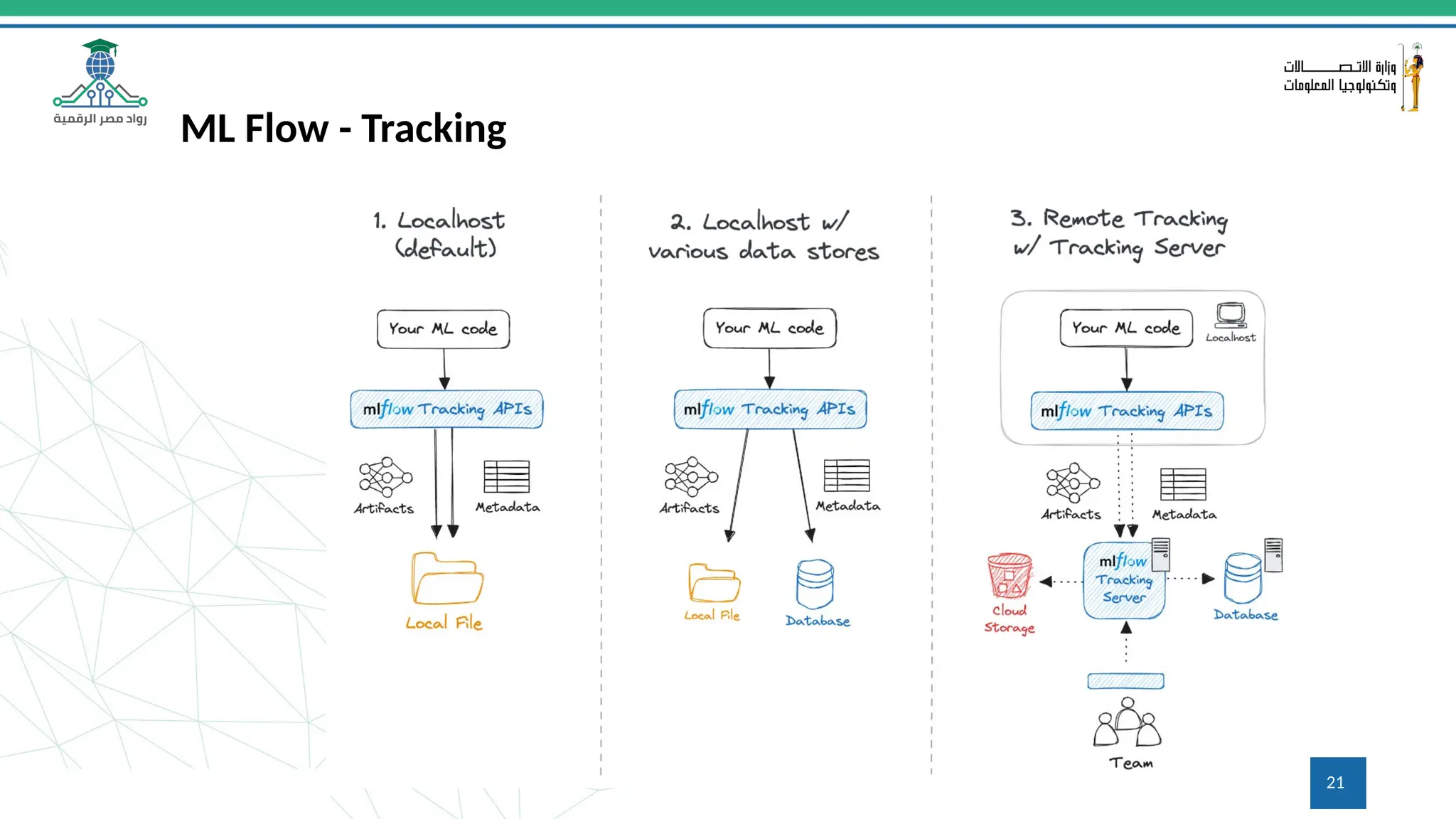
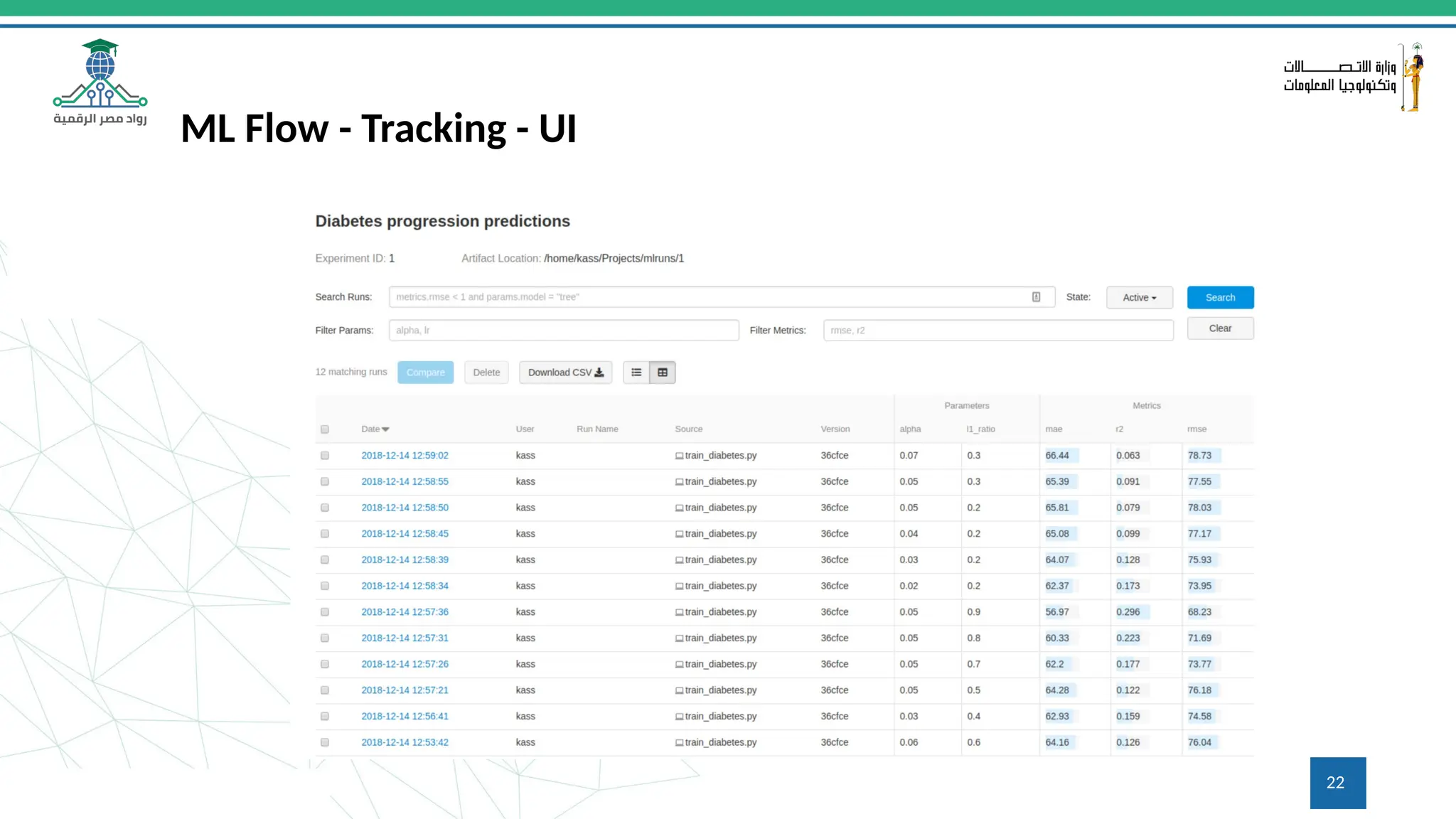
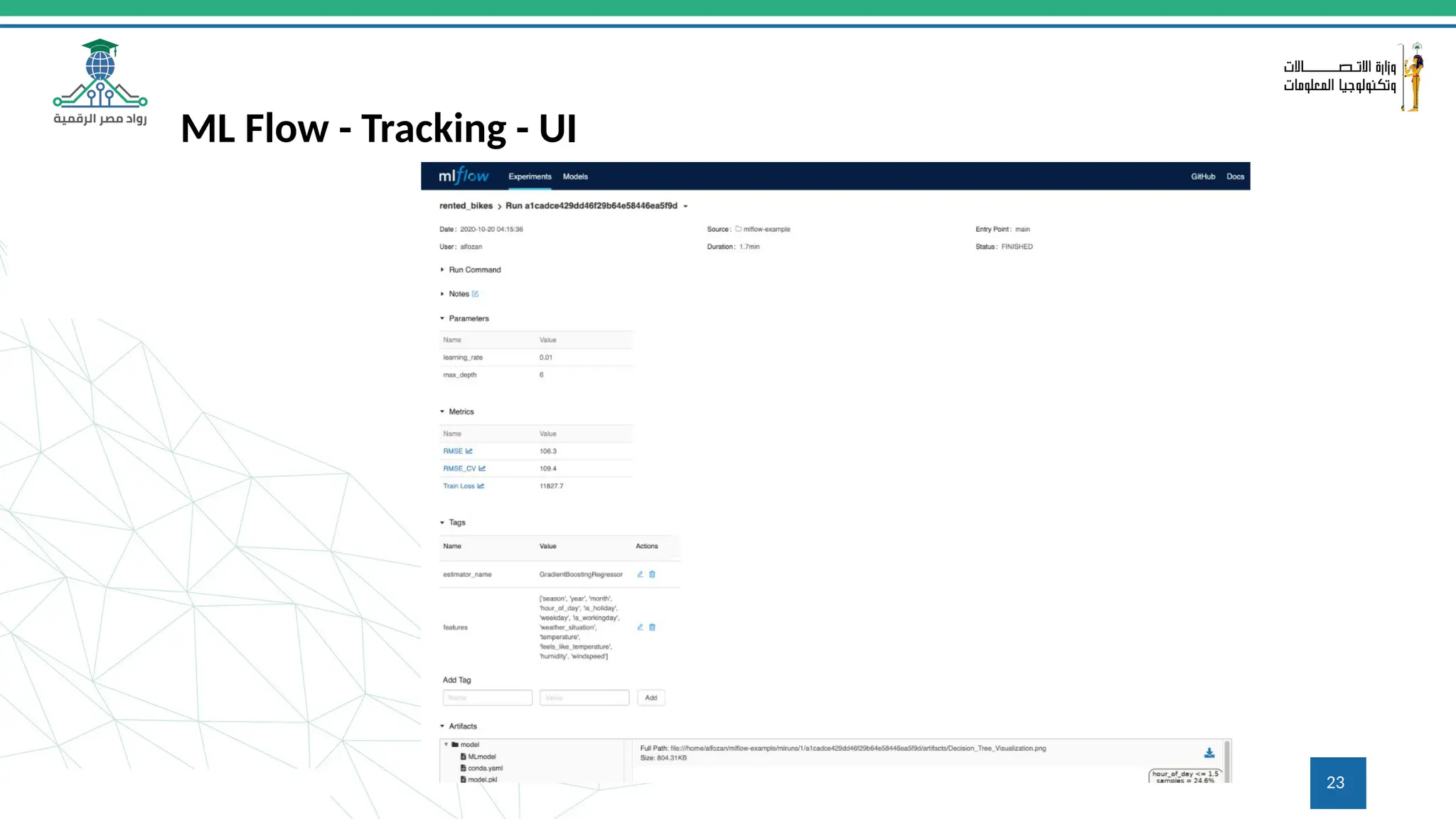
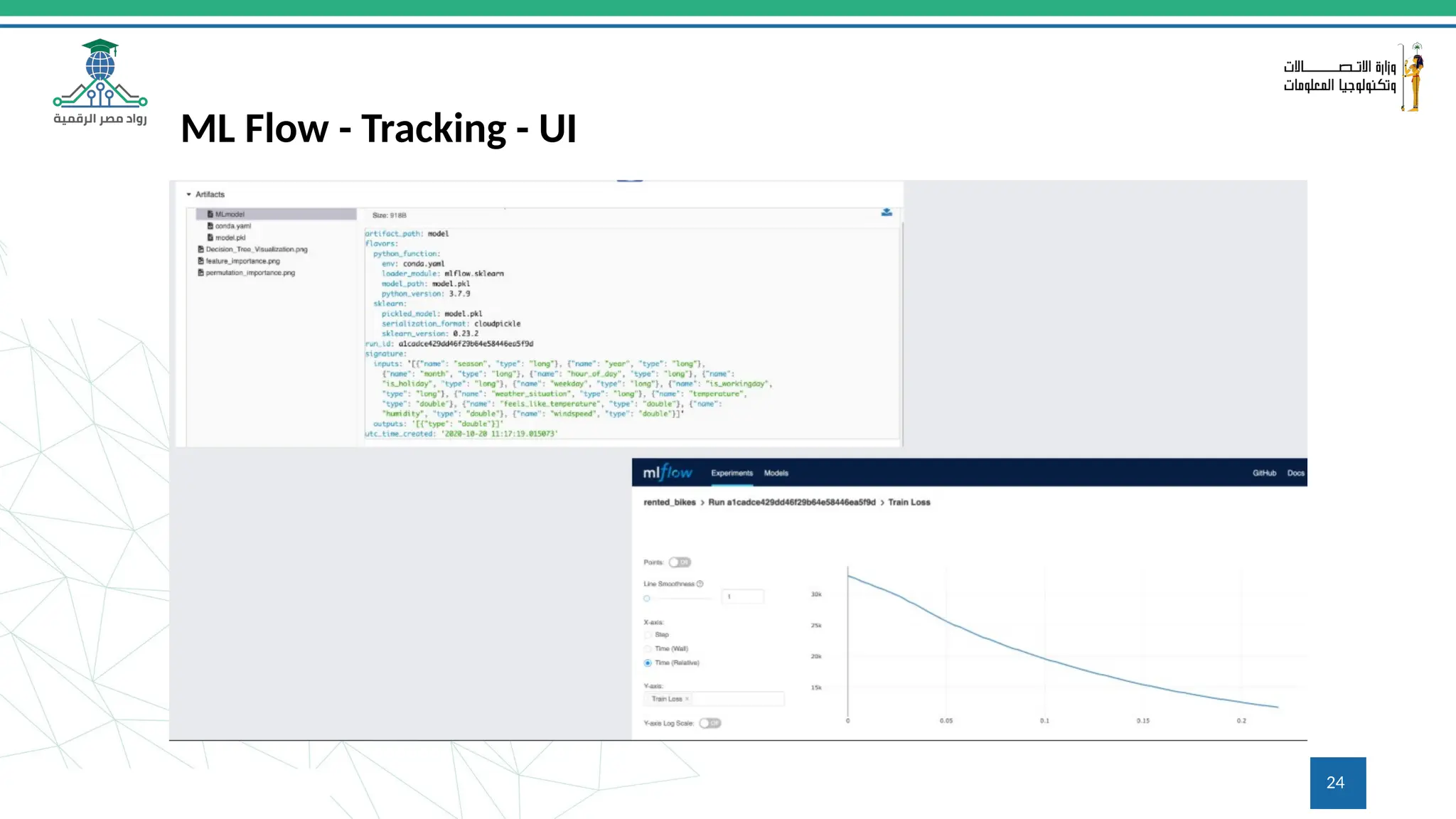
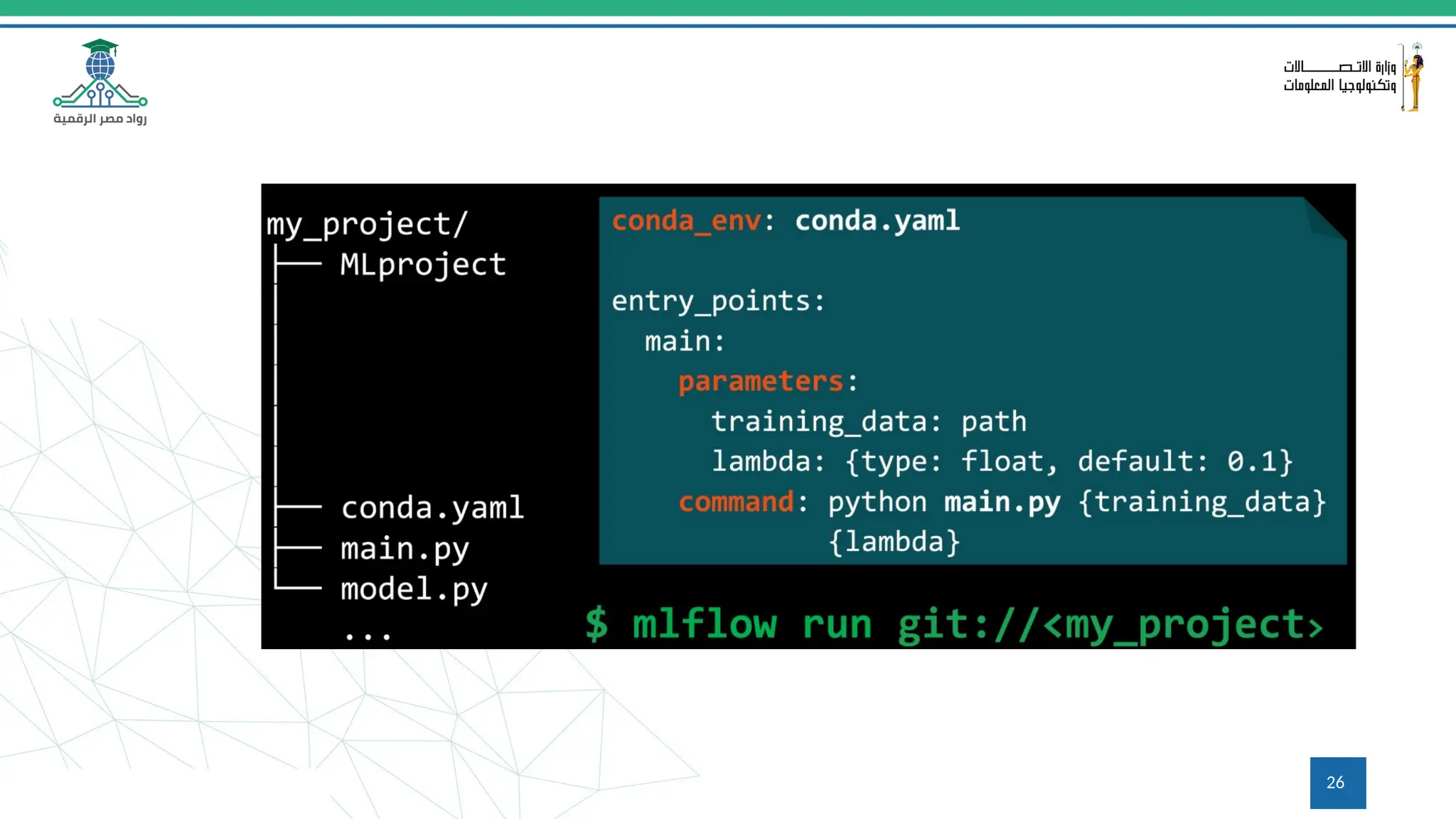
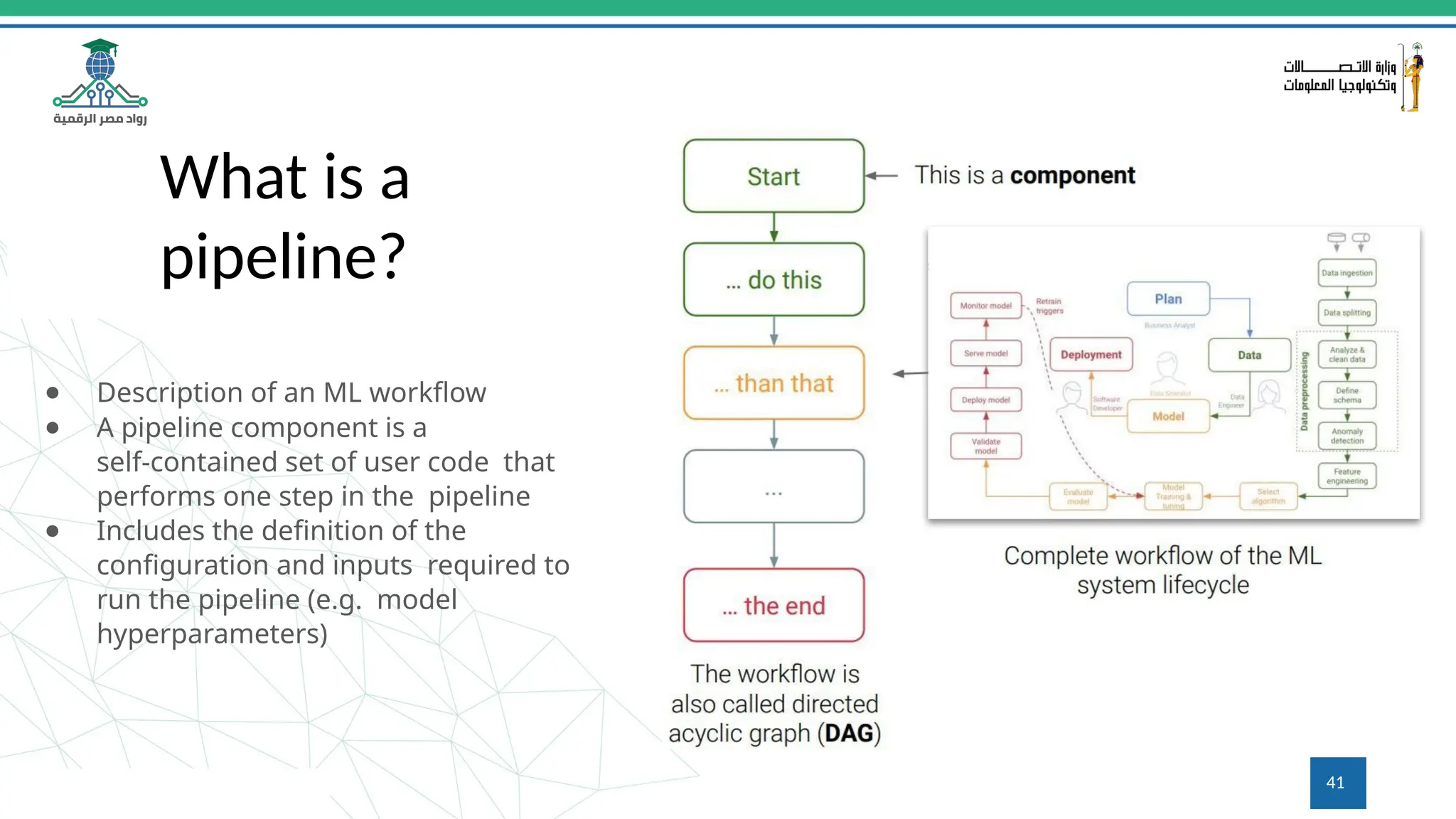
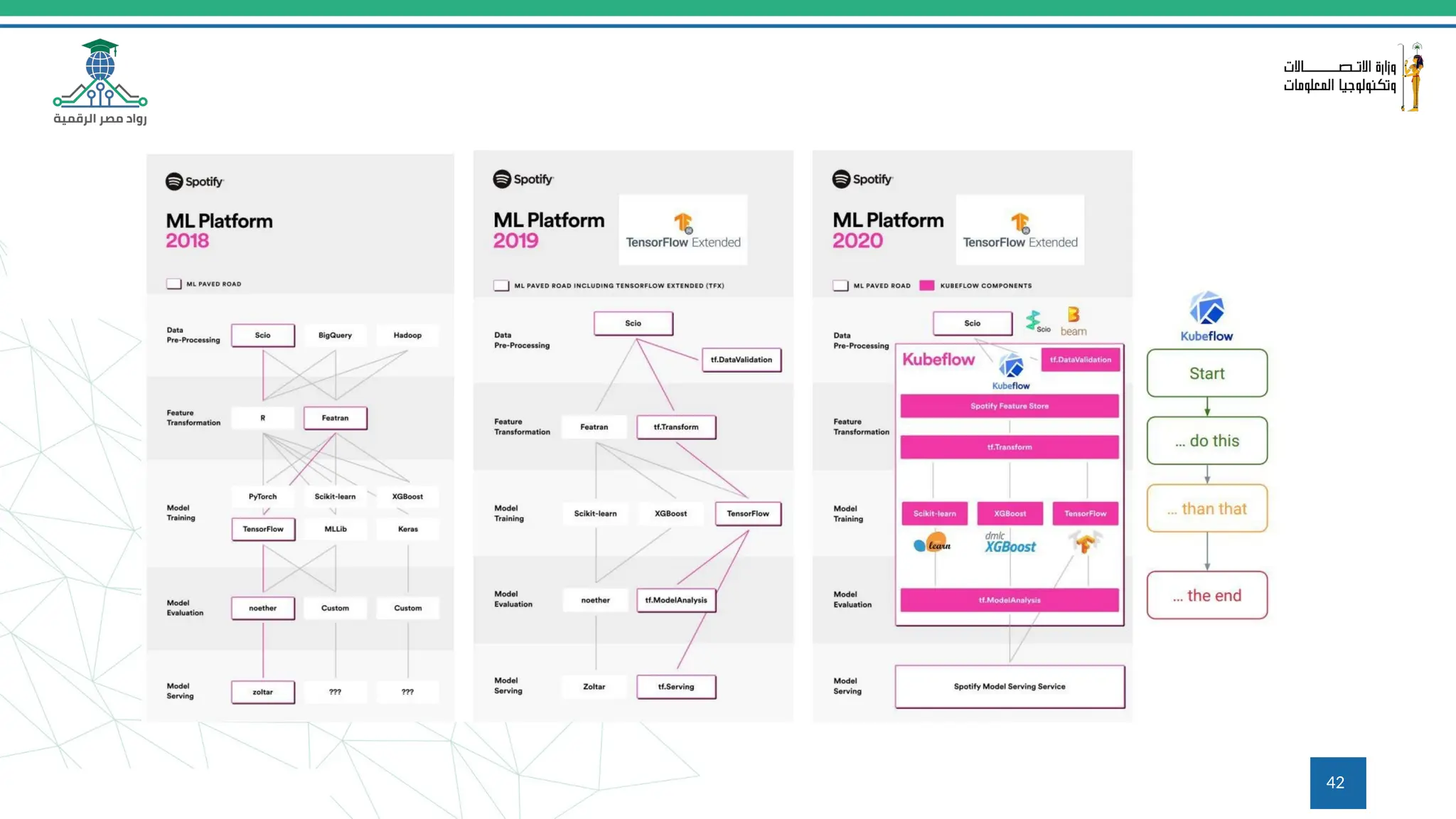
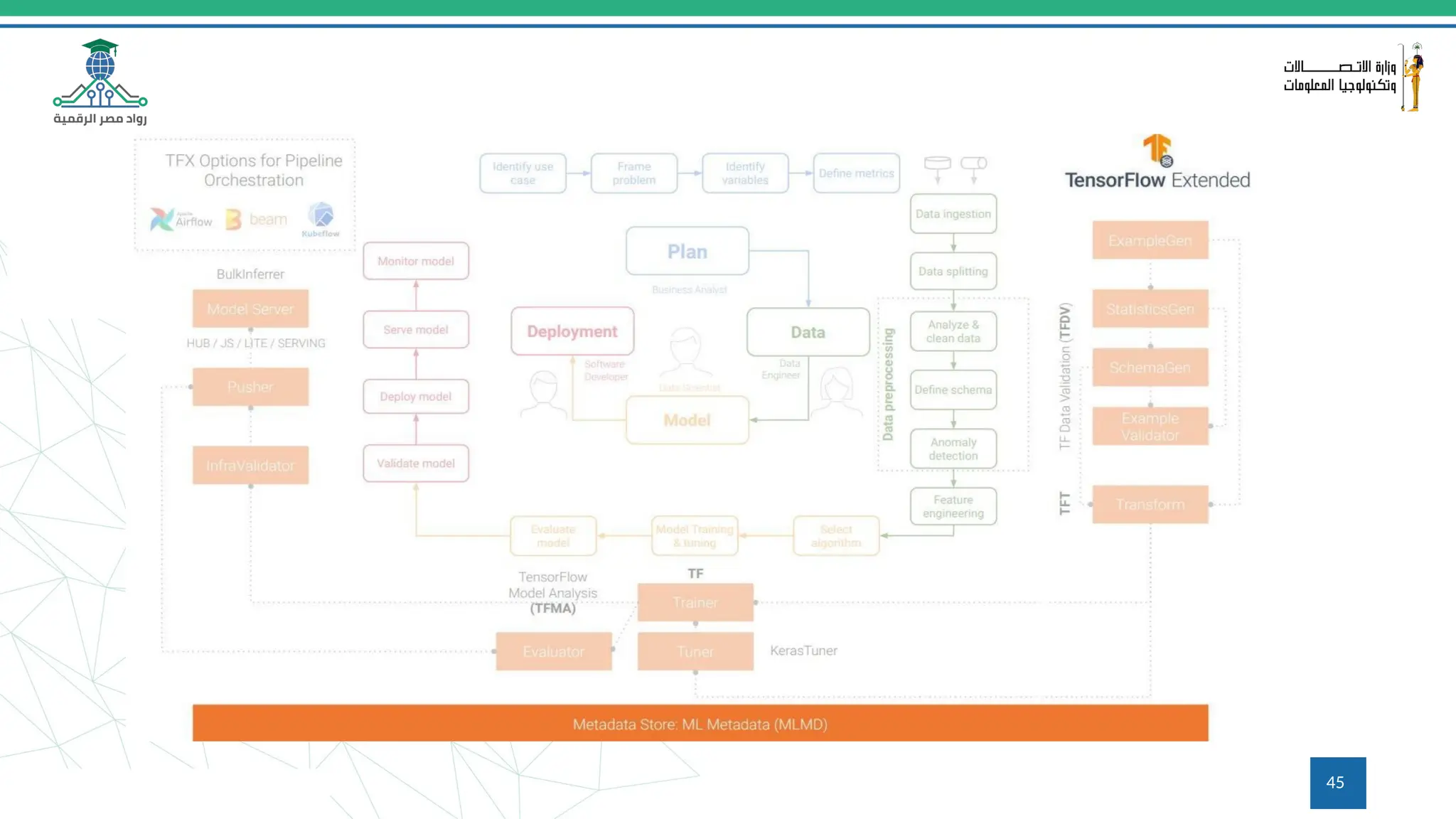
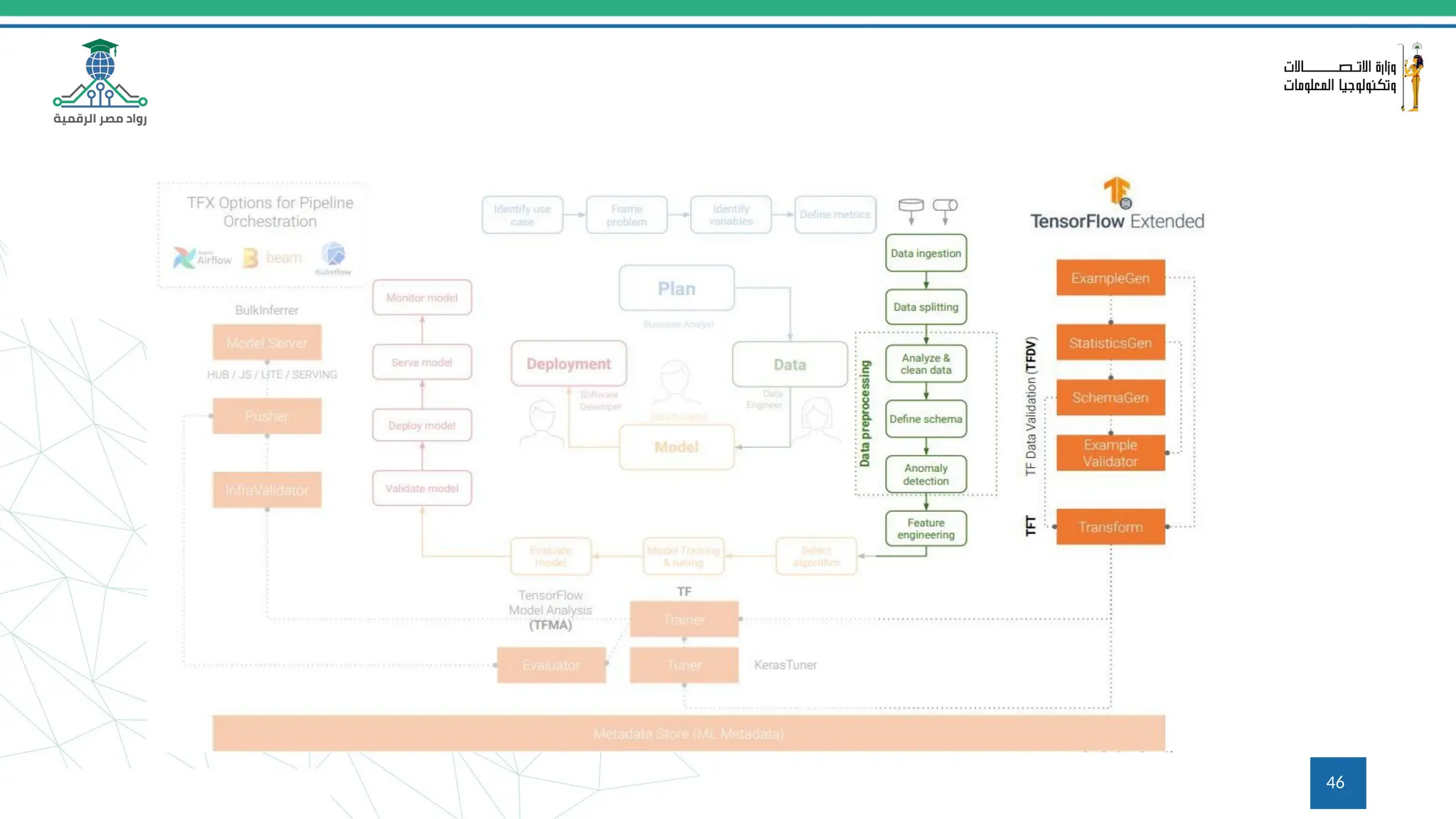
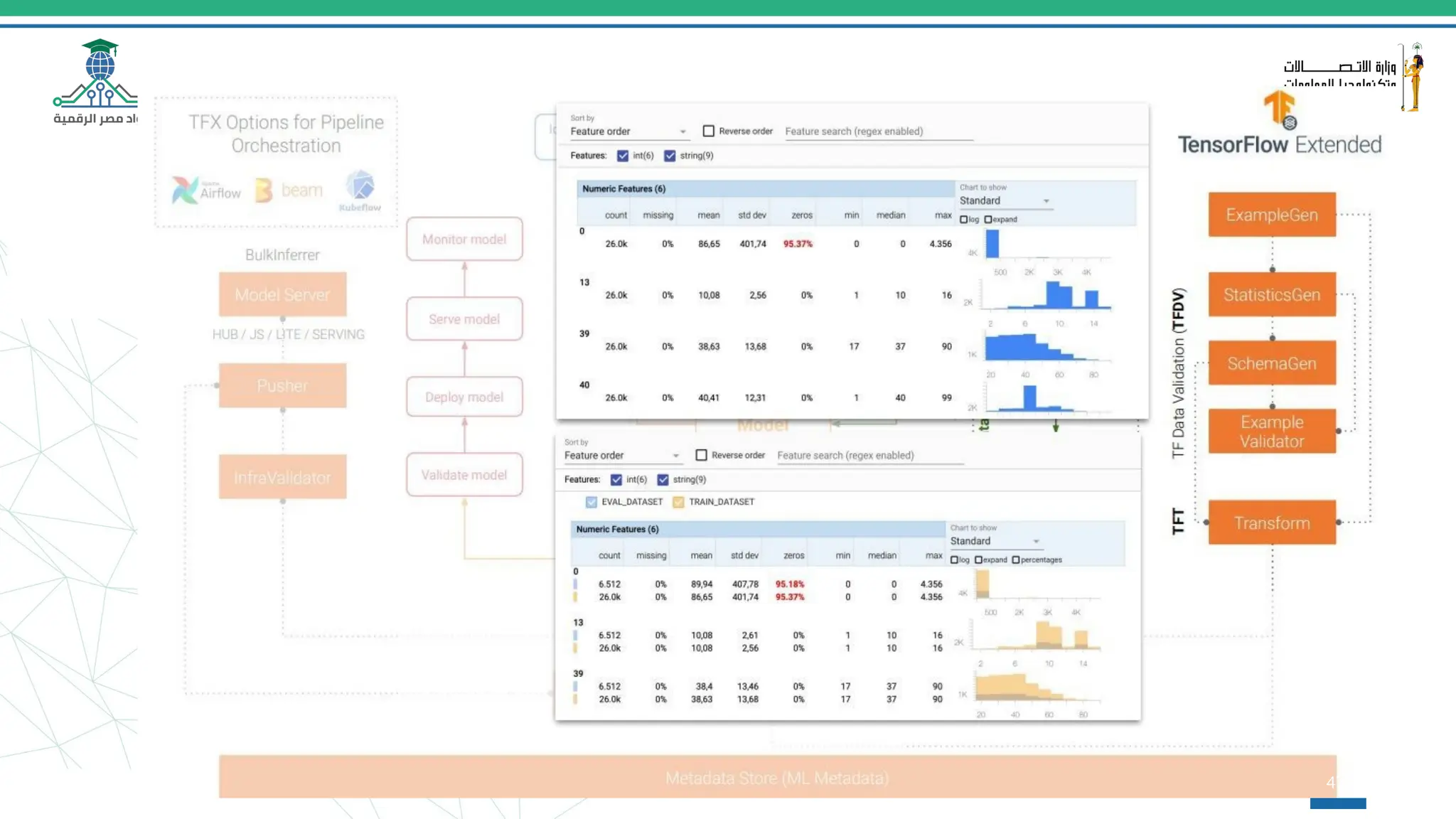
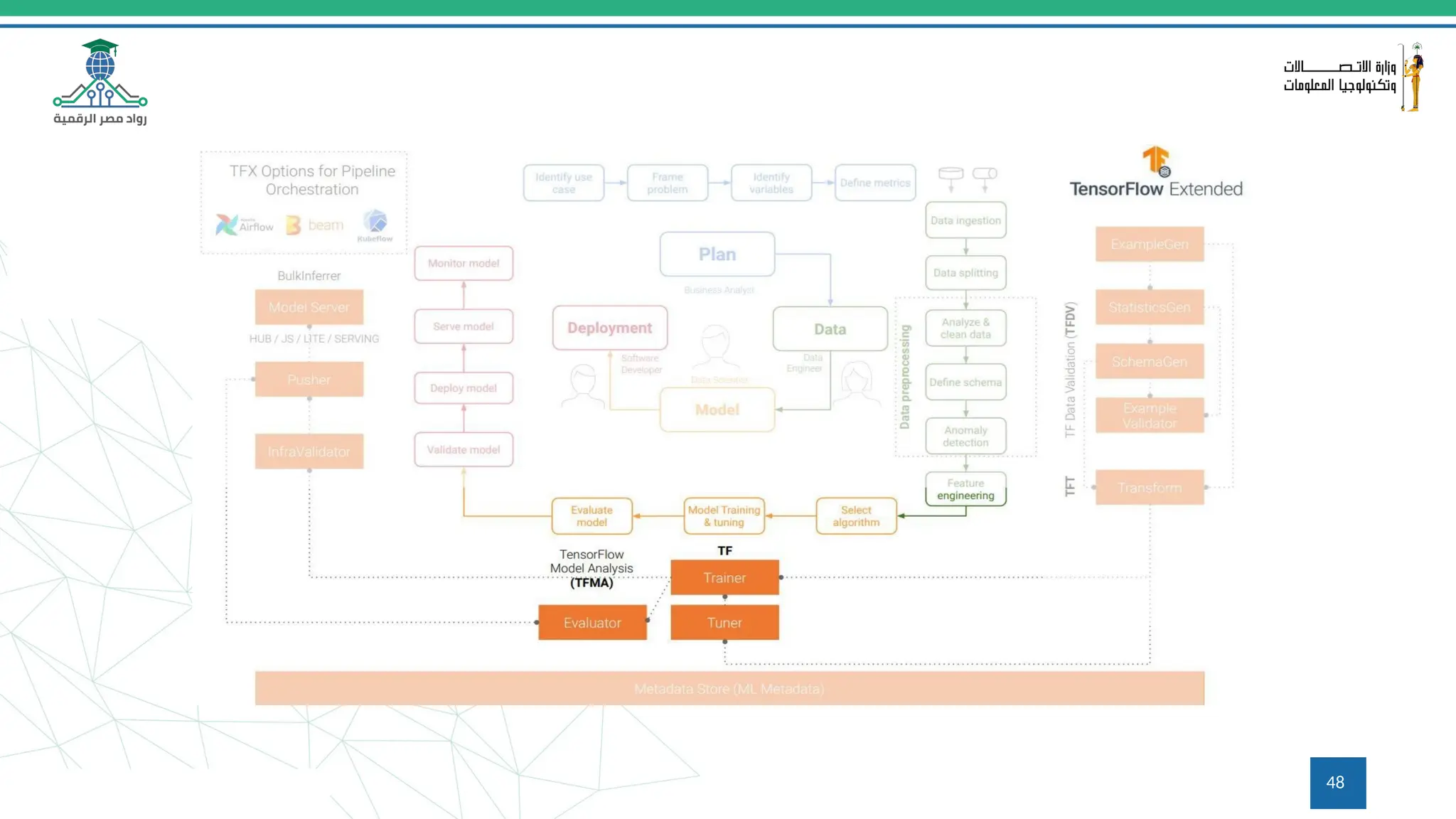
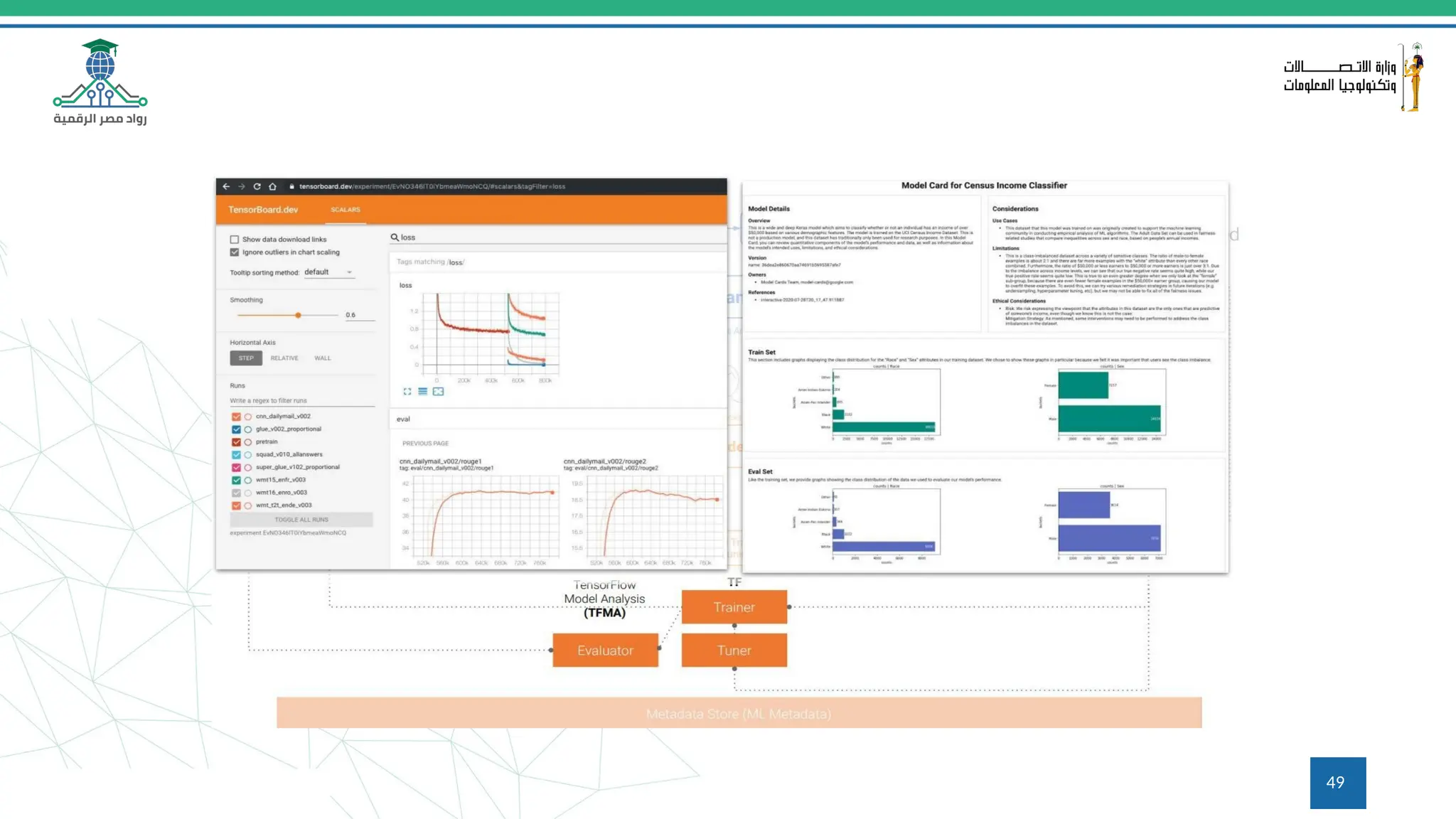
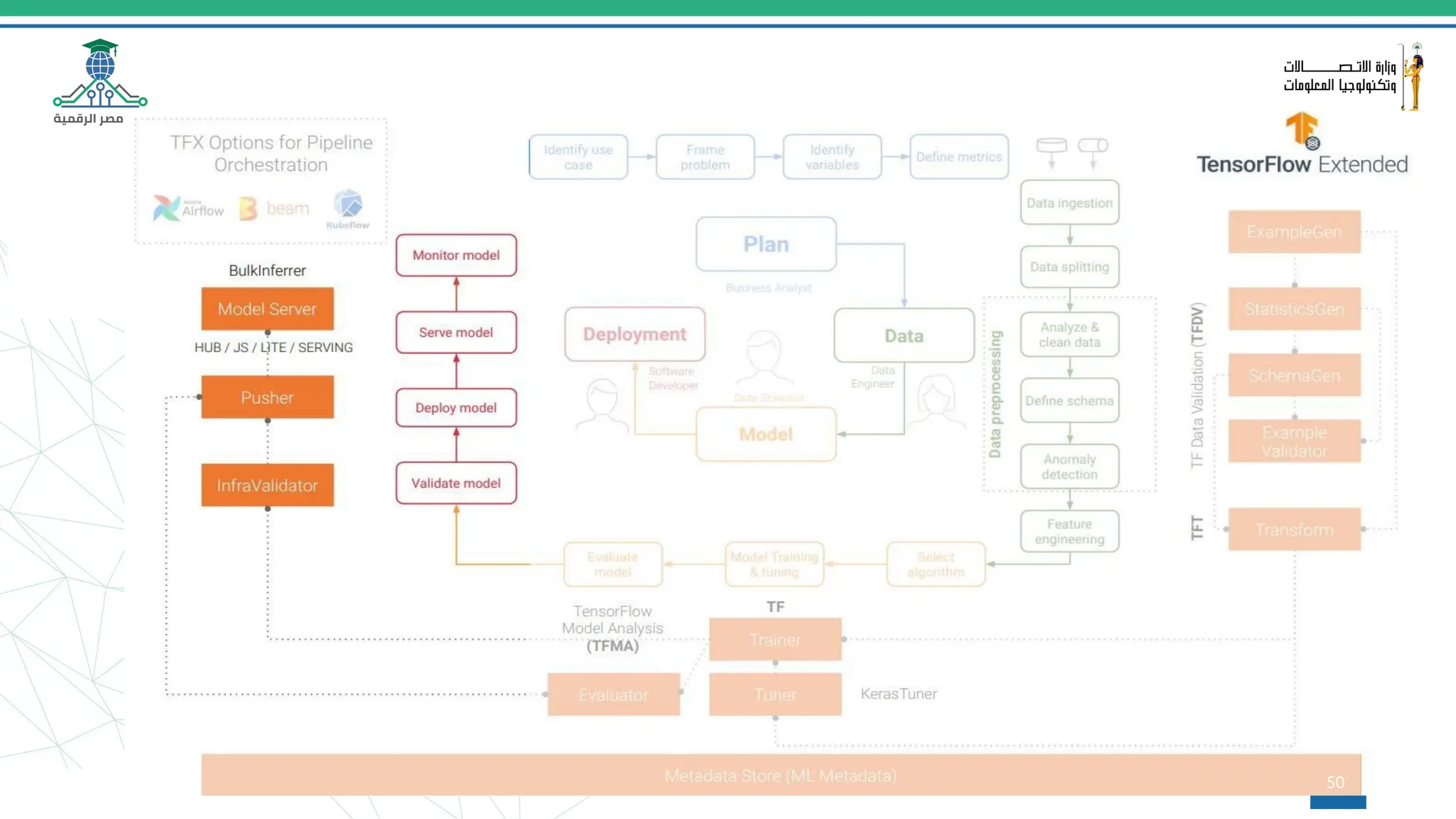
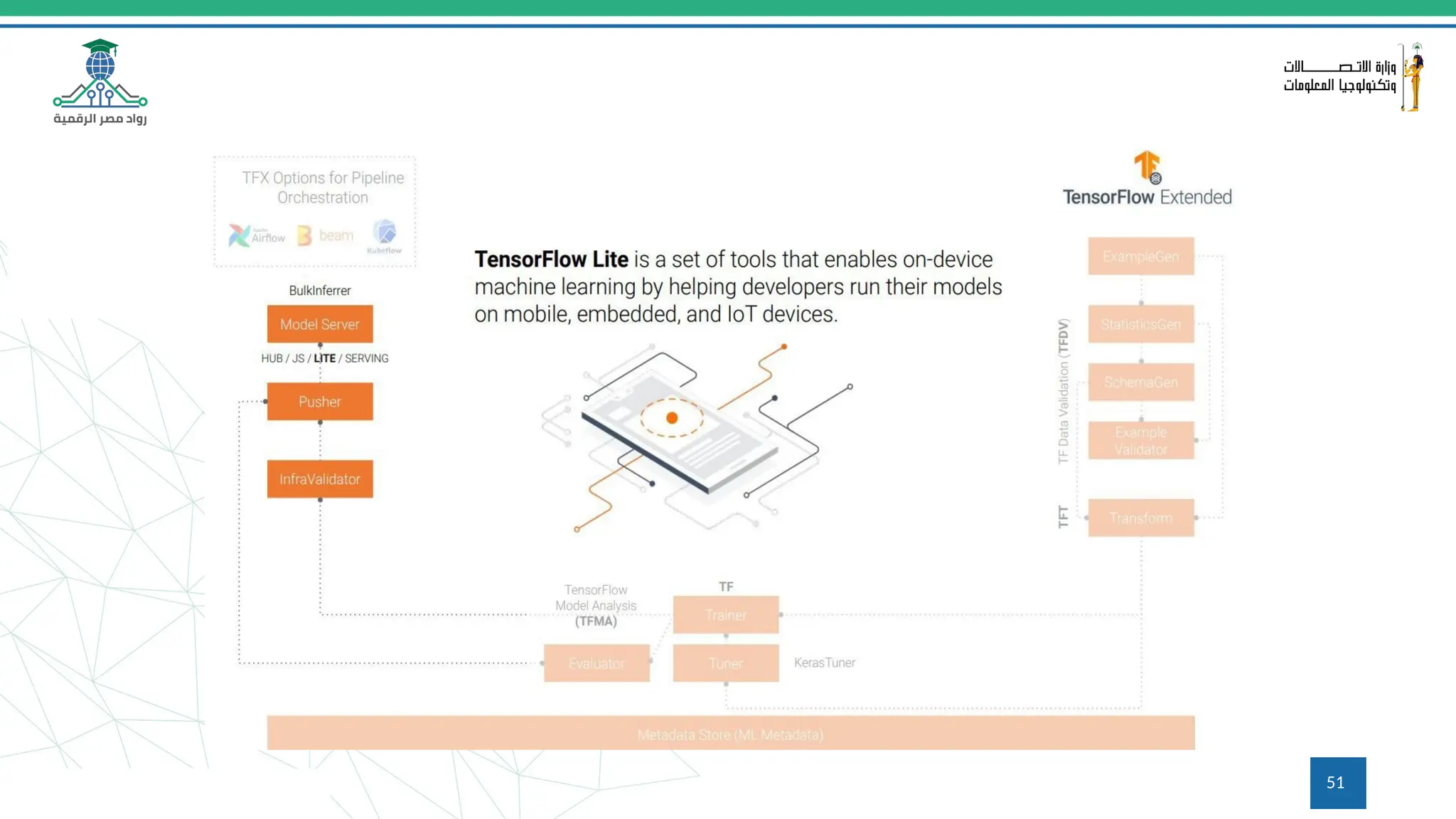
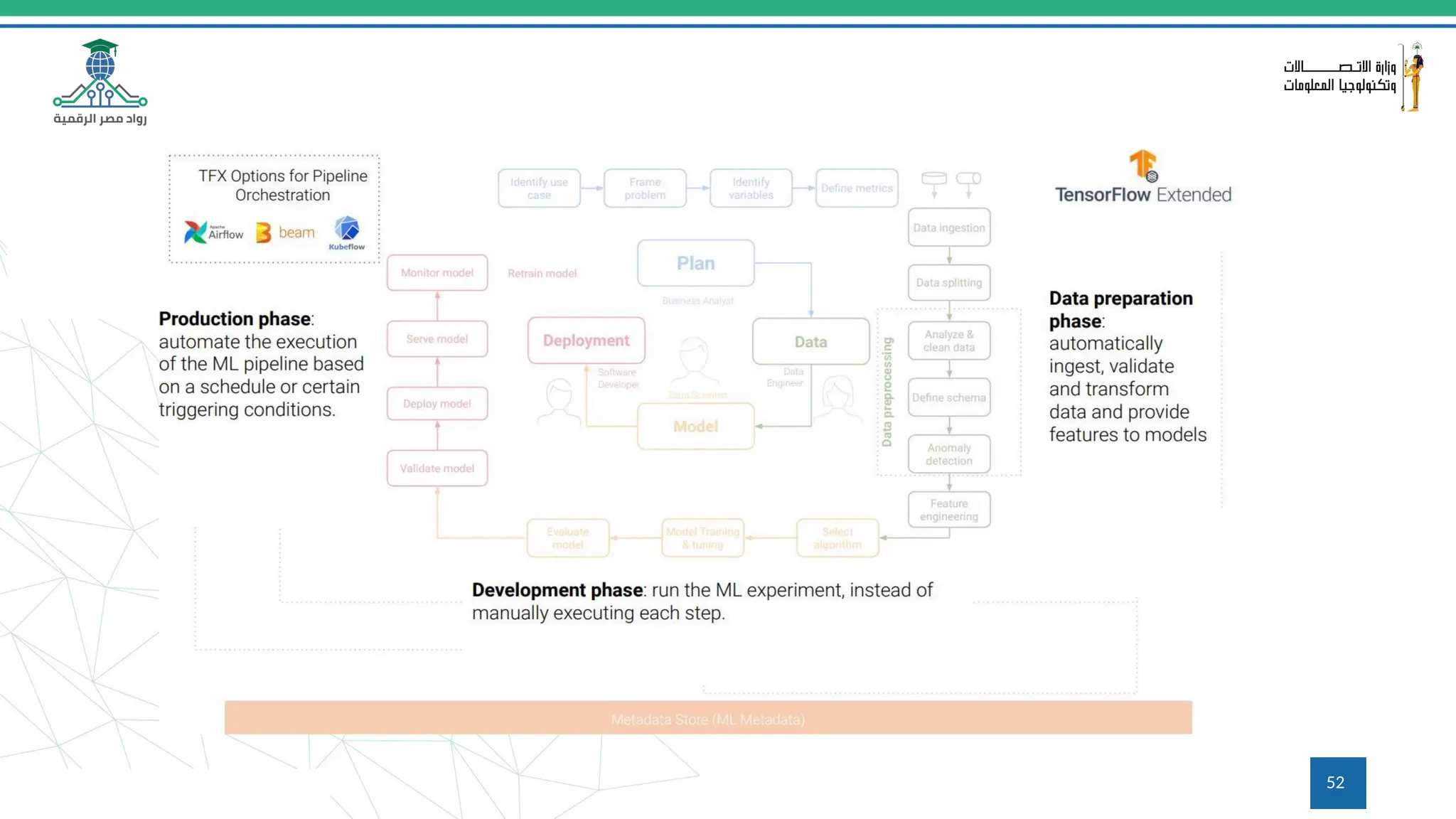
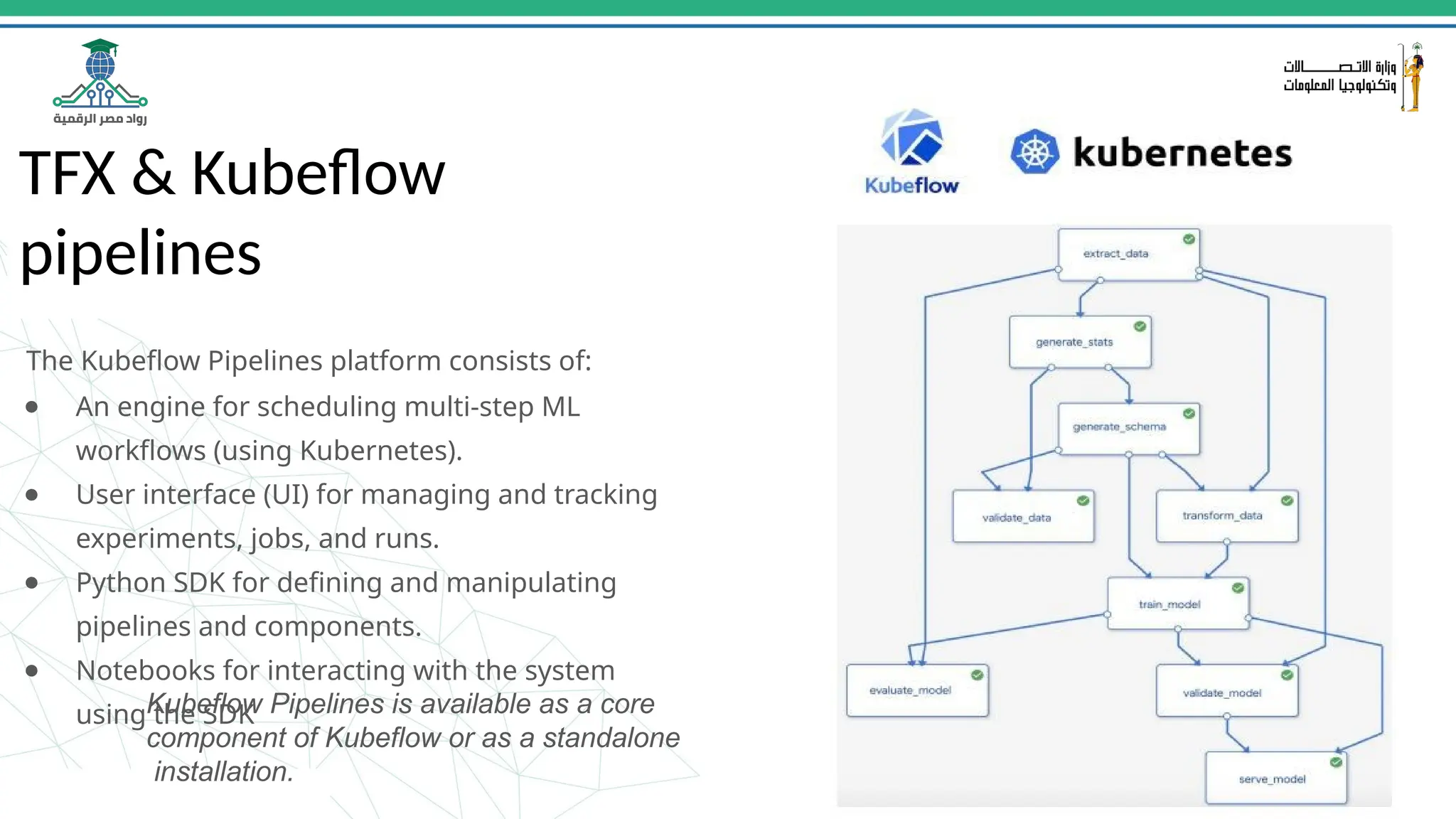
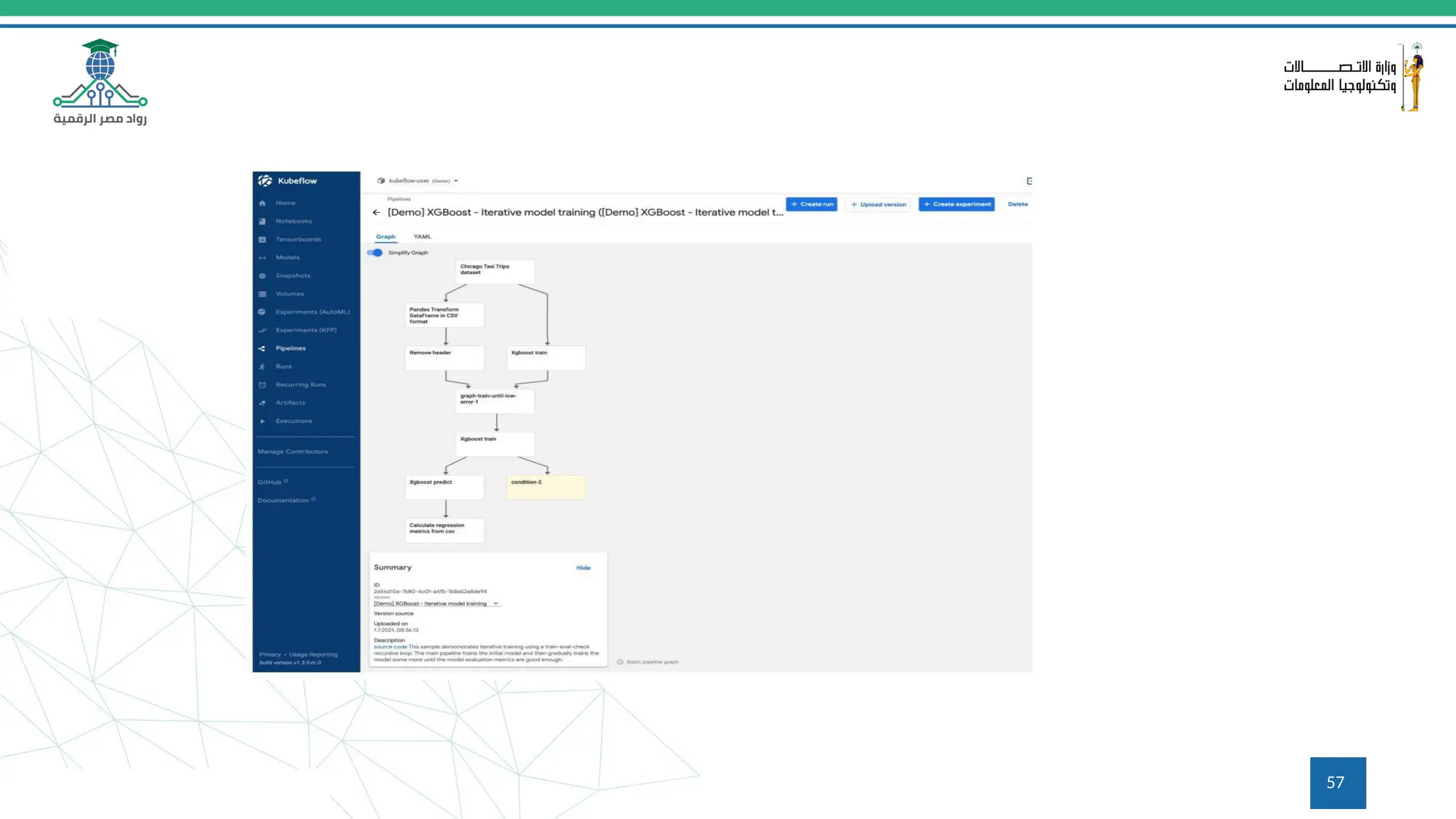
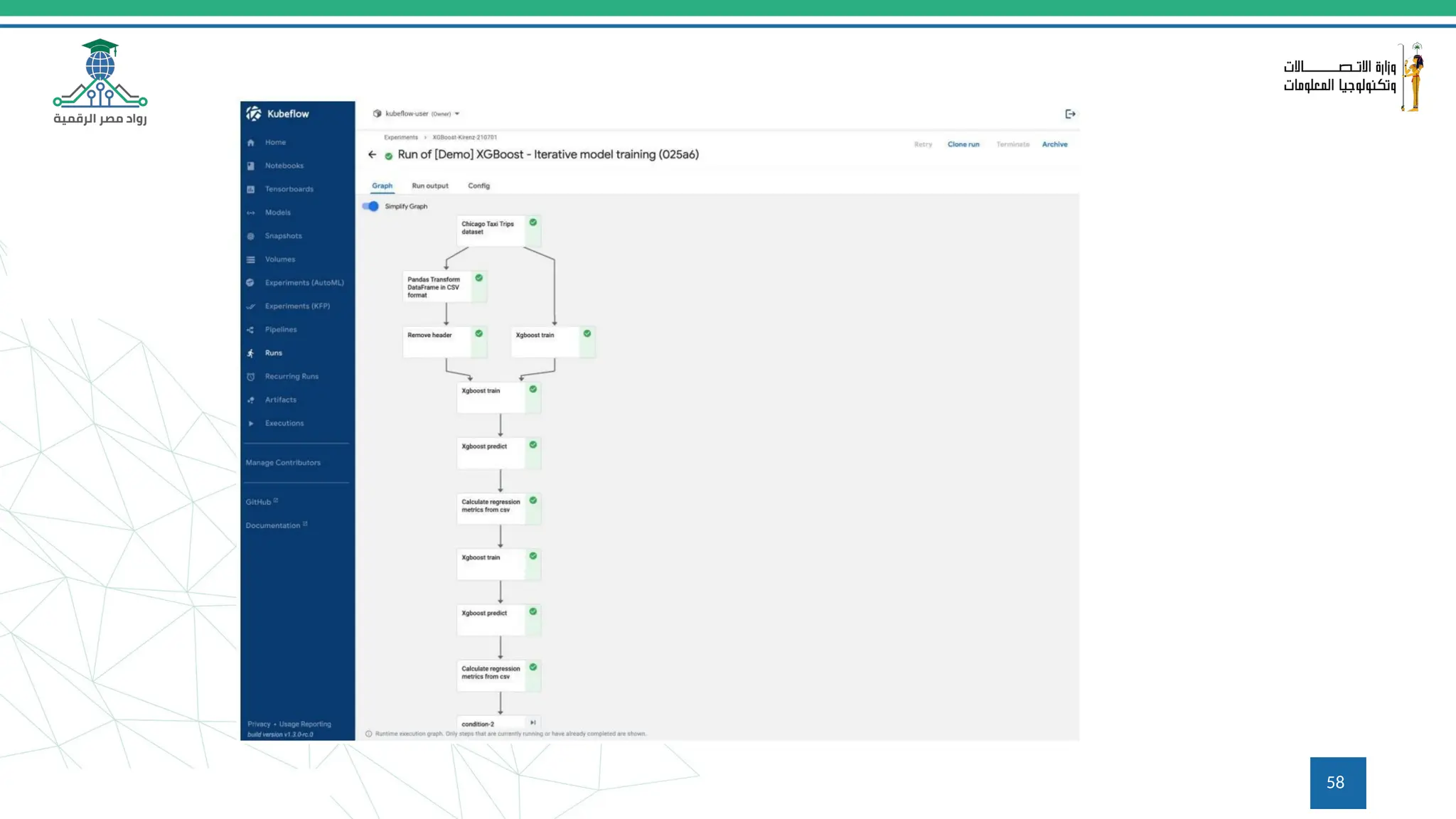
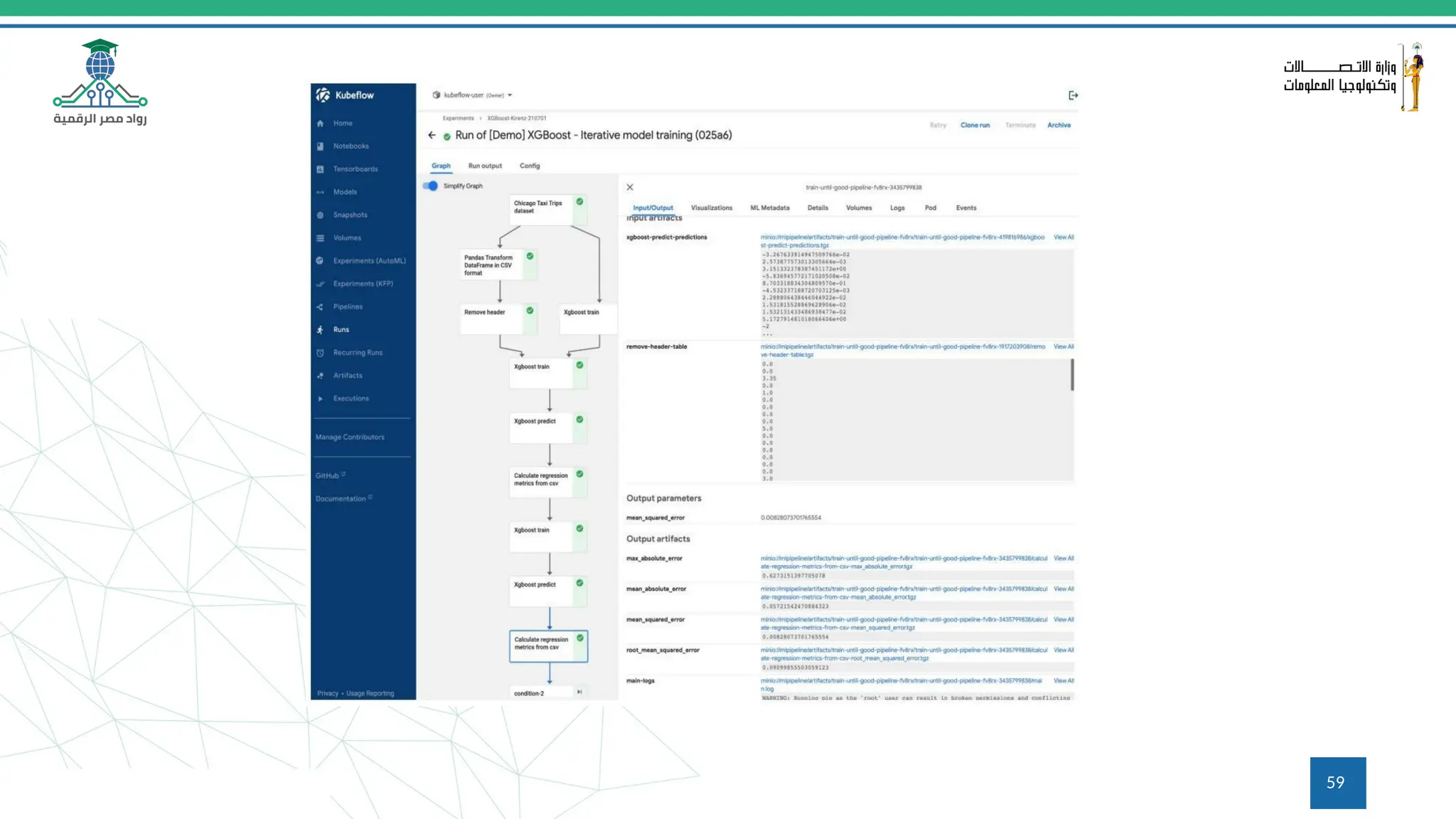
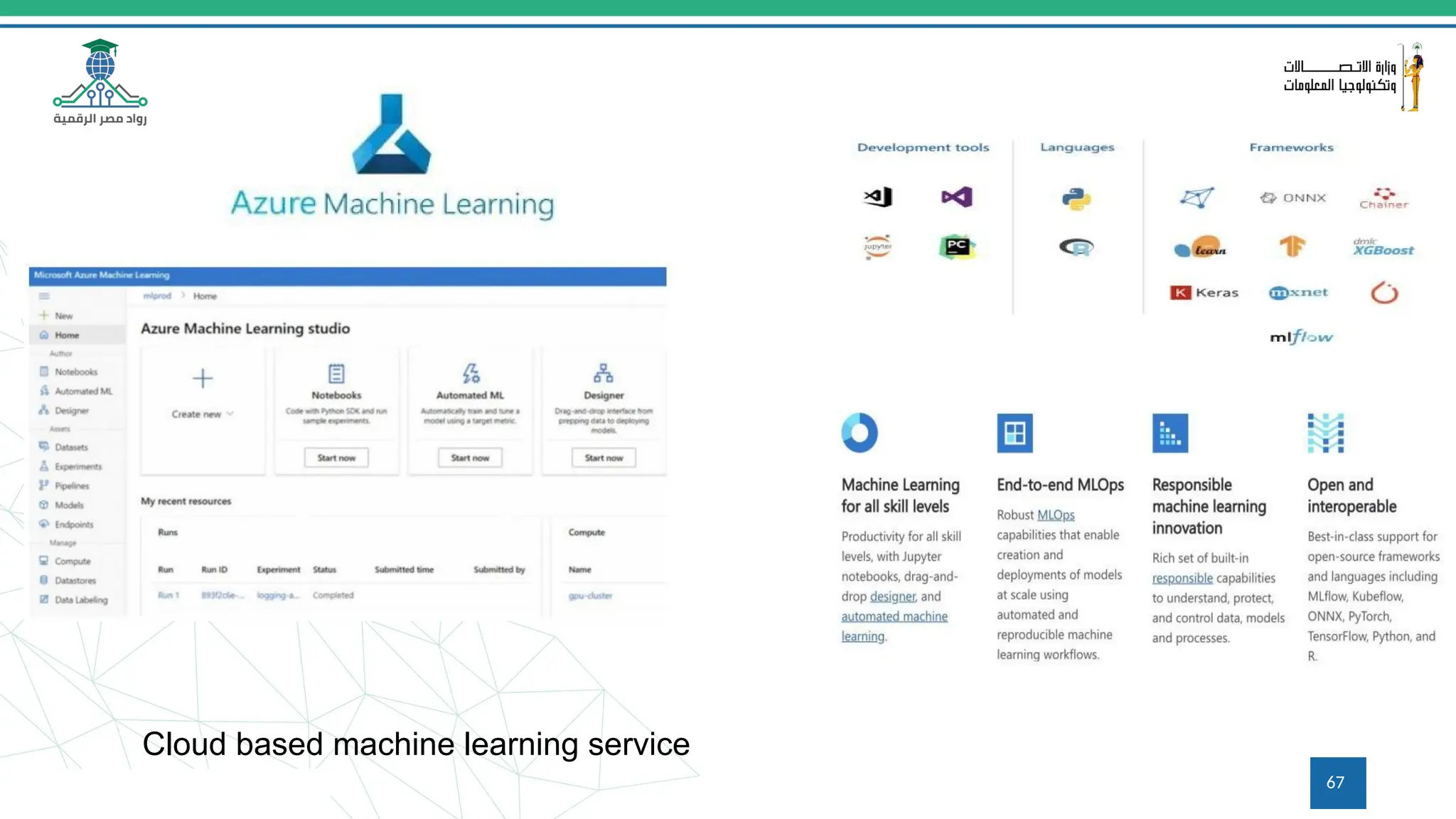
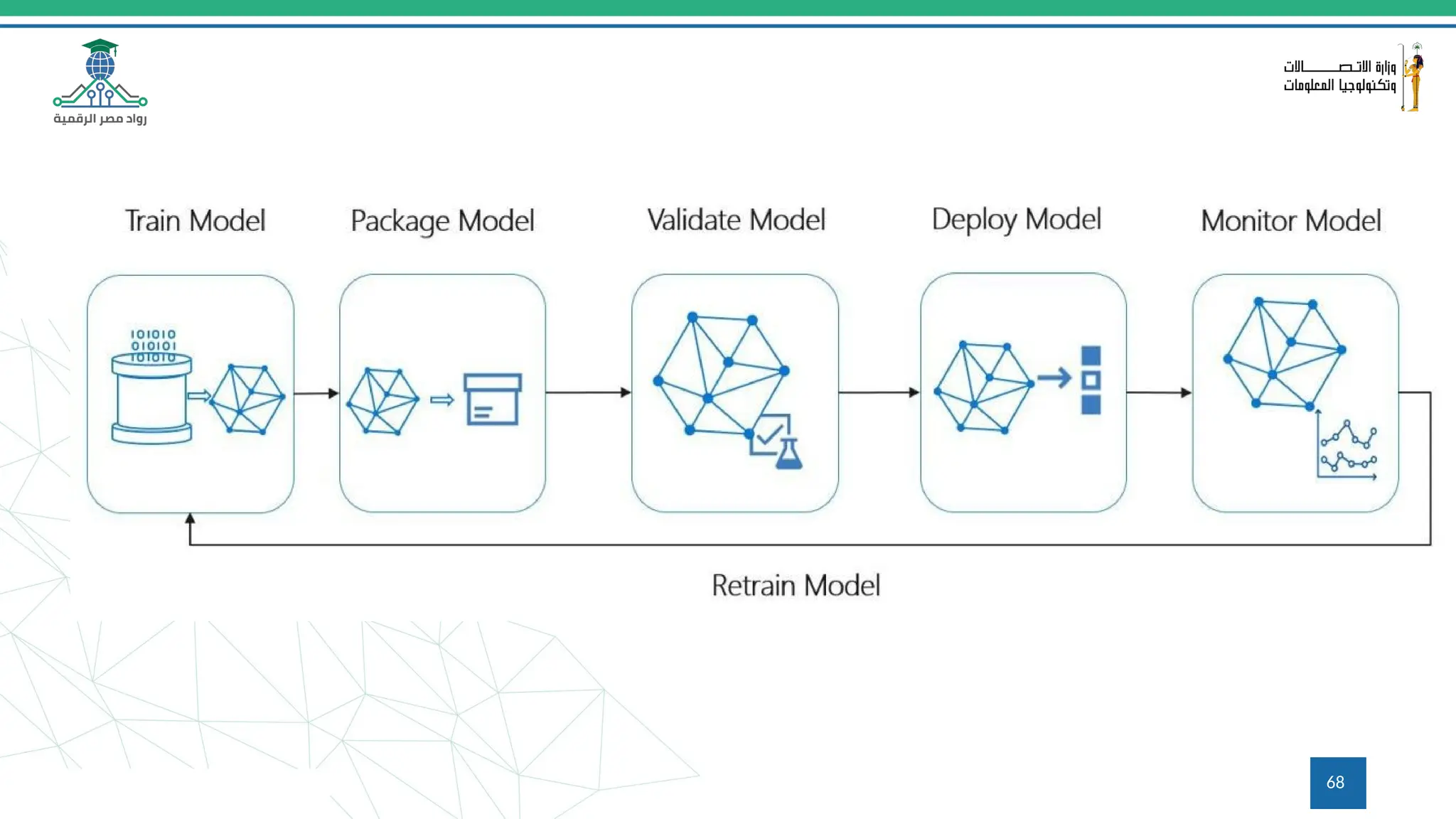
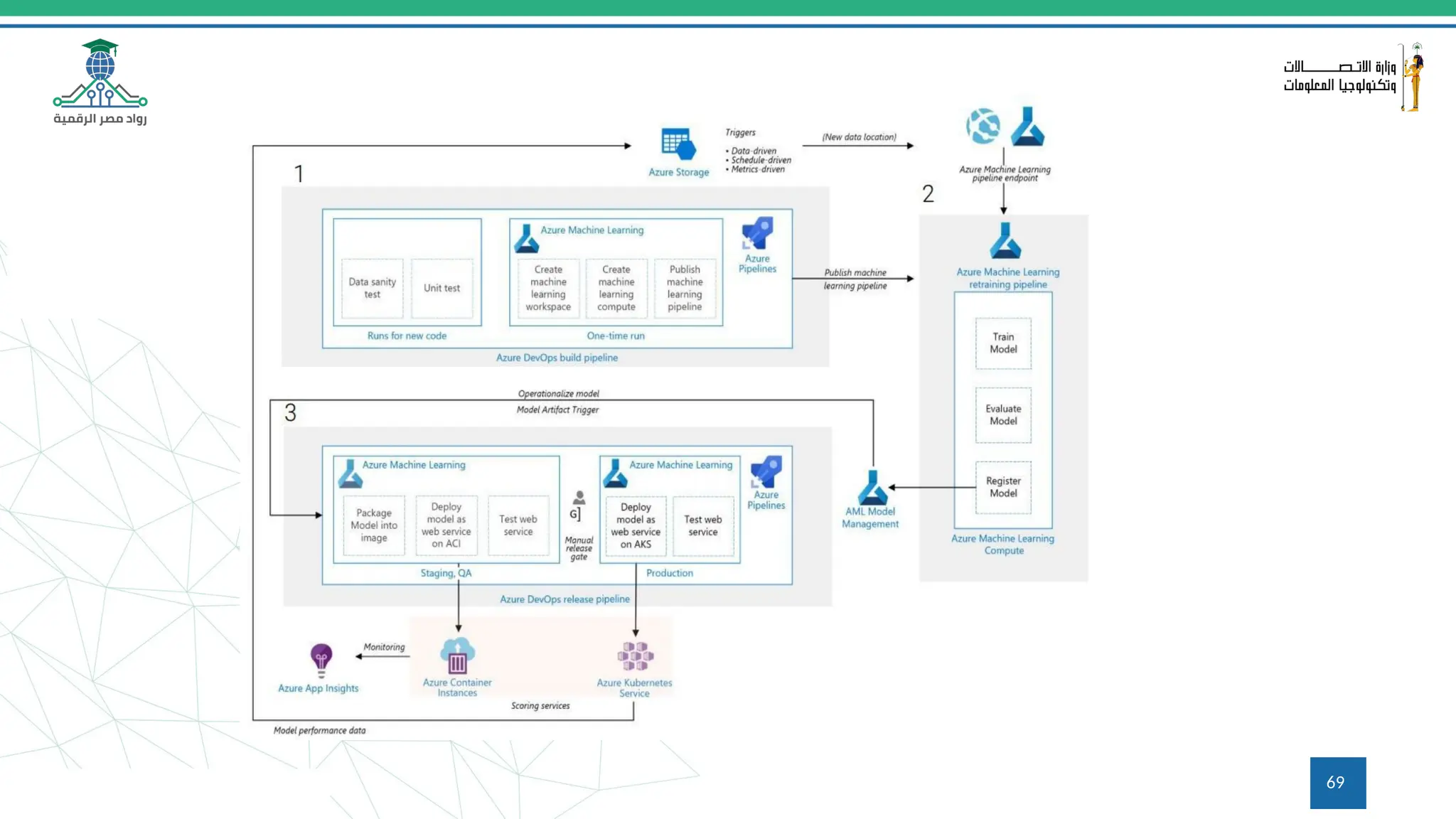
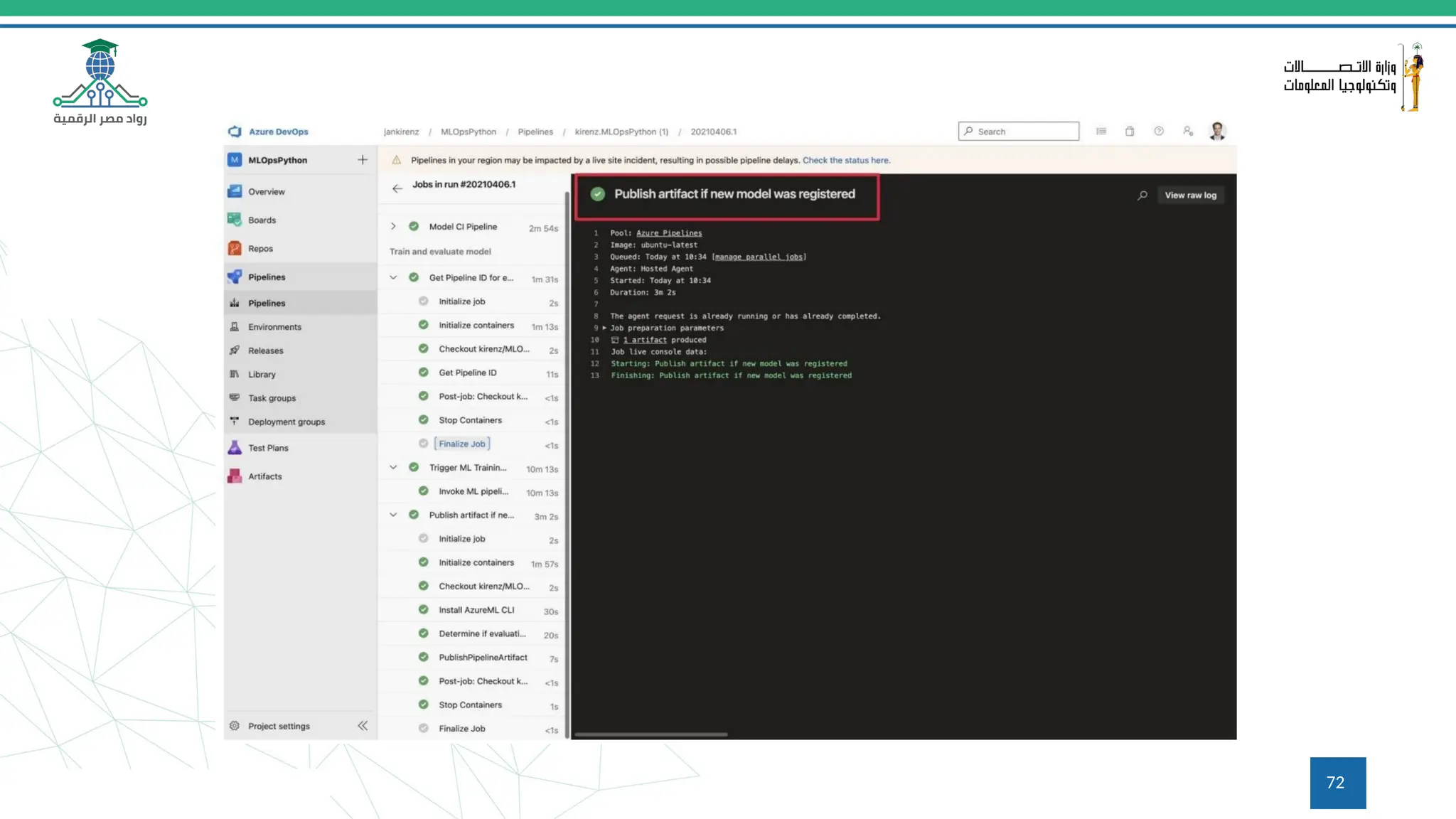
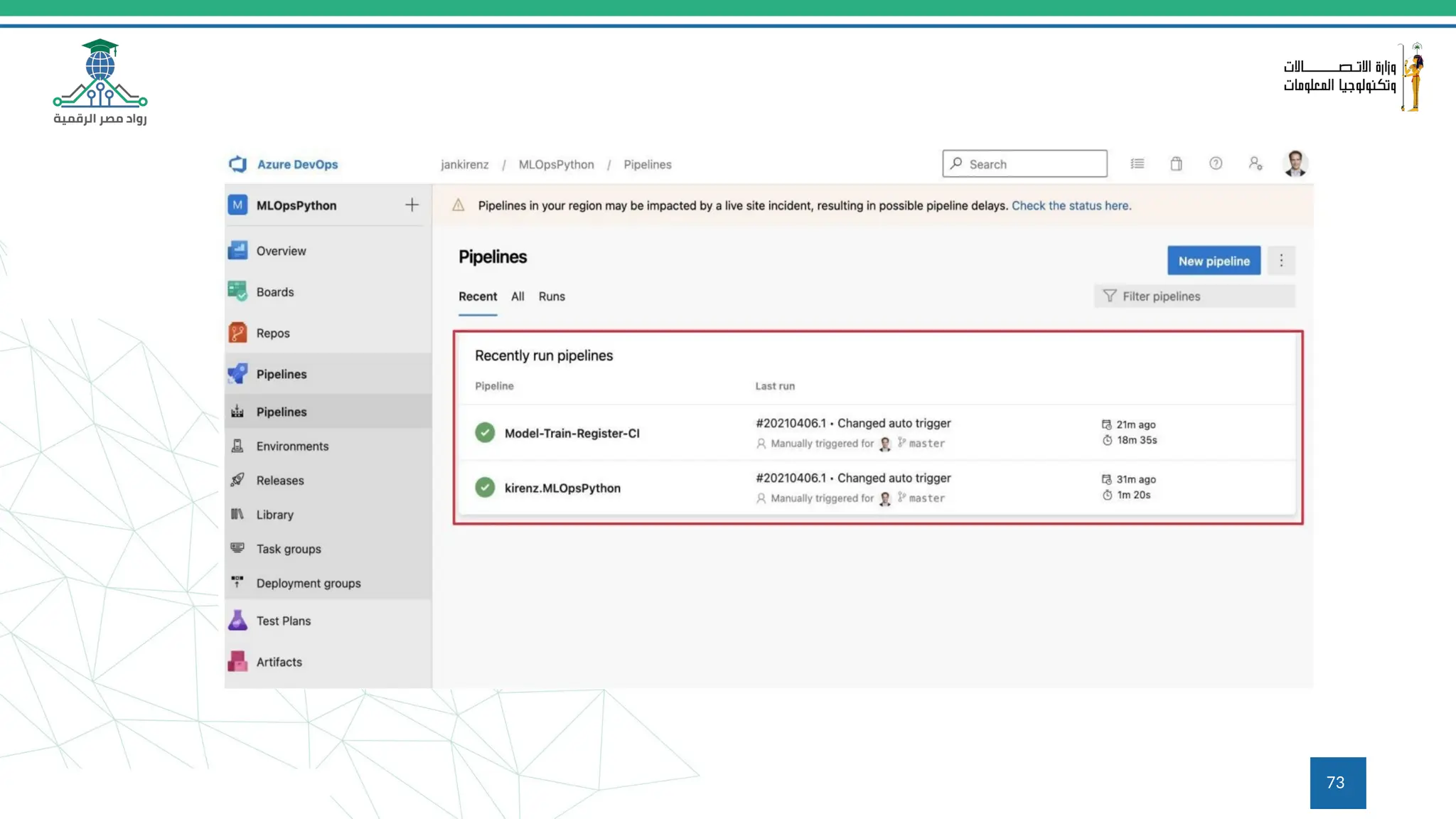
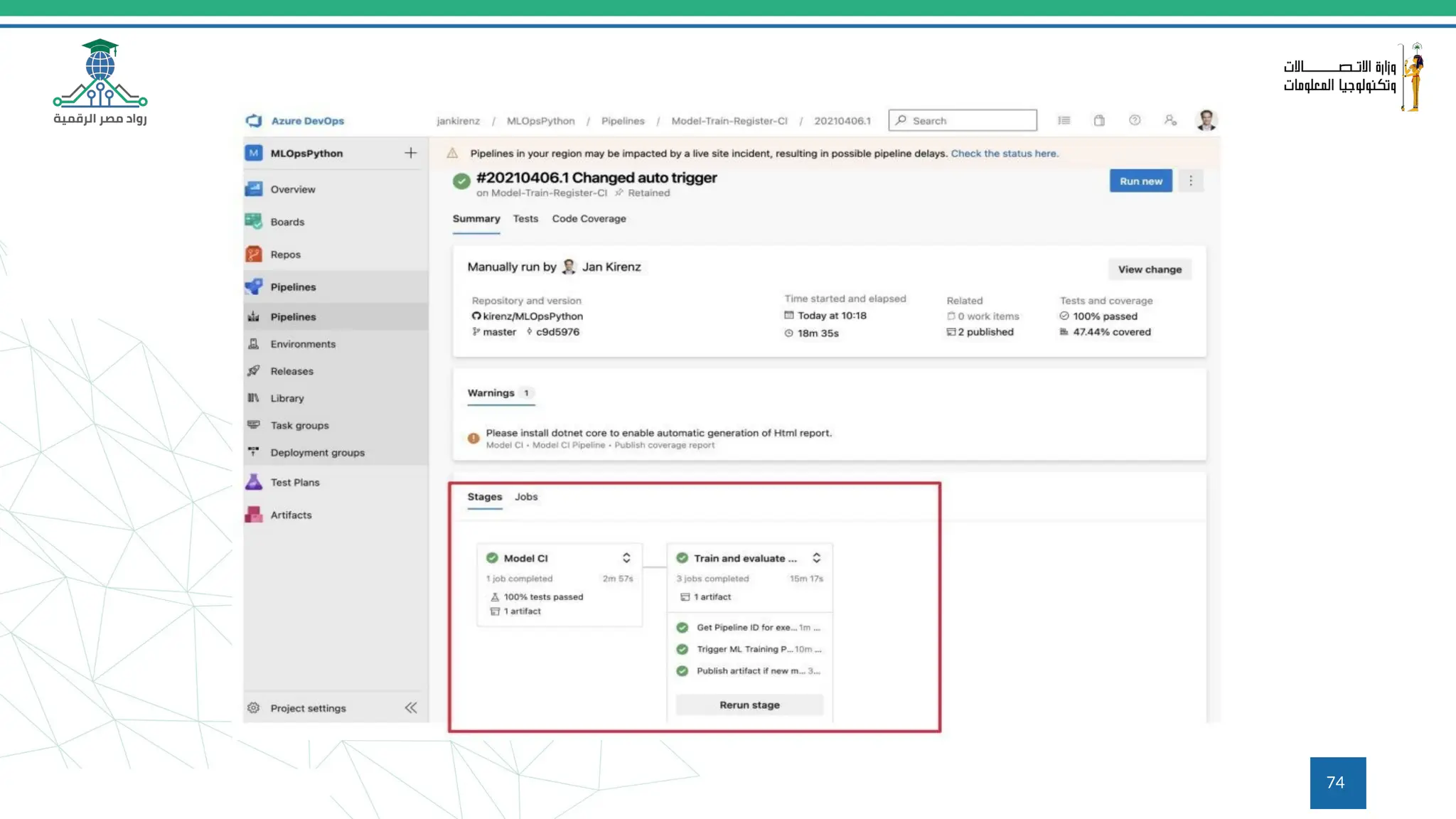
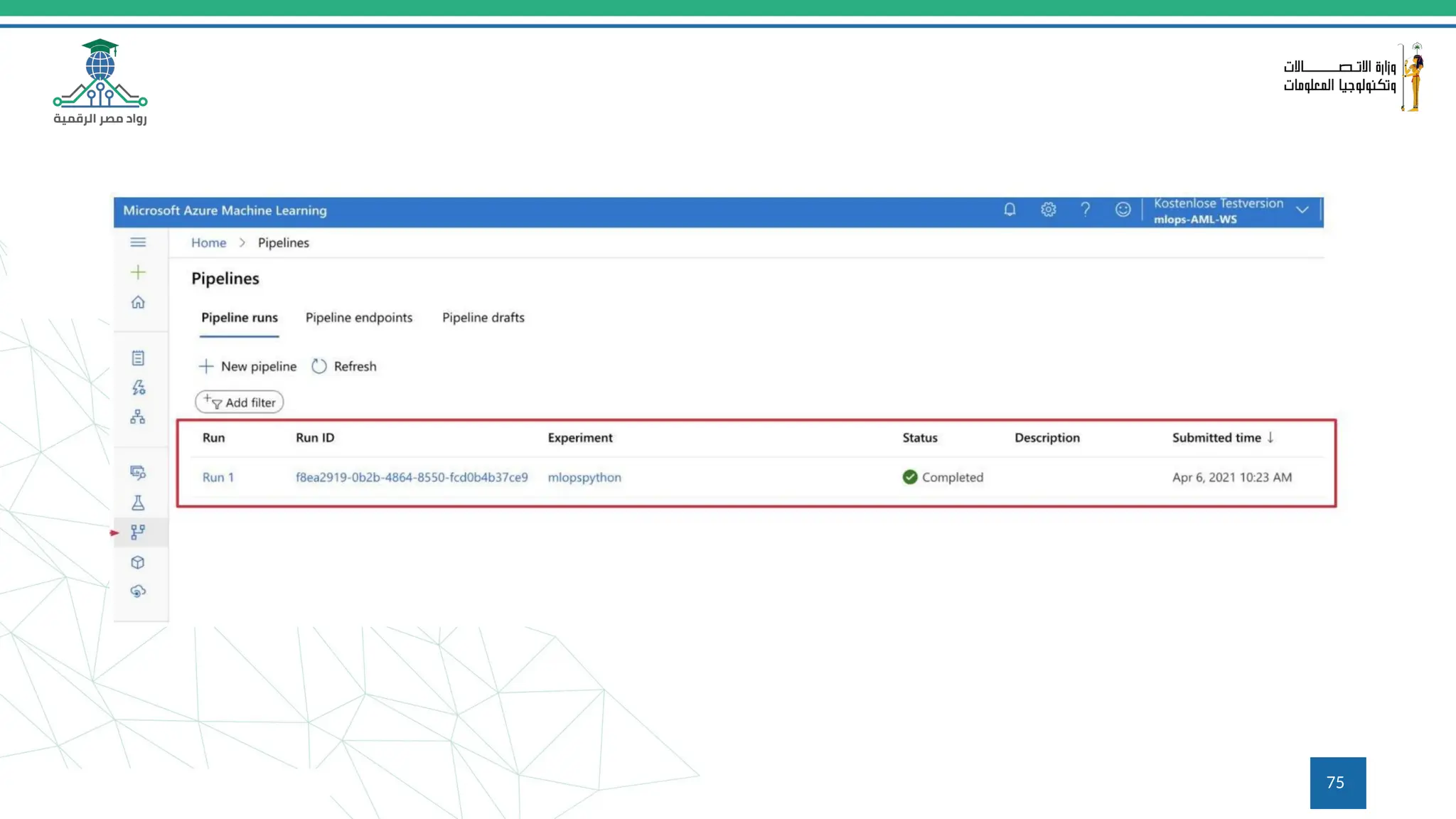
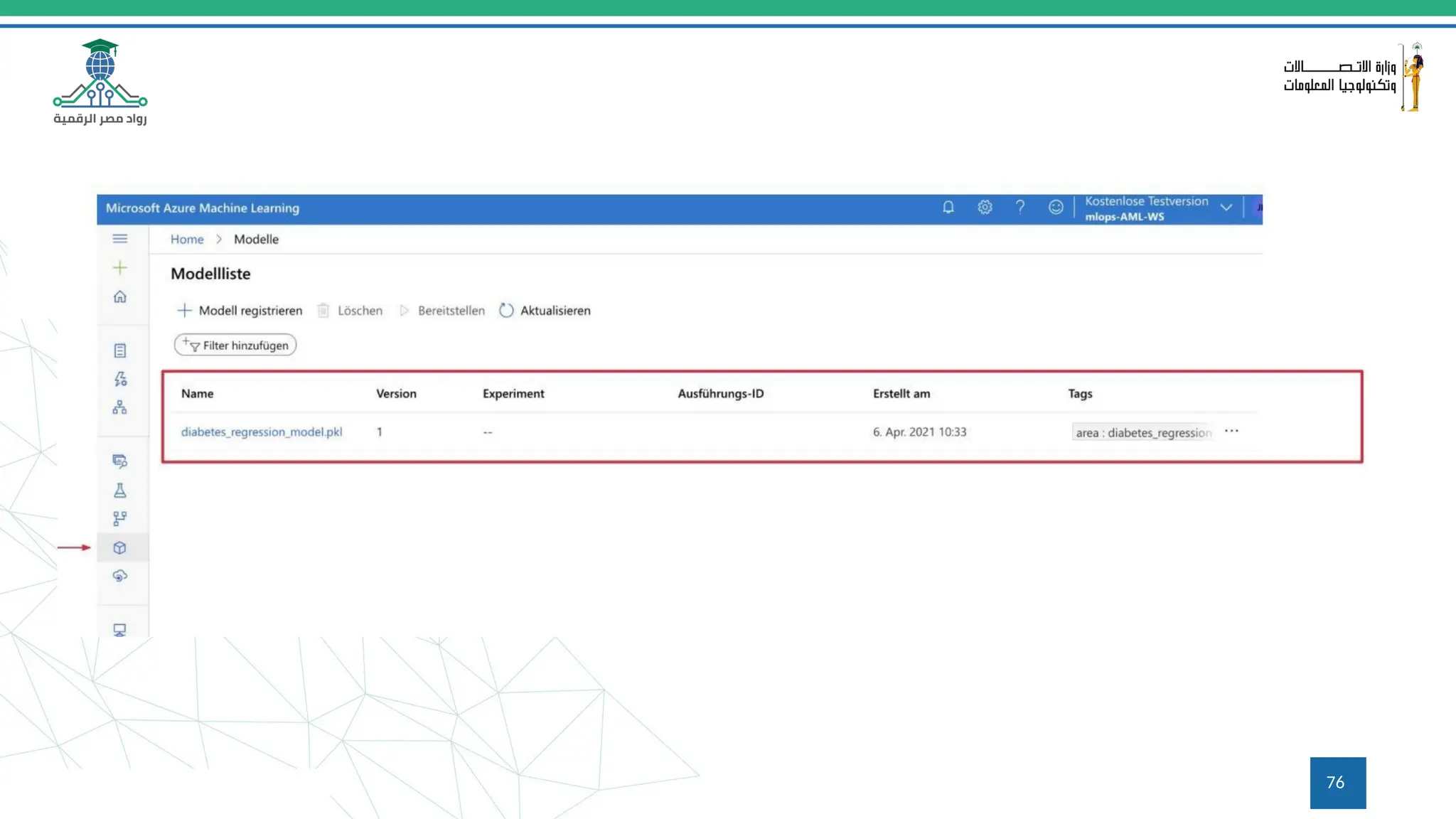
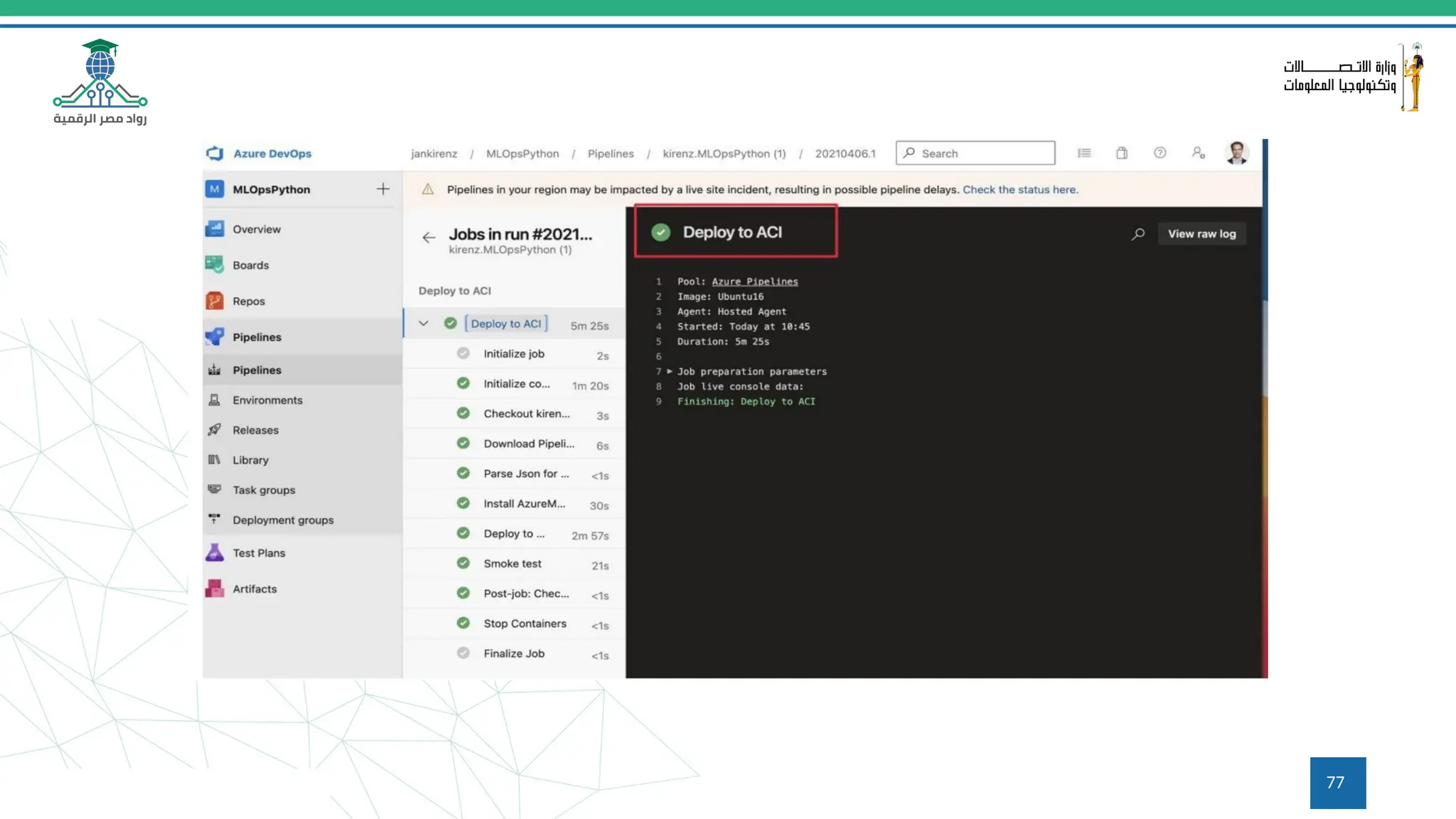
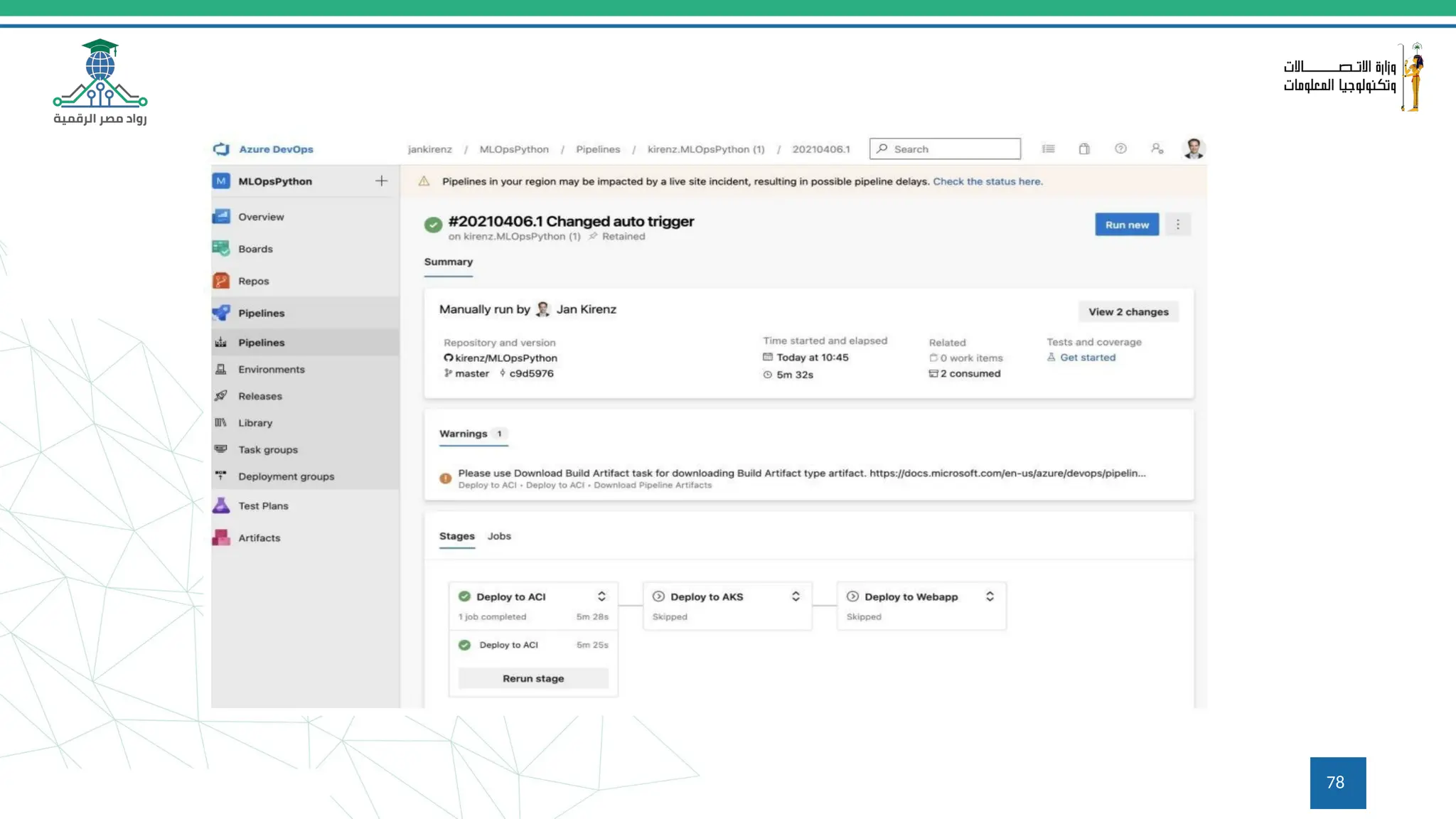
This document provides an overview of a course on MLOps tools, specifically focusing on MLflow and Hugging Face, highlighting their functionalities for managing machine learning operations. The course covers the ML lifecycle, the significance of standardizing workflows, and practical applications such as tracking experiments and deploying models. It also discusses issues like the gap from proof of concept to production and introduces concepts like pipelines and orchestration with tools like TensorFlow Extended (TFX) and Apache Airflow.