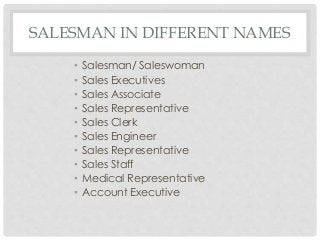
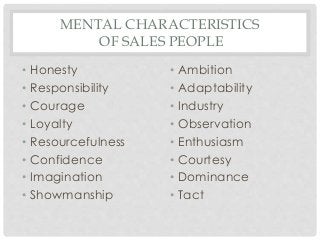
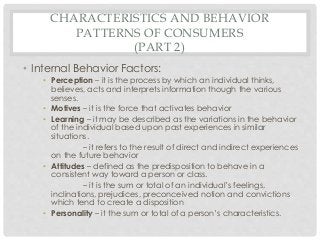
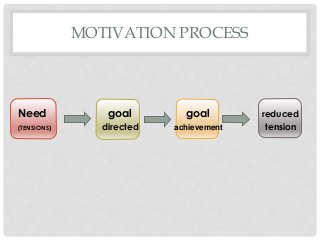
The document covers the essential aspects of professional salesmanship, detailing personal and non-personal selling methods, types of selling, and the selling process. It discusses the responsibilities and qualifications of salespeople, the advantages and disadvantages of a career in sales, various compensation plans, and the characteristics of buyers. Additionally, it addresses motivation theories, differences between direct selling and multilevel marketing (MLM), and the attributes of legitimate marketing practices.