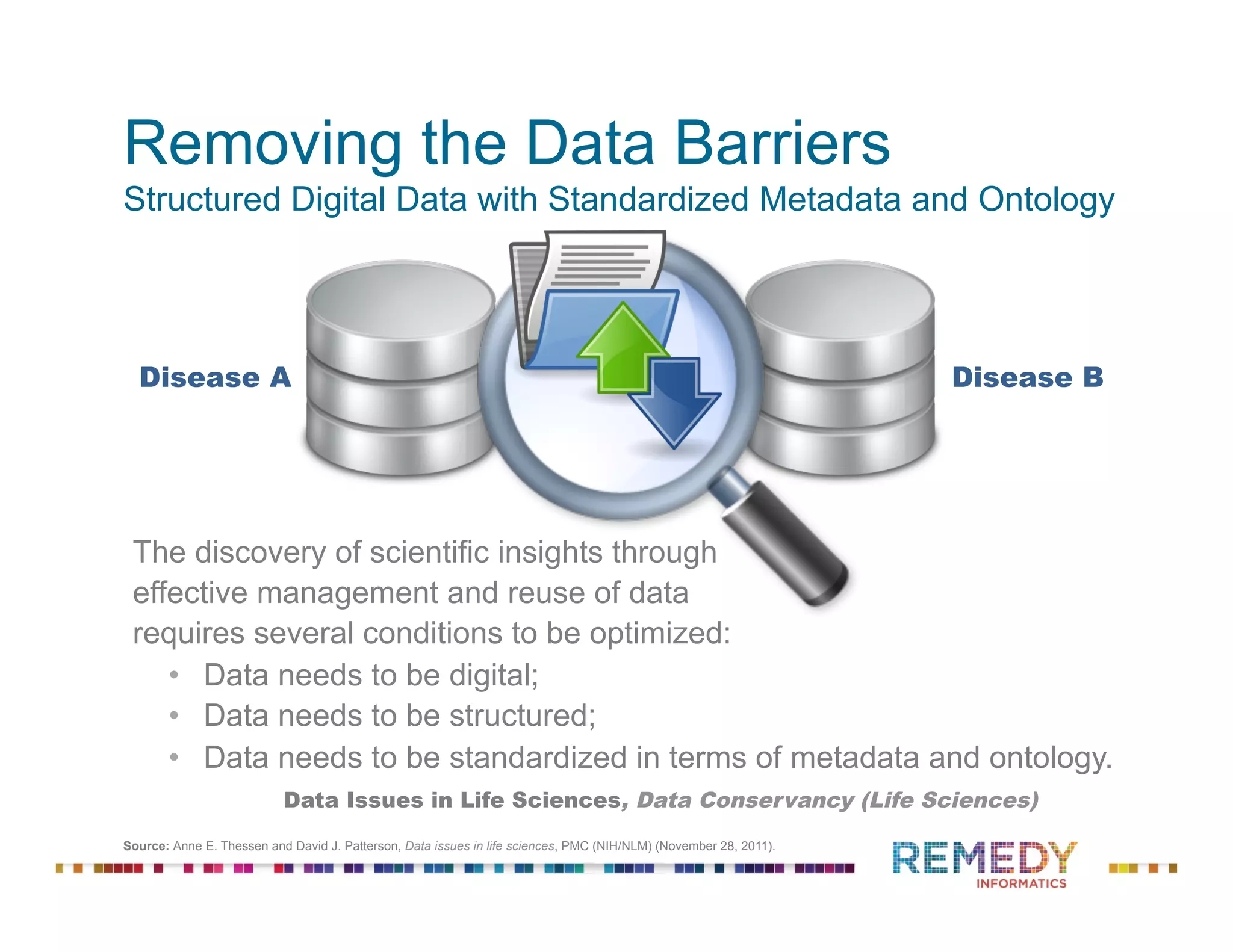
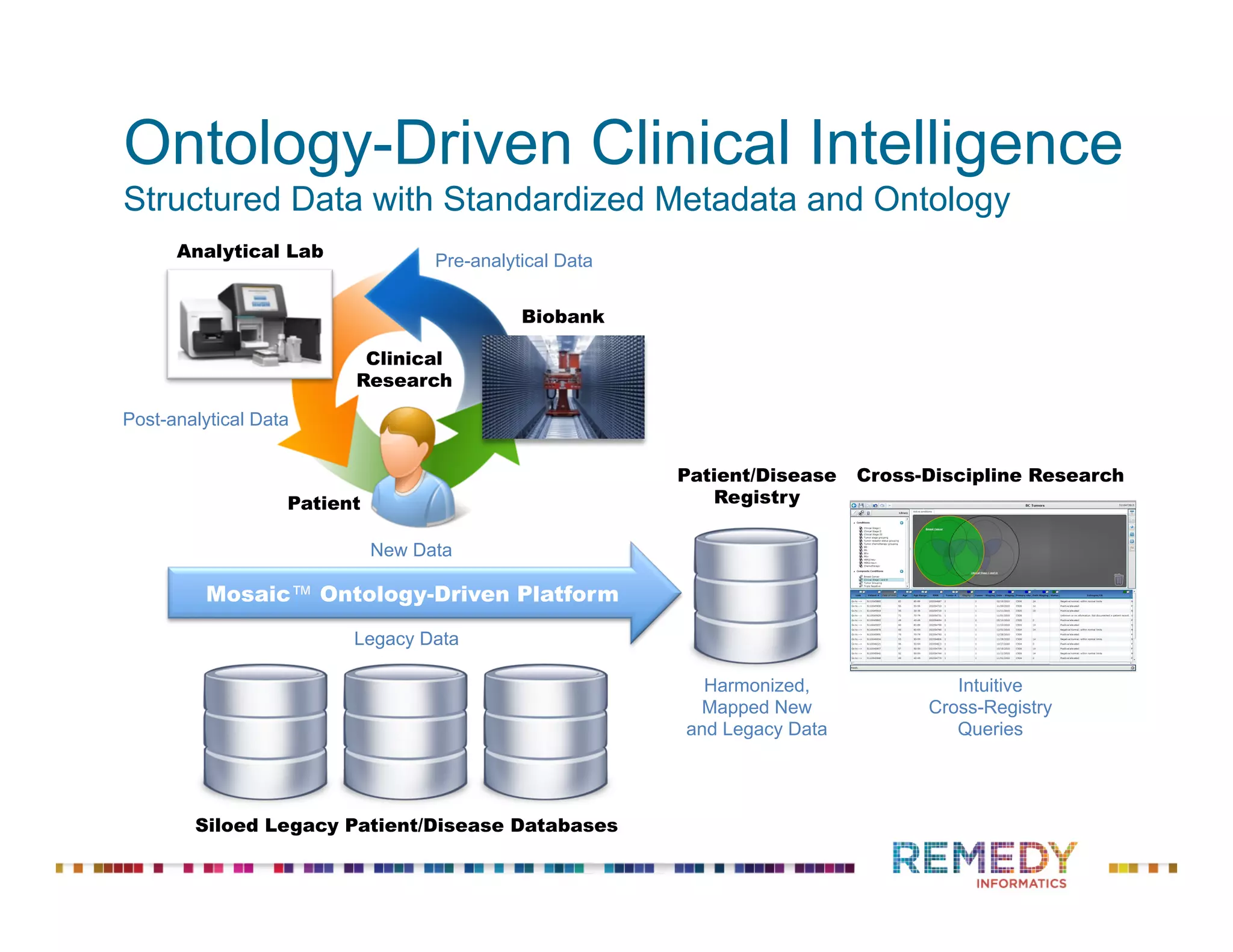
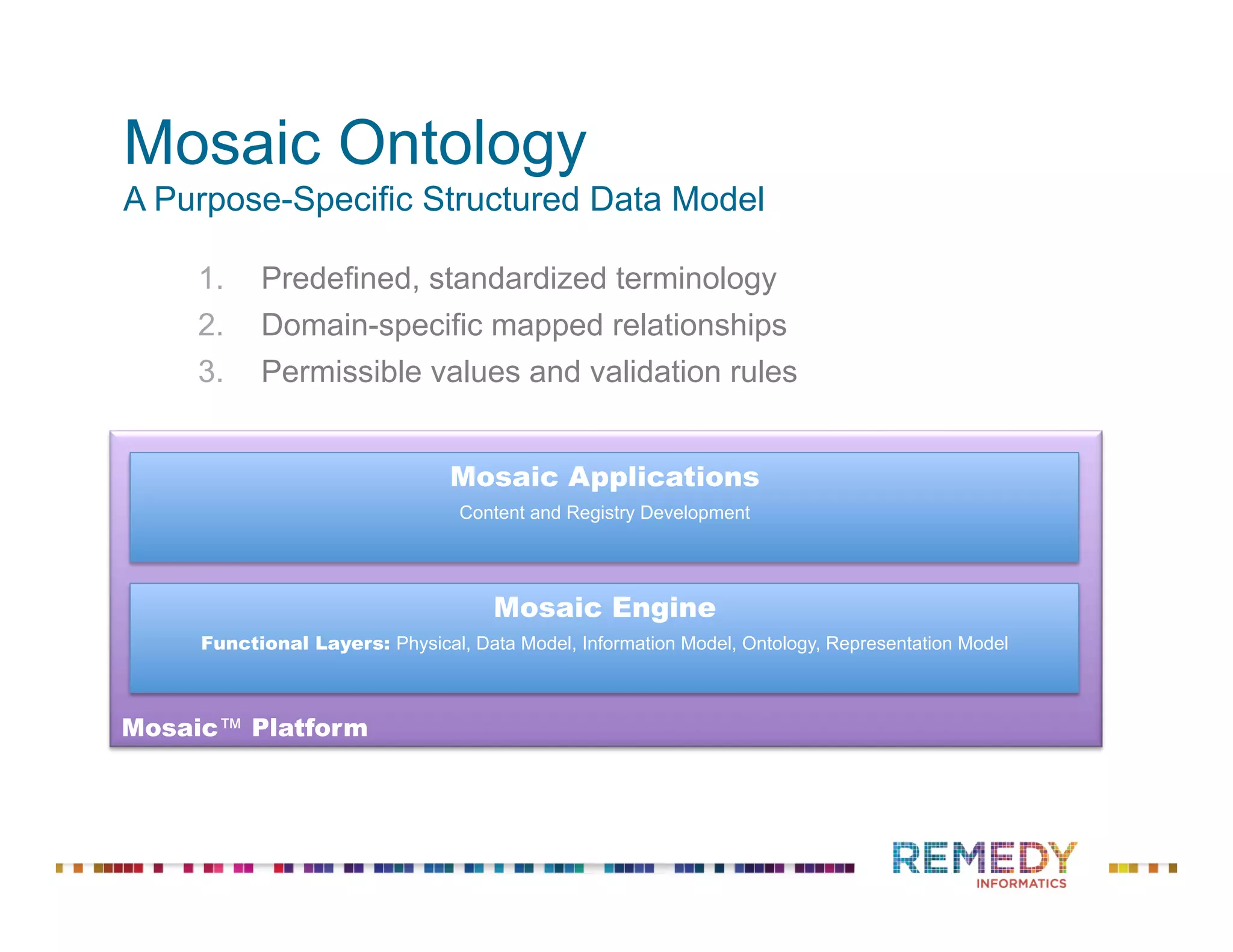
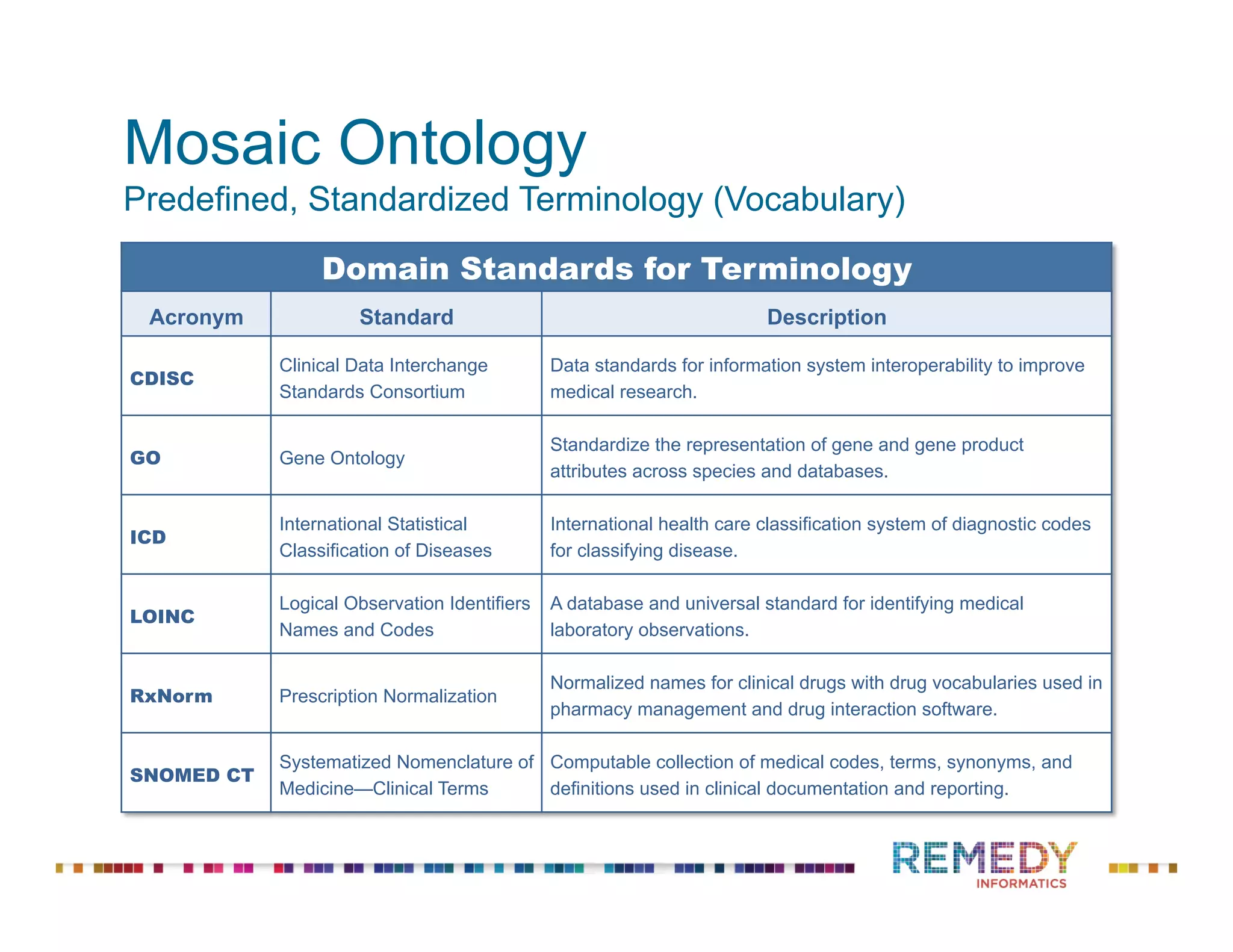
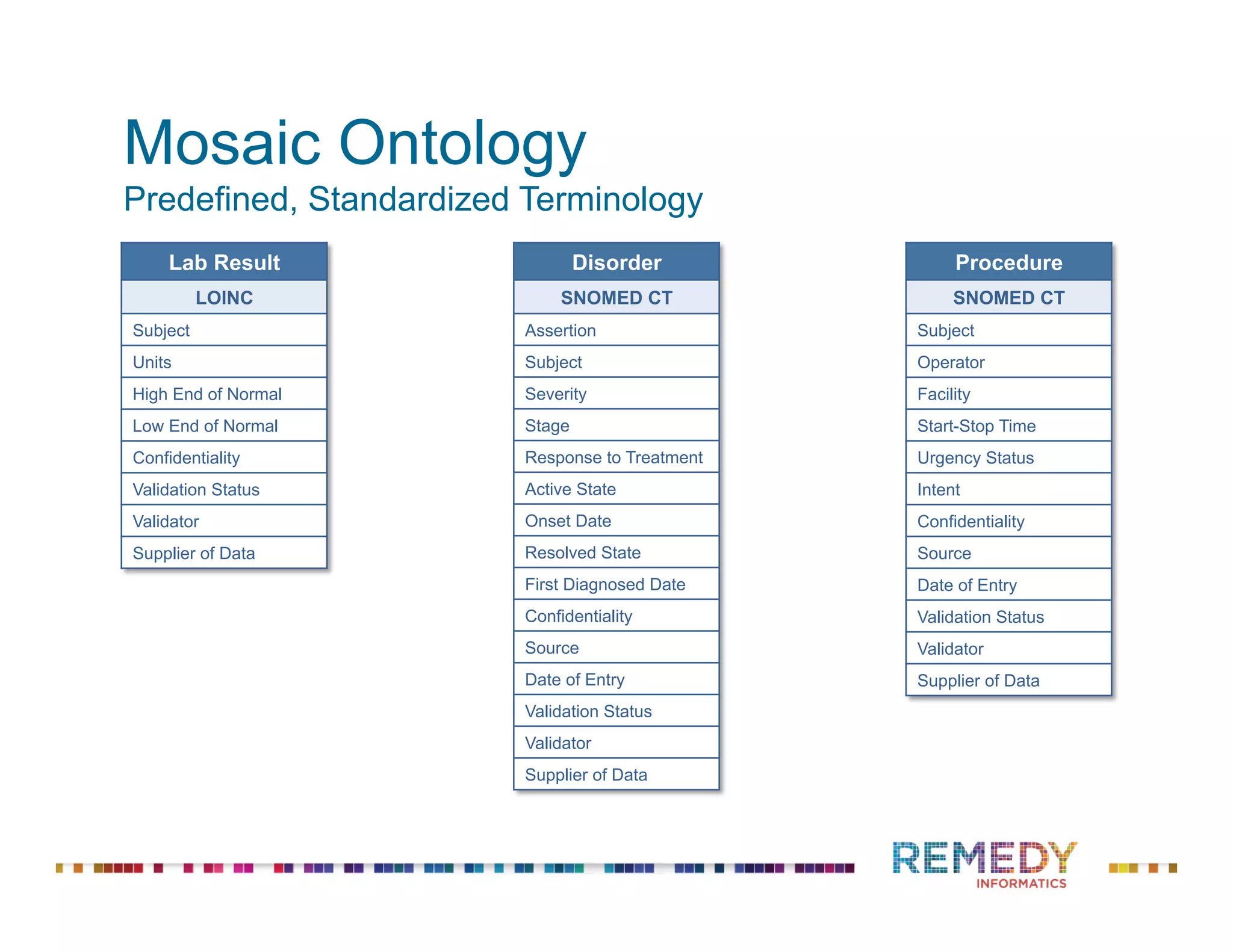
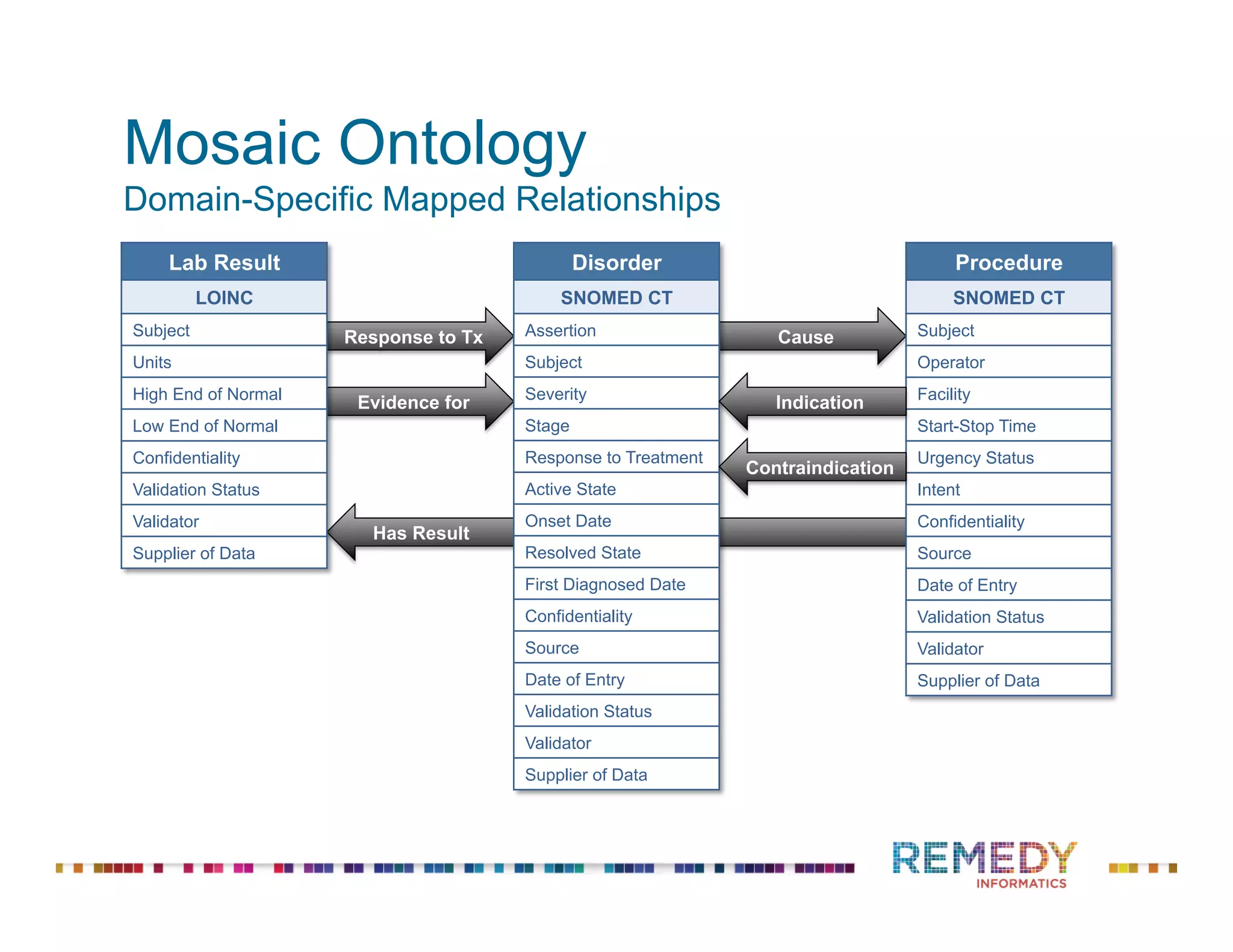
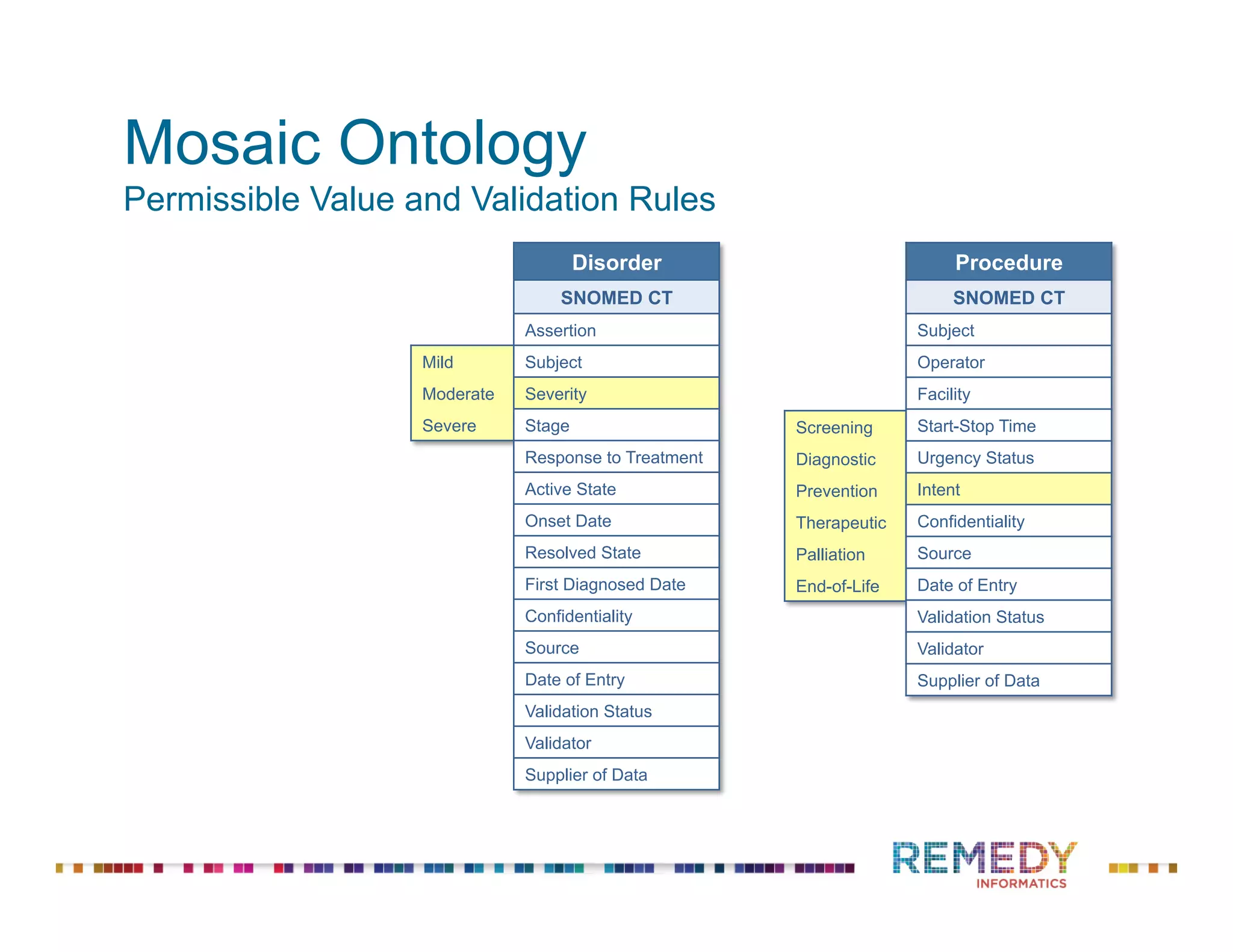
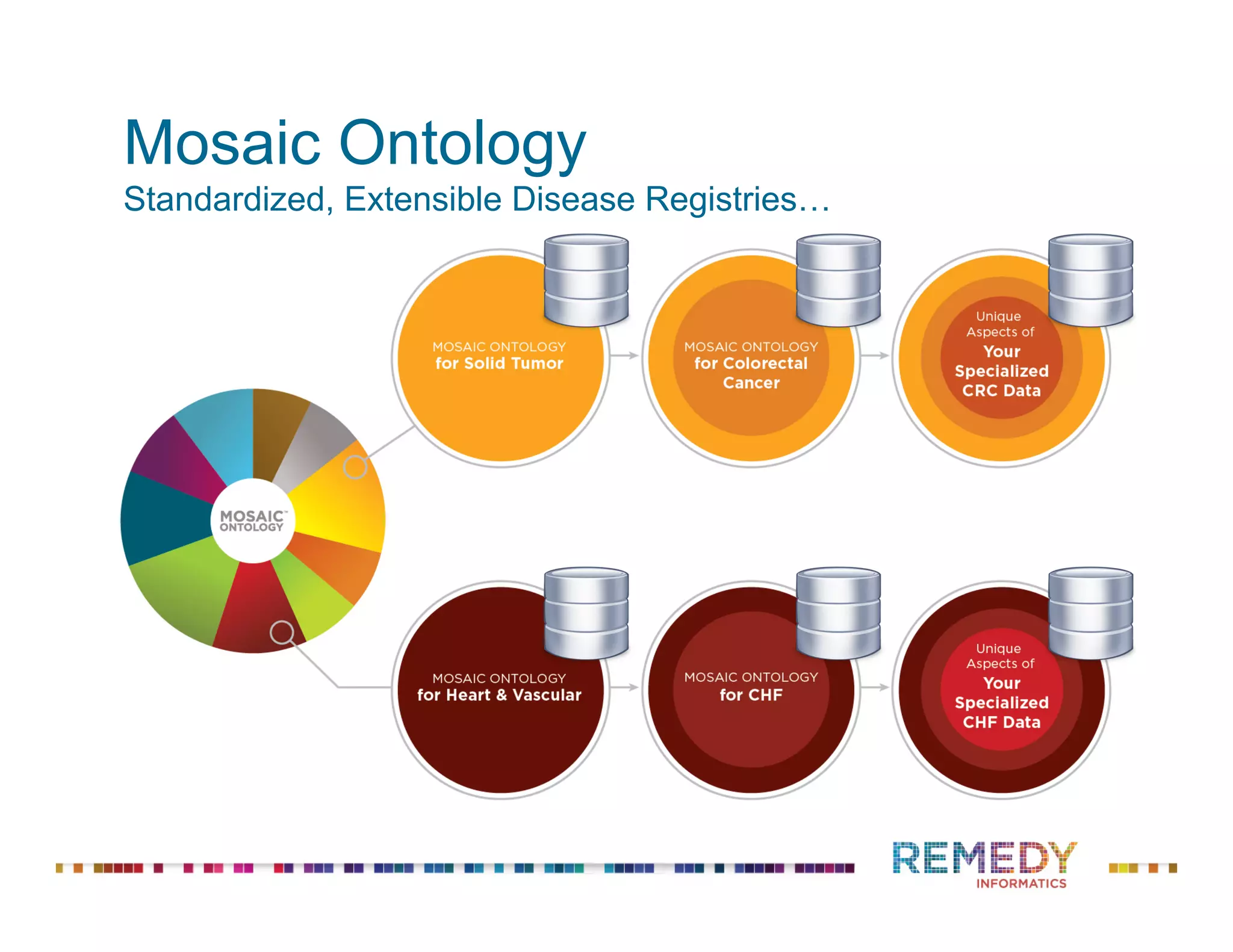
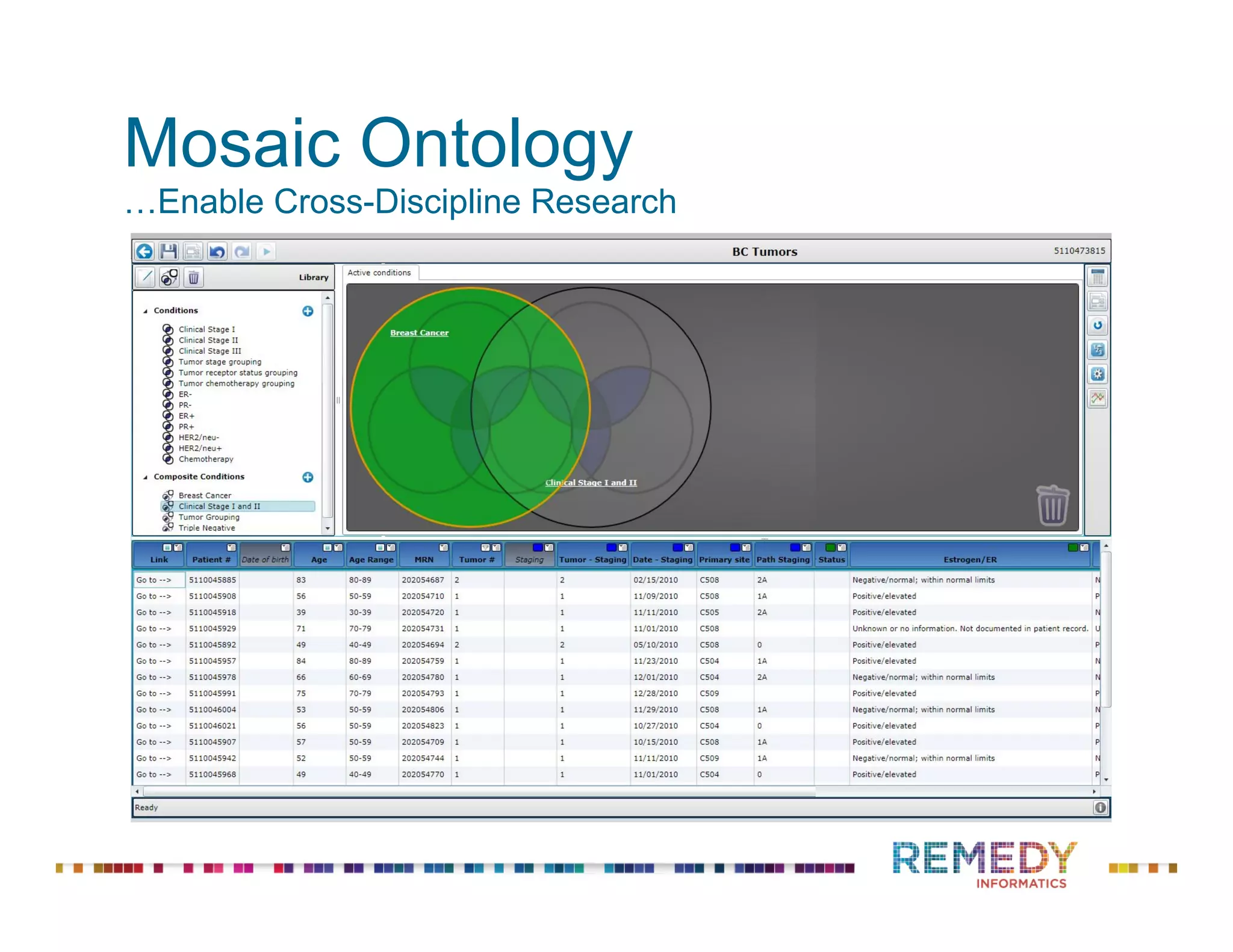
The document discusses the importance of ontology-driven clinical intelligence to overcome data barriers in cross-discipline research, highlighting that critical clinical data is often dispersed across independent systems. It emphasizes the need for digital, structured, and standardized data to facilitate scientific insights and effective research management. Remedy Informatics is presented as a solution provider that helps organizations collect, harmonize, and analyze clinical data to improve healthcare and accelerate research.