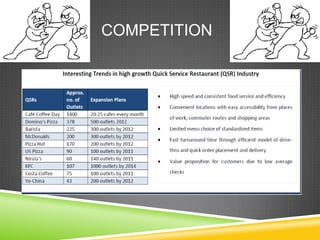
This document provides an analysis of the business models of international food chains operating in India. It begins with objectives and scope, defining key terms like international marketing and fast food. It then examines reasons for foreign chains entering the Indian market and common entry strategies like strategic alliances, joint ventures, and standalone entries. Case studies of McDonald's and Domino's entry into India via joint venture and franchising respectively are described in detail. Challenges faced by foreign food chains in India are also outlined. The document concludes with limitations coming from sole use of secondary data sources.