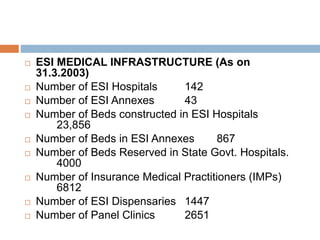
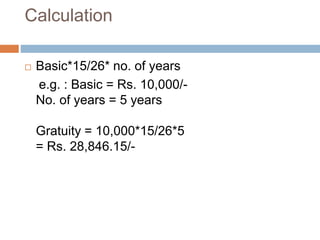
The document discusses various Indian labor laws regarding minimum wages, bonus payments, provident funds, gratuity, and leave policies. It provides details on:
1) Minimum wage rates that were set in India in 1996, 1998, and 1999 based on recommendations to ensure a basic subsistence level.
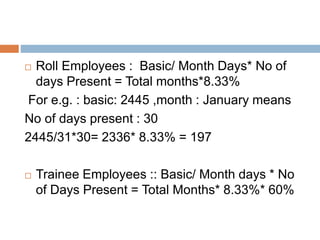
2) Eligibility and calculation methods for bonus payments under the Bonus Act, such as a minimum bonus of 8.33% of wages for those earning up to Rs. 3,500 per month.
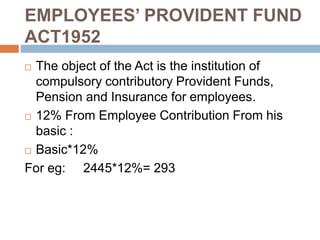
3) Employee and employer contribution rates and caps for provident funds under the Employees' Provident Fund Act.
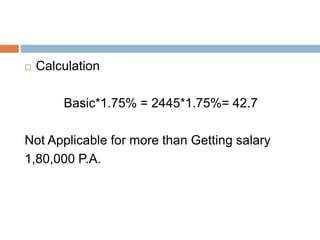
4) Contribution rates of 1.75% of basic wages for the Employees'





![Minimum wage fixation… Rates can be fixed on
basis of hour, day or month, or even larger
period. [section 3(3)(b)]. - - The rate shall
consist of basic rate of wages with or without
allowance for cost of living allowance based
on ‗cost of living index number.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minimumwagesact-150116222920-conversion-gate02/85/Minimum-wages-act-6-320.jpg)