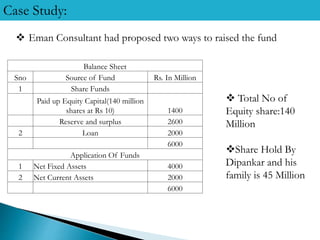
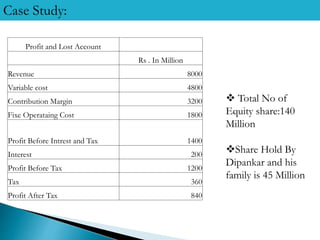
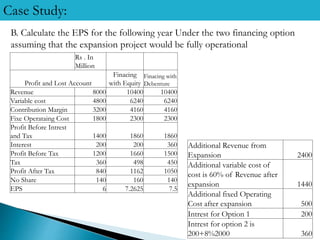
1) Divya Electronics is planning a Rs. 2000 million expansion project that will generate annual revenue of Rs. 2400 million. They are considering equity financing through a public issue or debt financing through debentures.
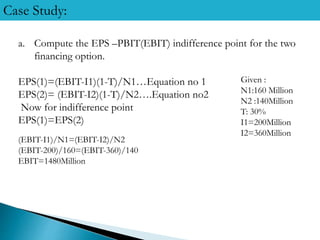
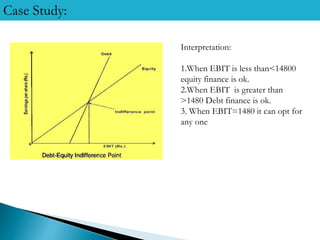
2) The indifference point between the two options is an EBIT of Rs. 1480 million - below this, equity is better, and above it, debt is better.
3) Given the projected EBIT of Rs. 1860 million after expansion, debt financing through debentures is the better option as it provides a higher EPS of Rs. 7.5.
4) Debt financing results in higher financial risk as evidenced by a higher degree of total leverage of 2.733 compared to