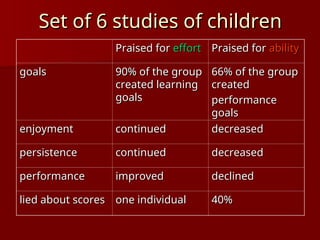
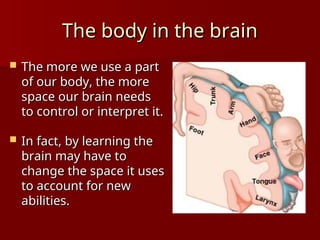
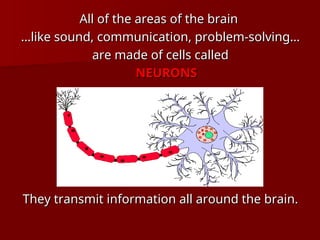
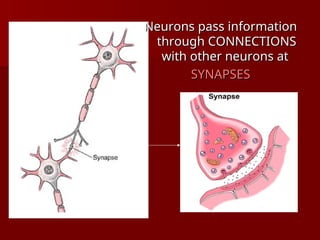
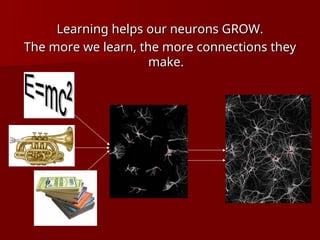
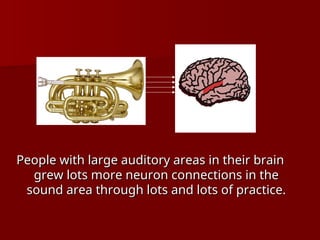
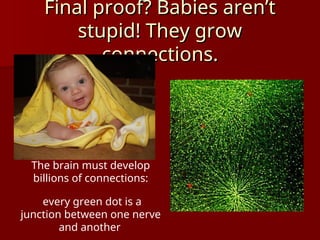
The document discusses the concept of growth vs. fixed mindsets, emphasizing that individuals with a growth mindset believe abilities can be developed, leading to higher motivation and success. It explores the implications of praise, stating that praising effort fosters a growth mindset, while praising ability may reinforce a fixed mindset. It concludes by highlighting the potential of the brain to change through learning and the importance of providing constructive feedback to encourage growth.