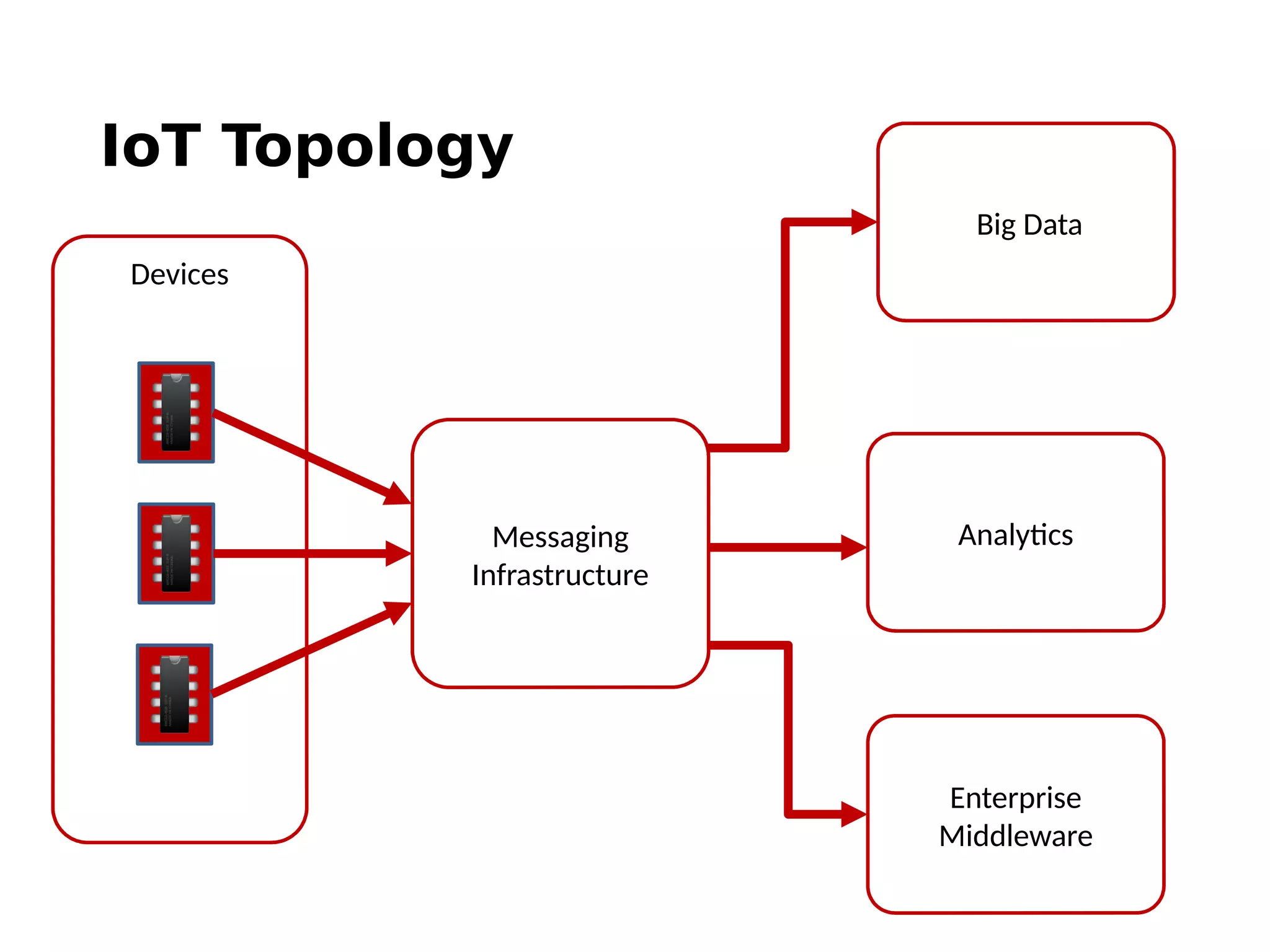
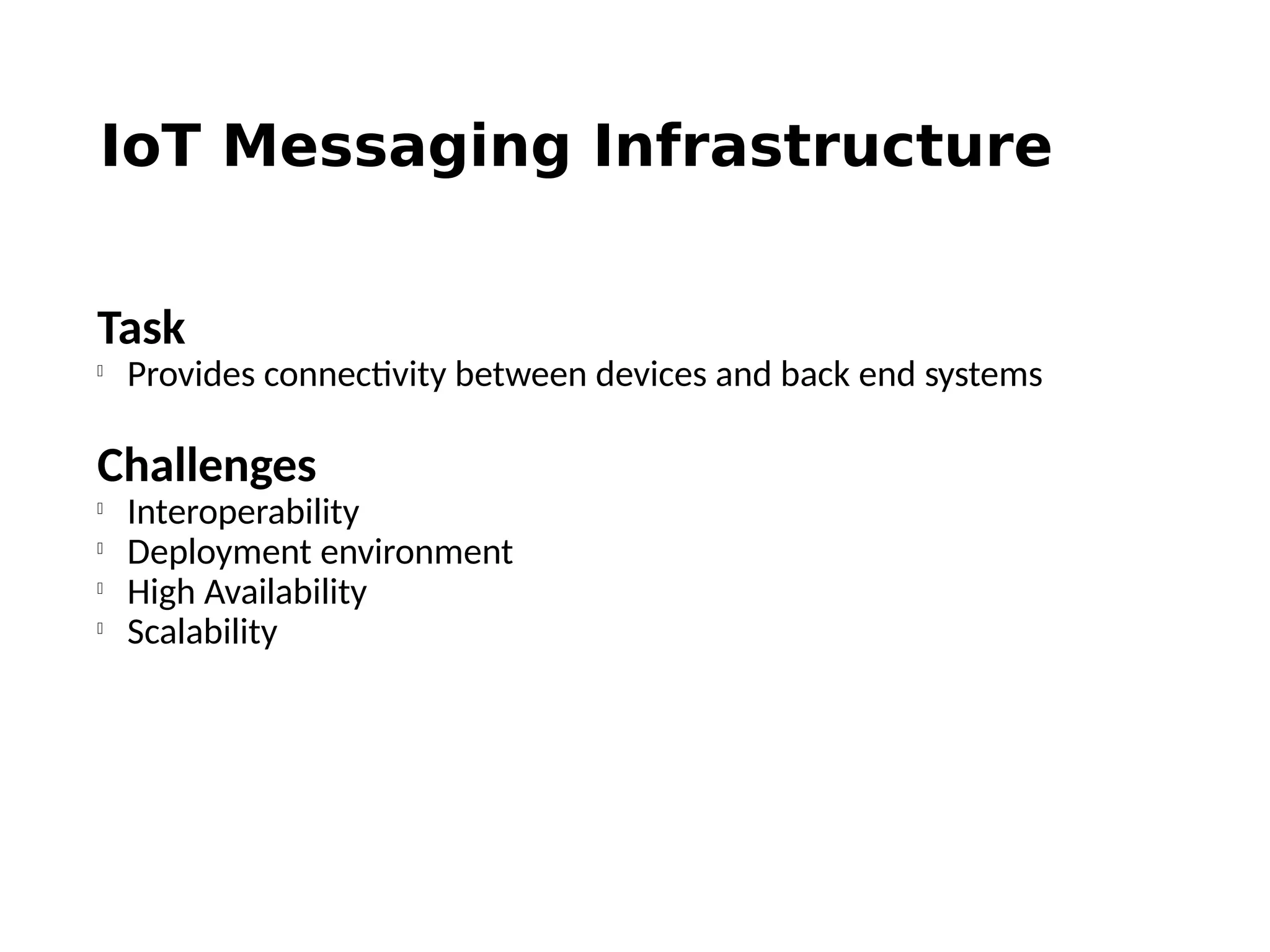
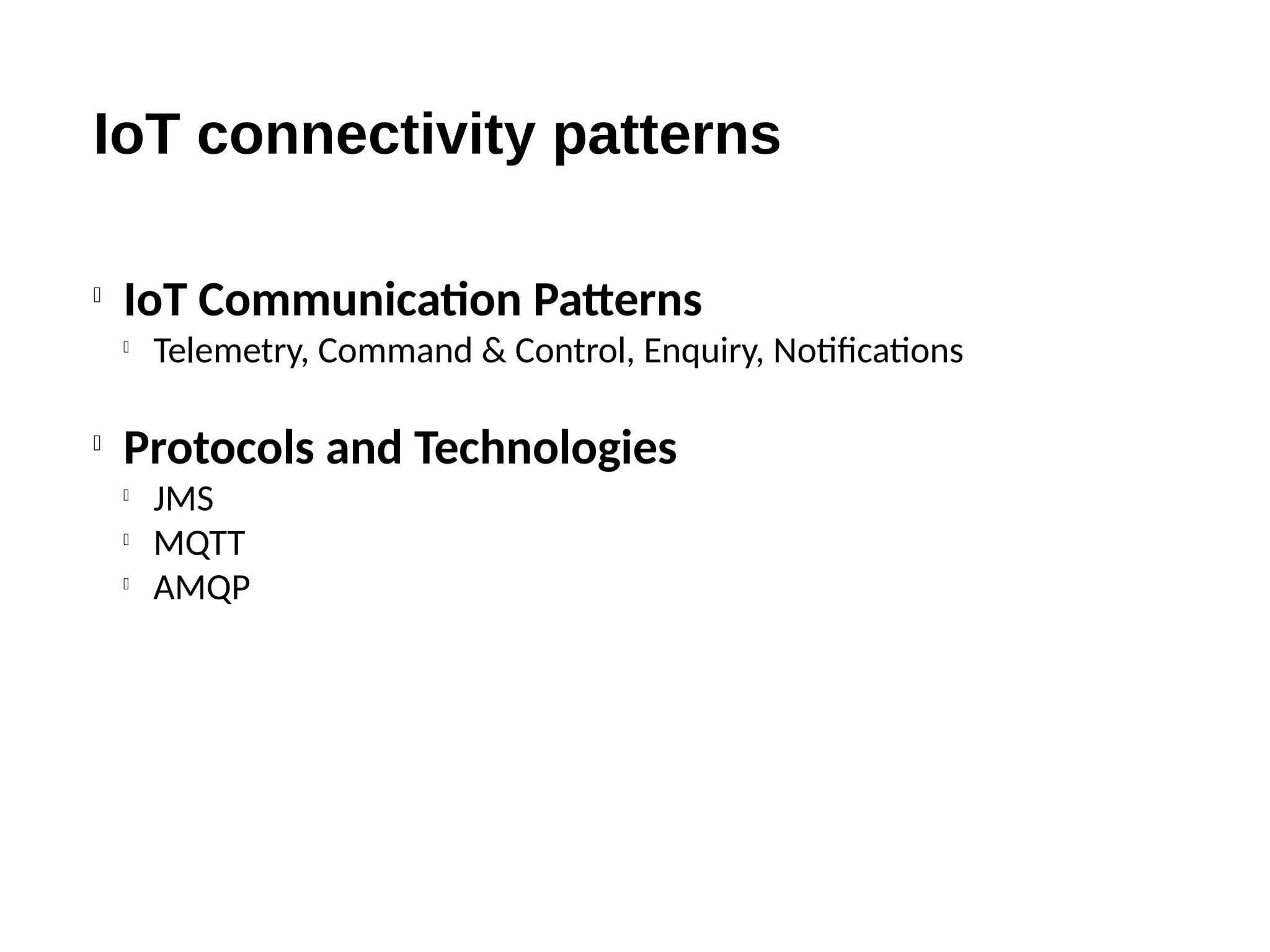
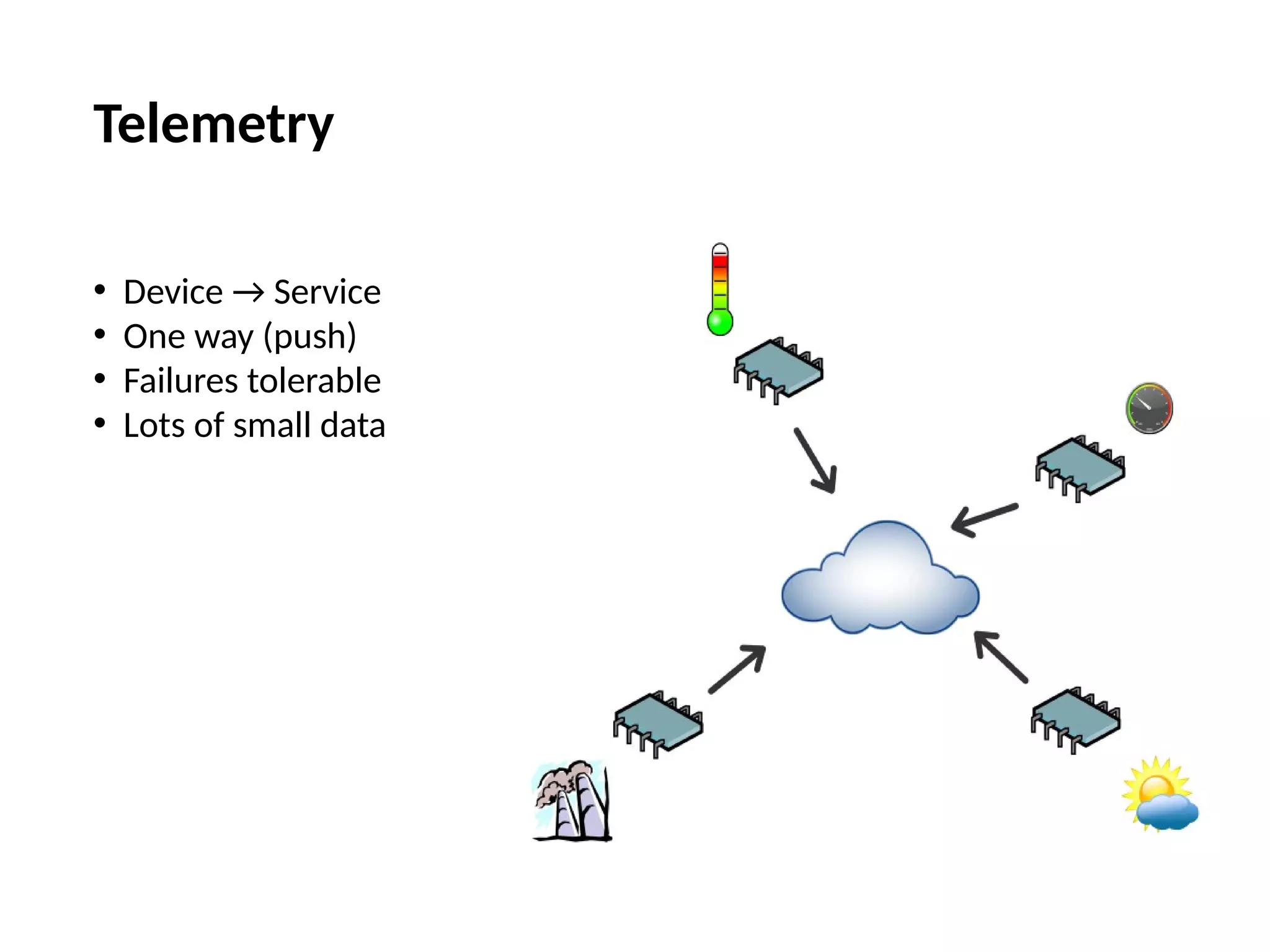
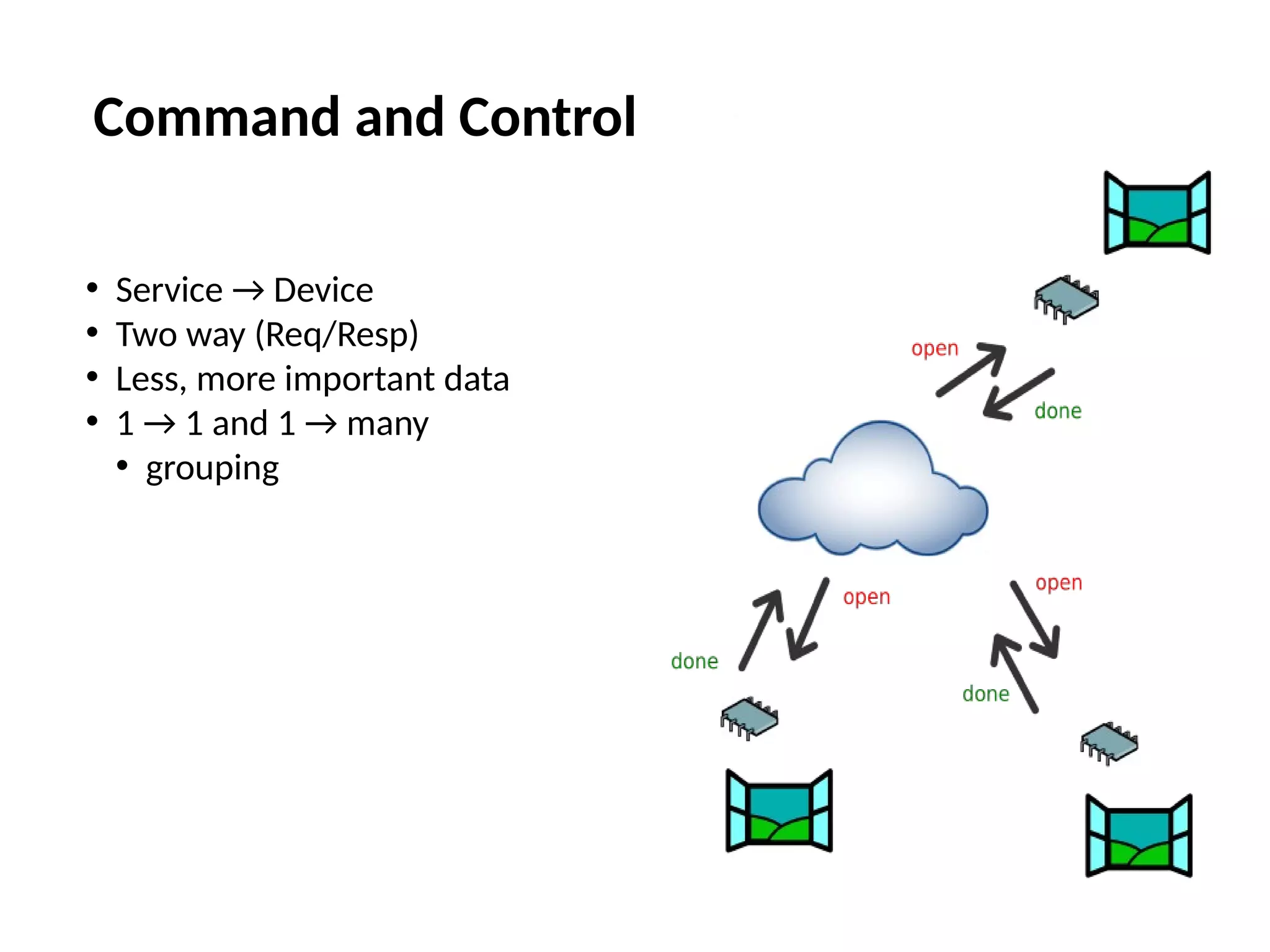
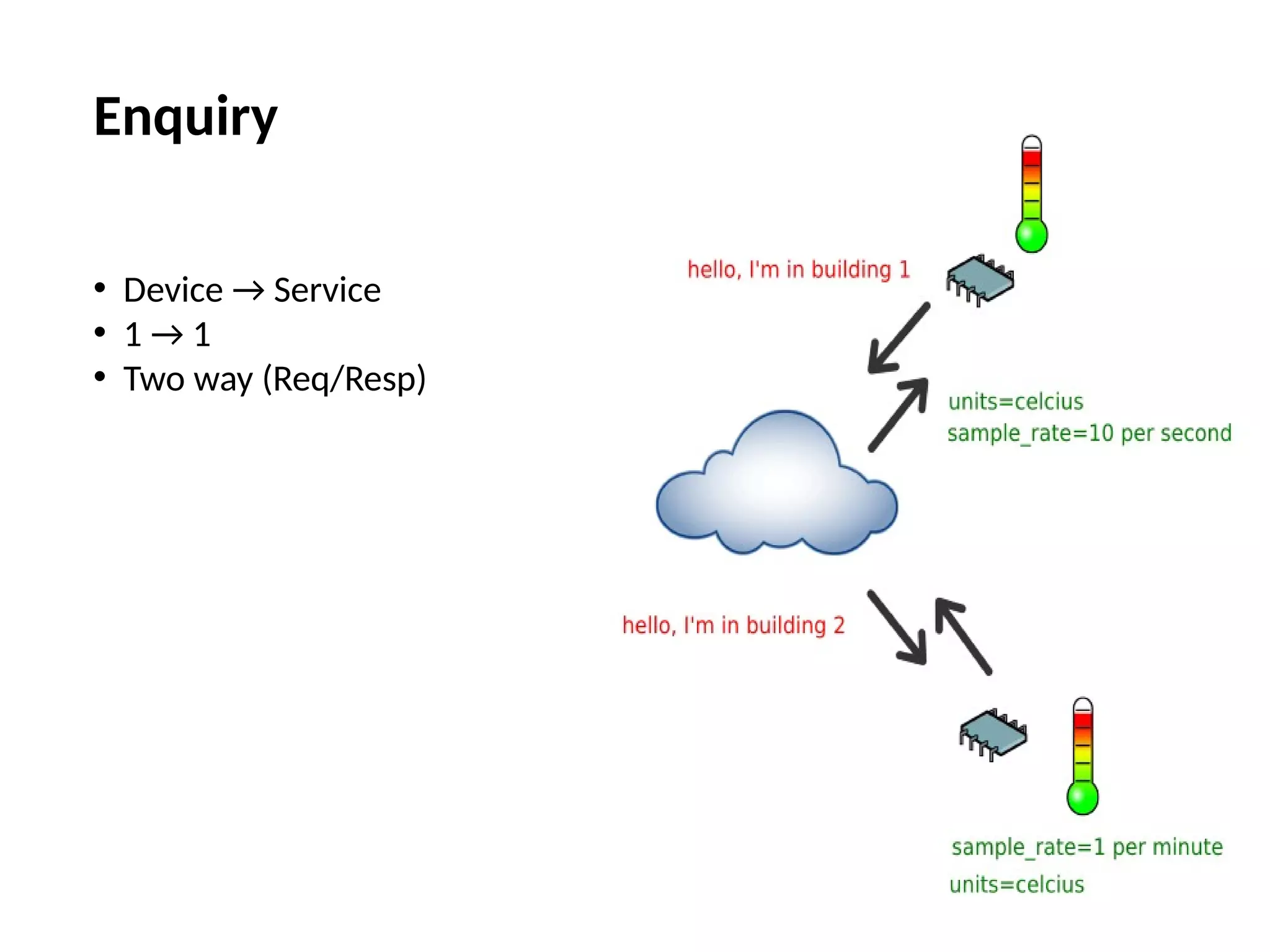
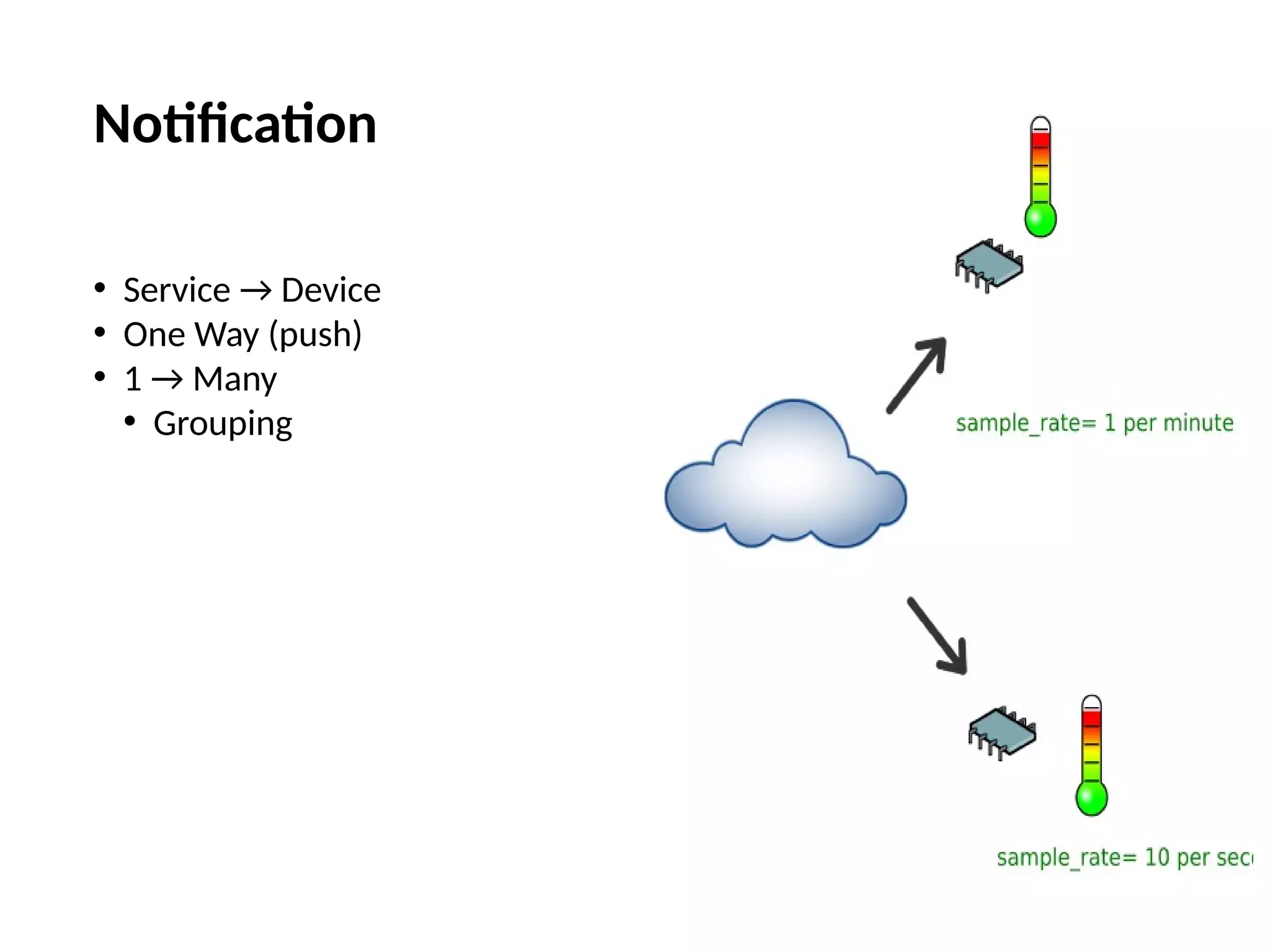
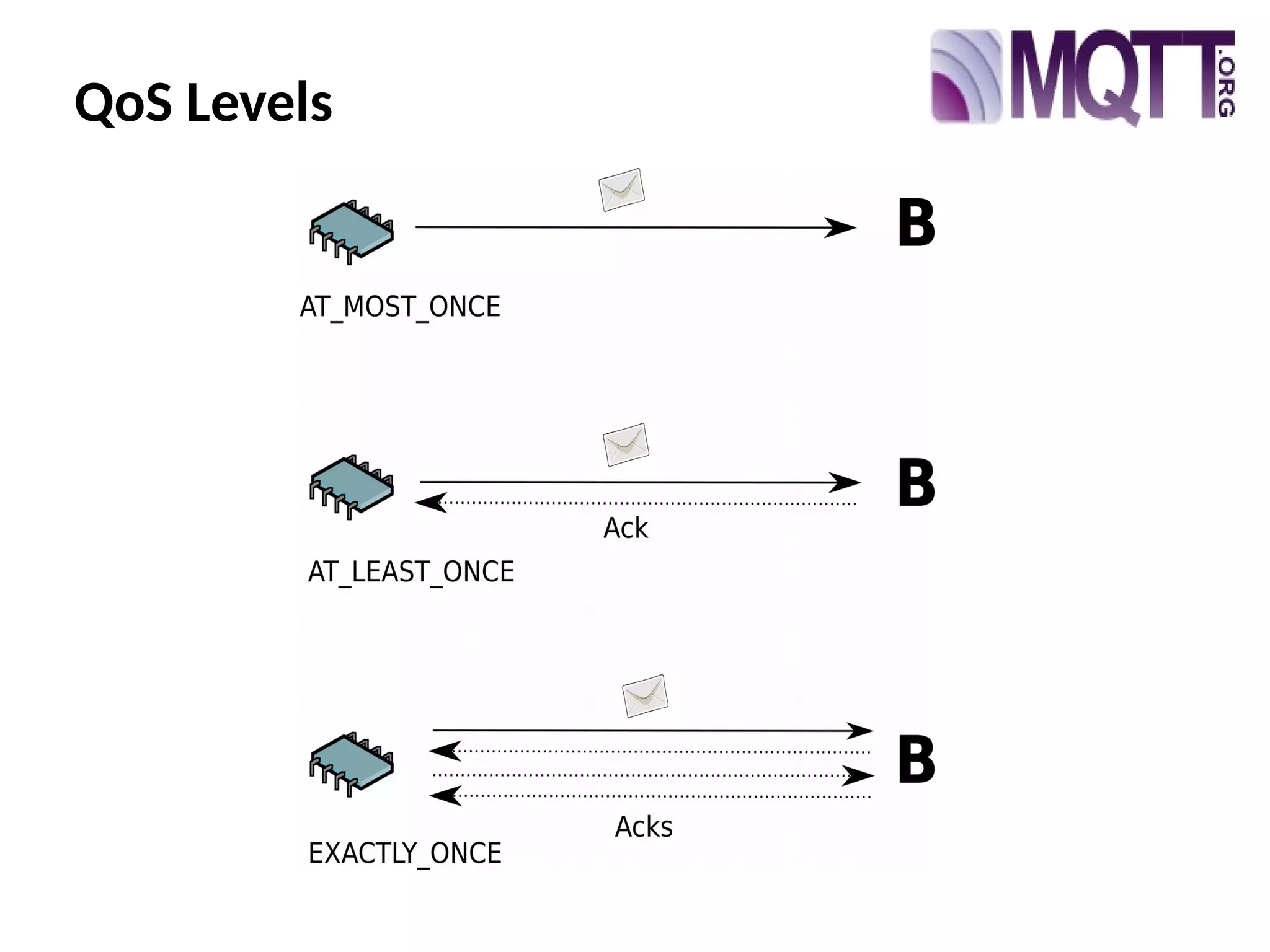
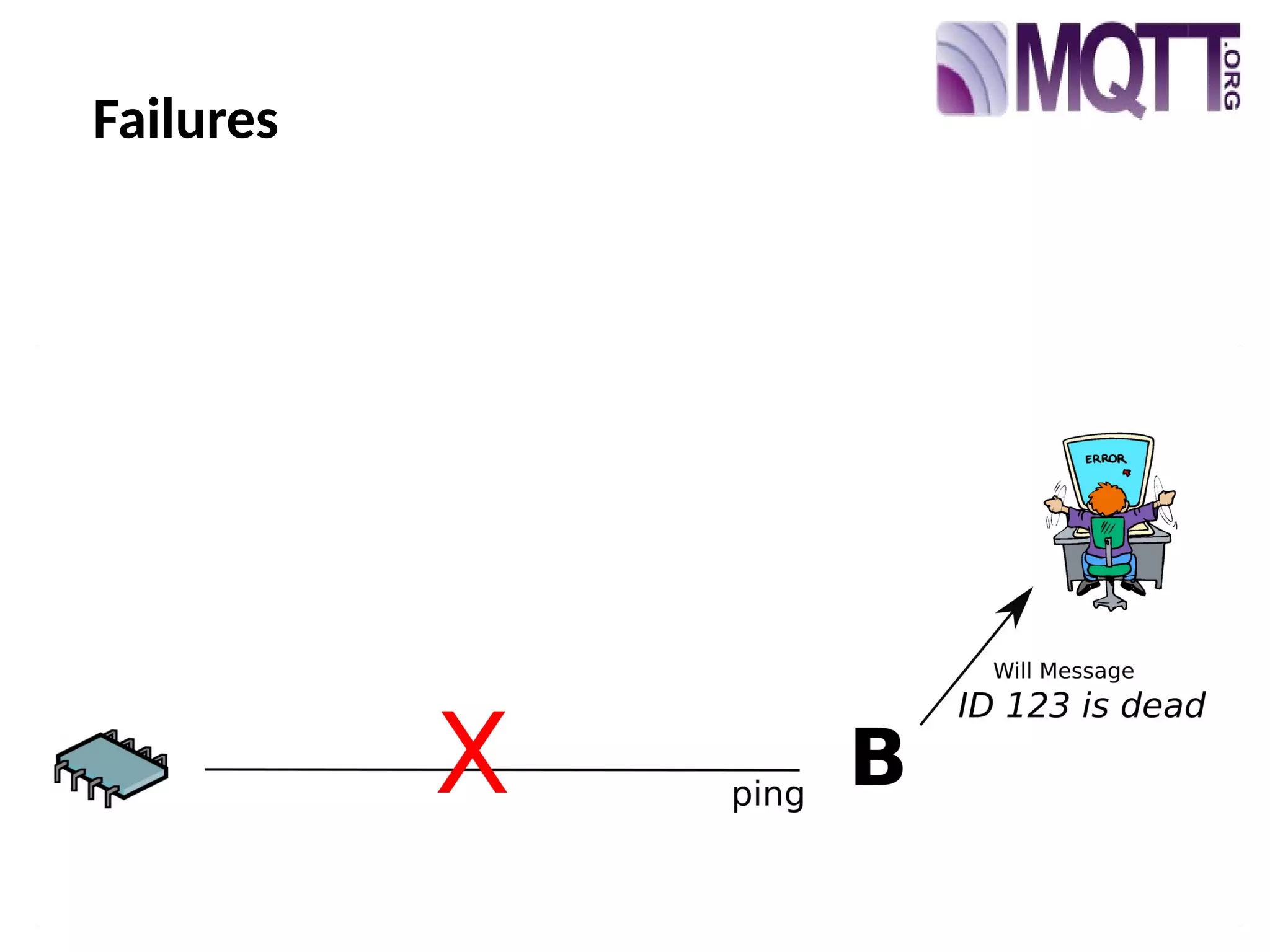
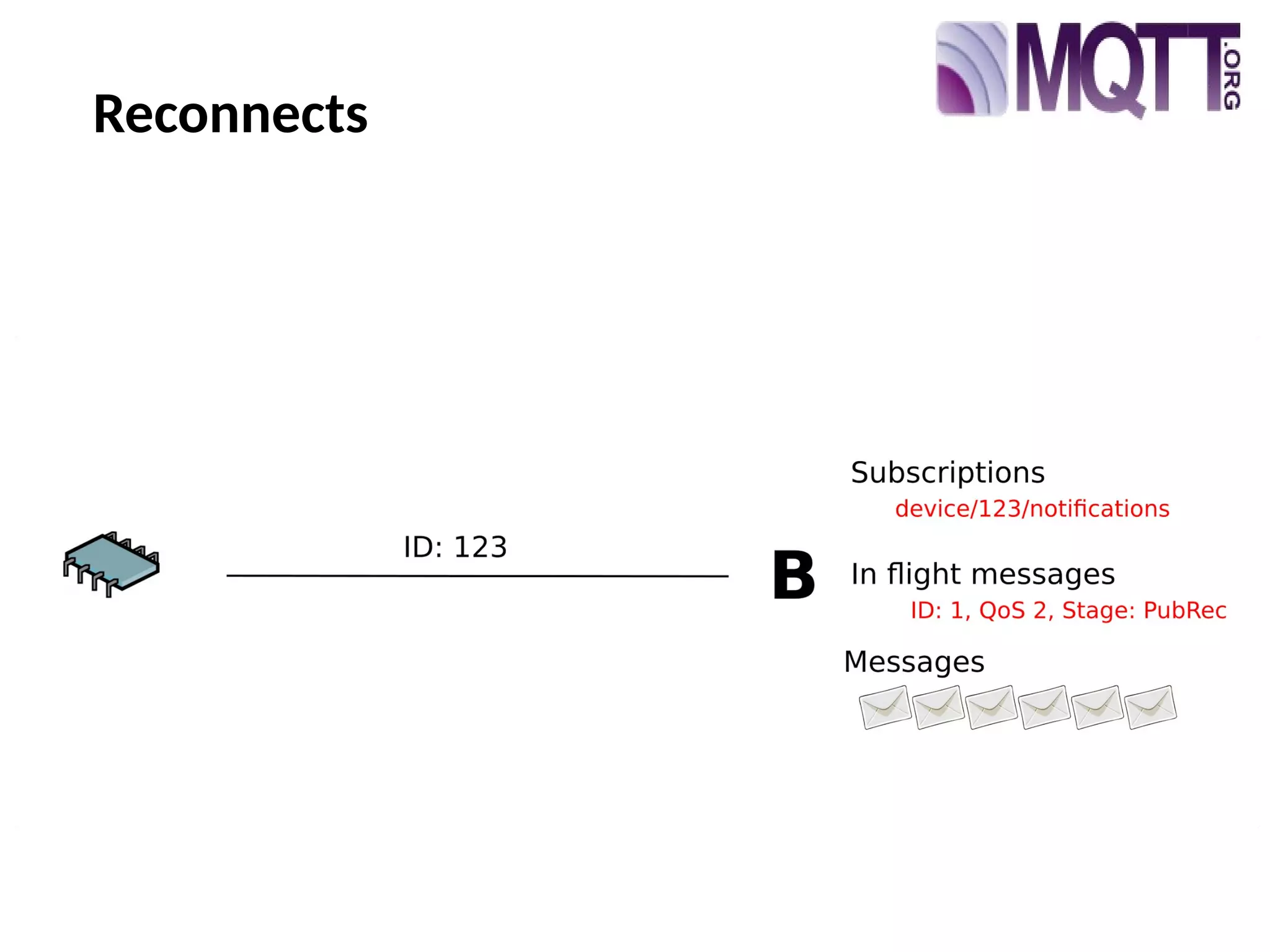
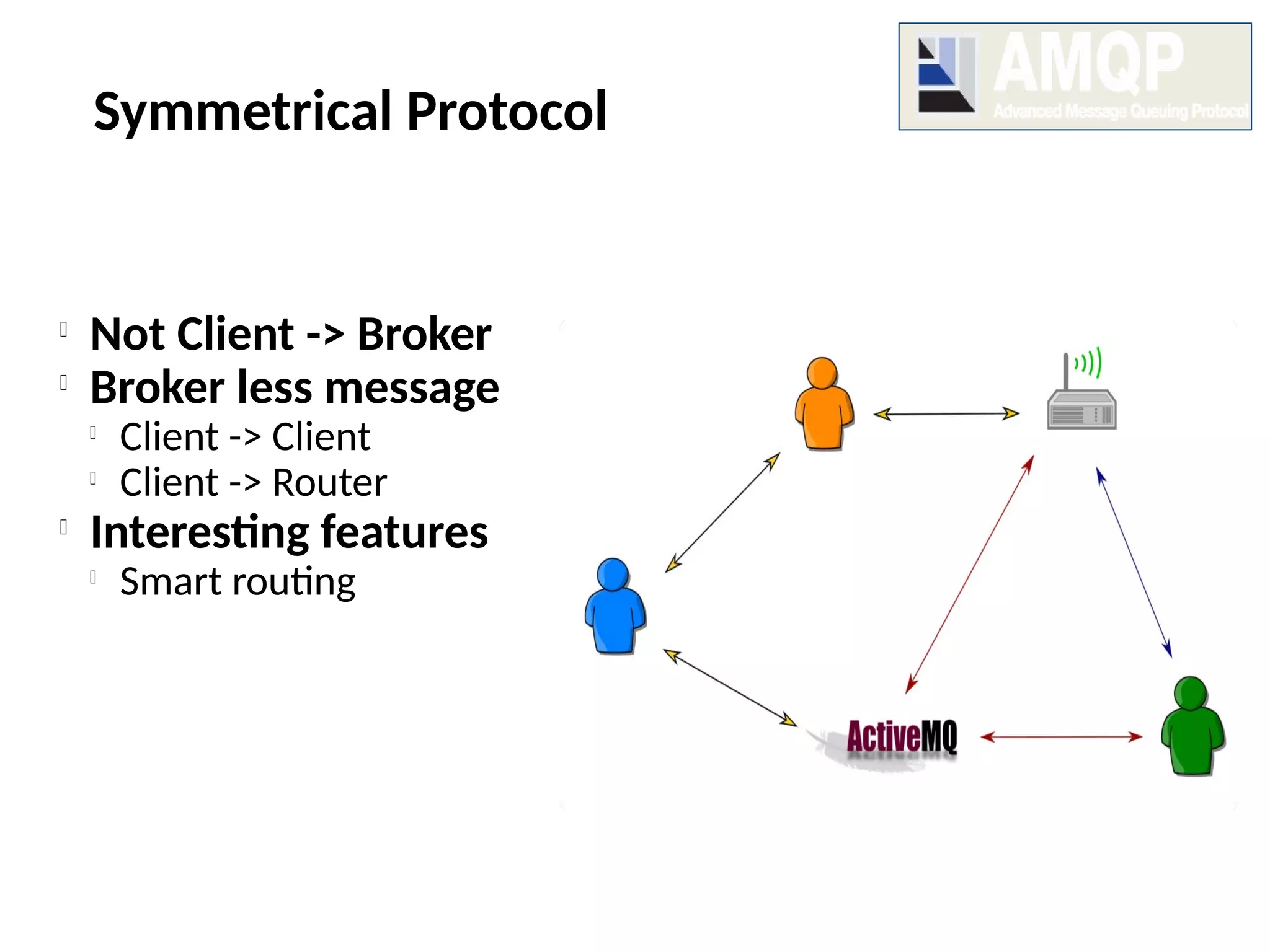
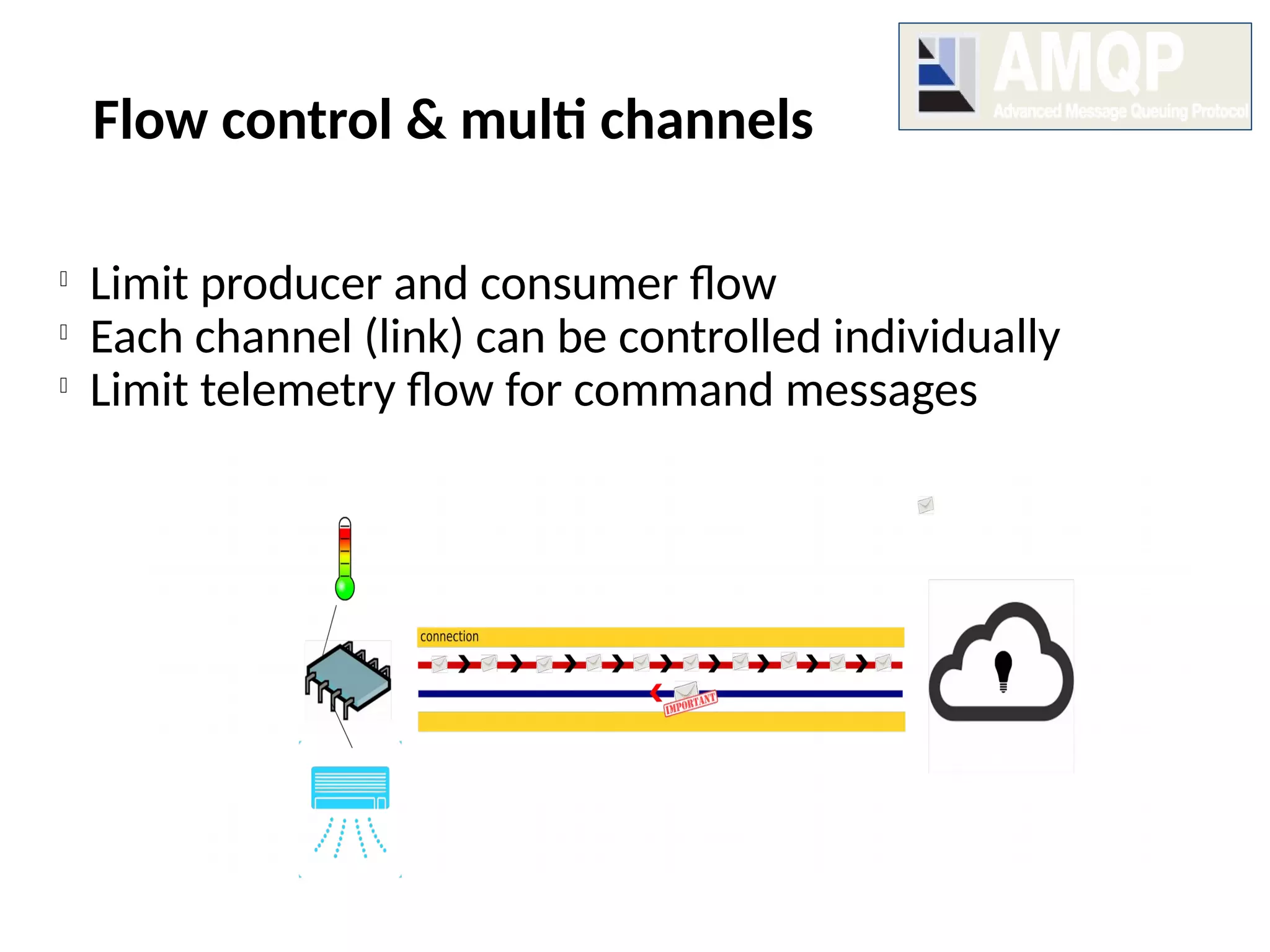
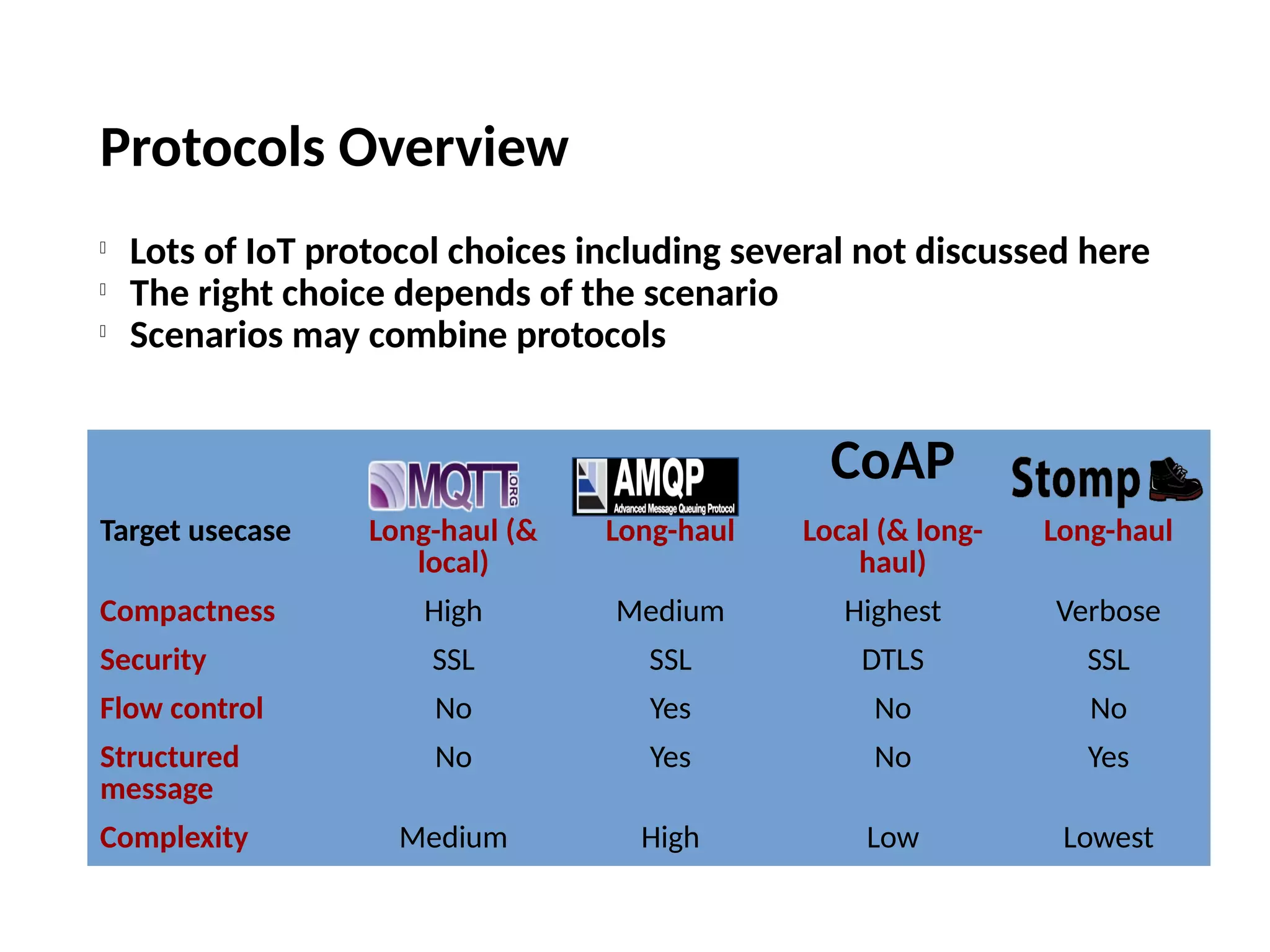
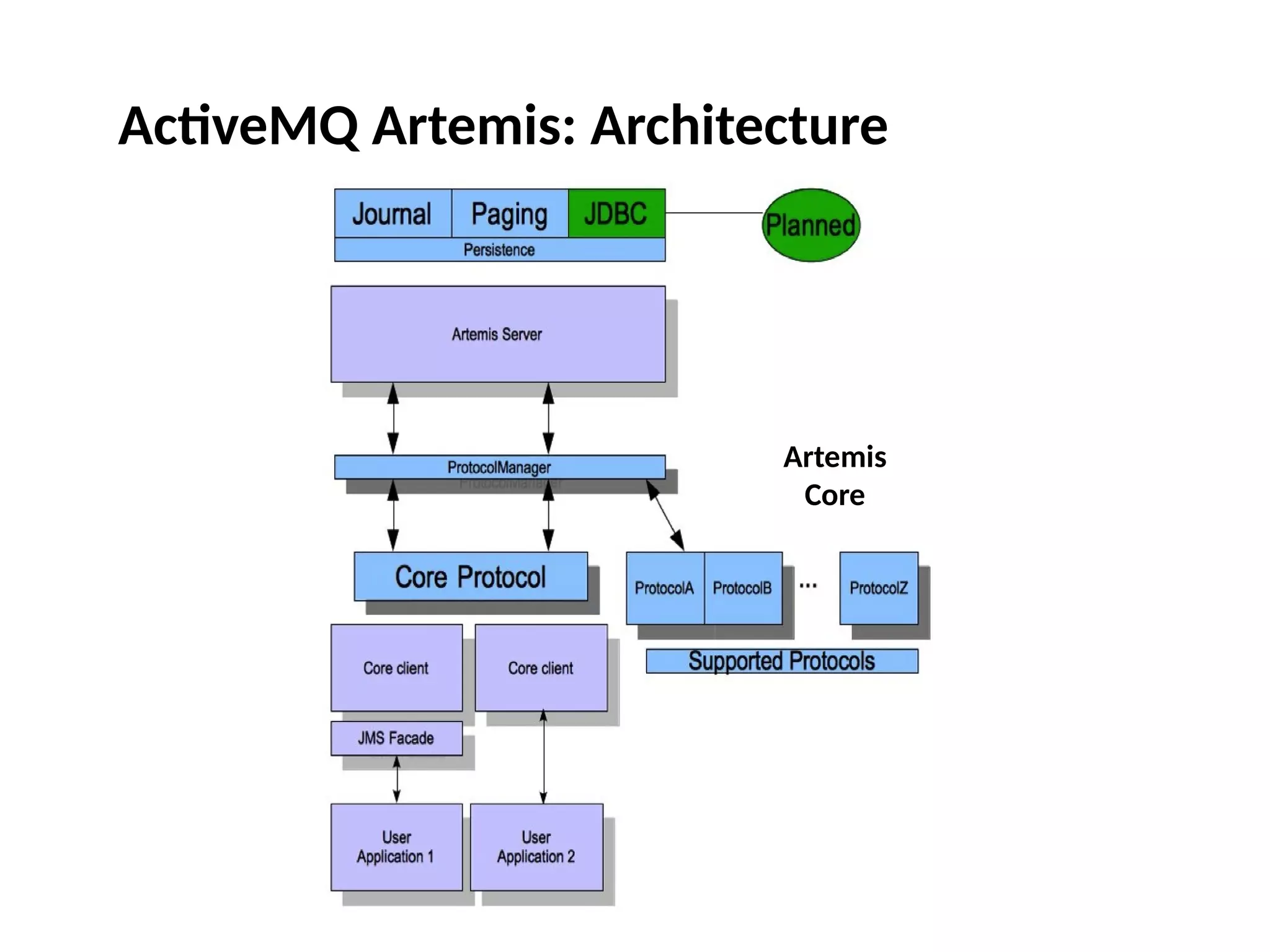
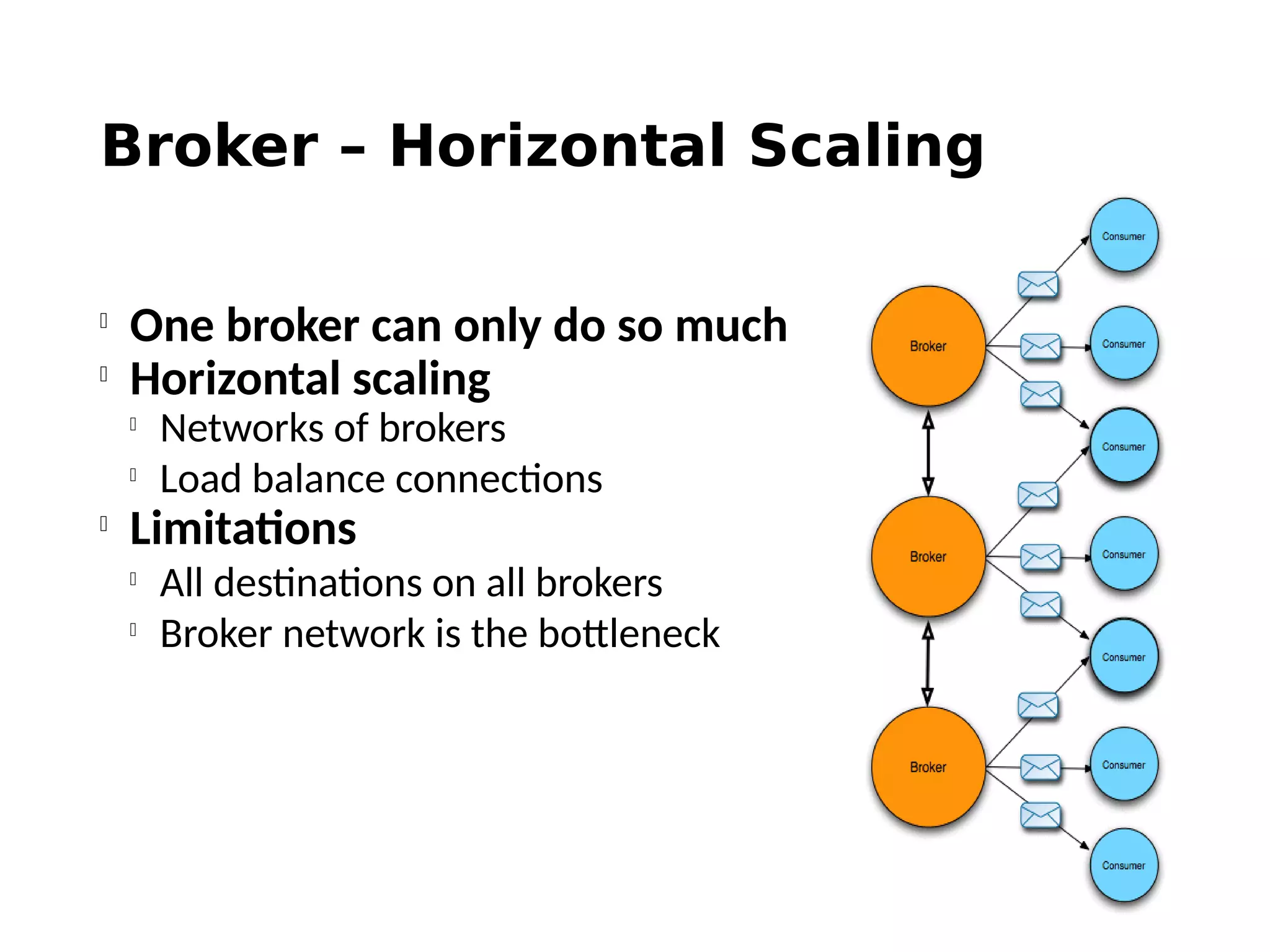
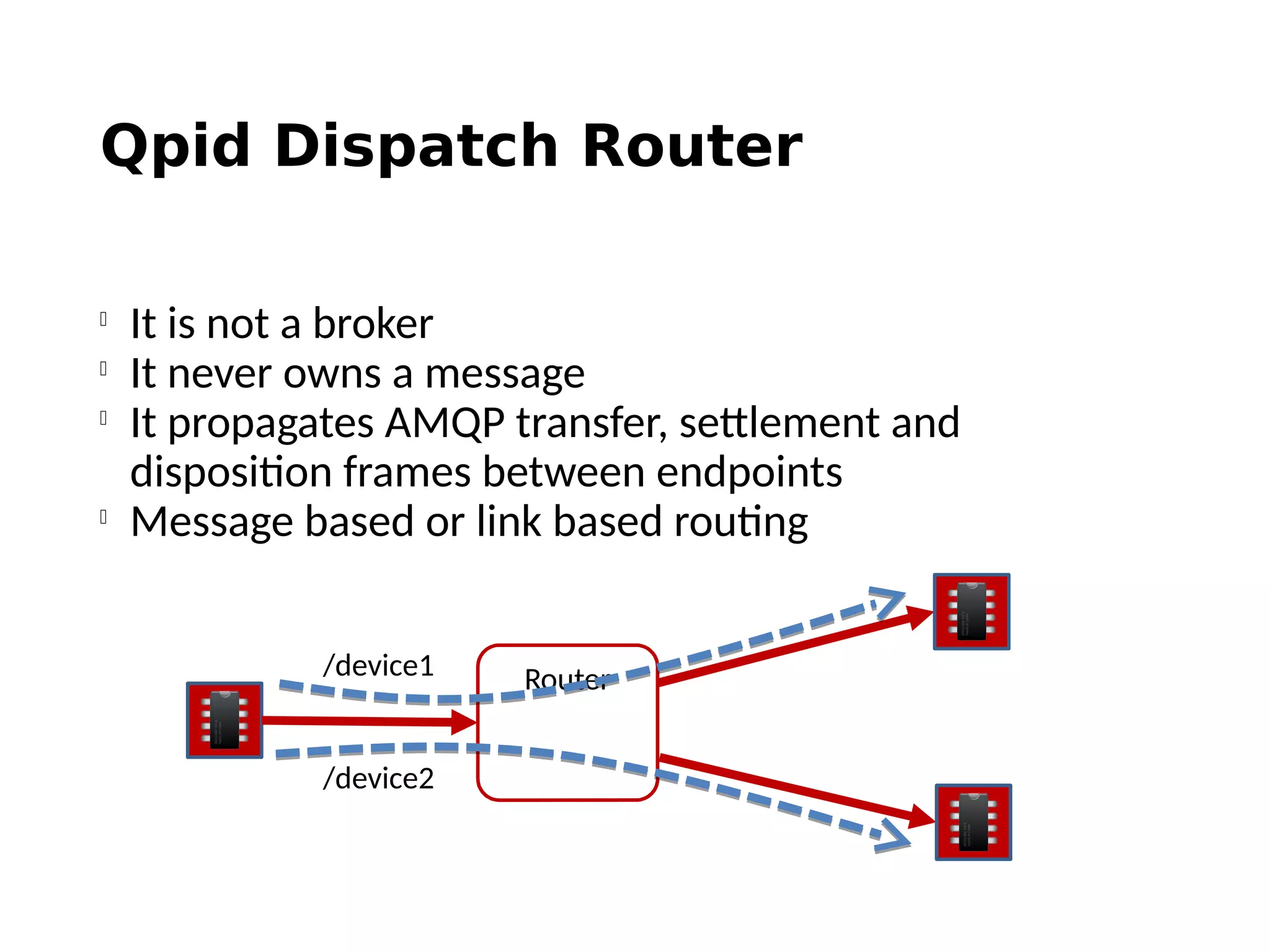
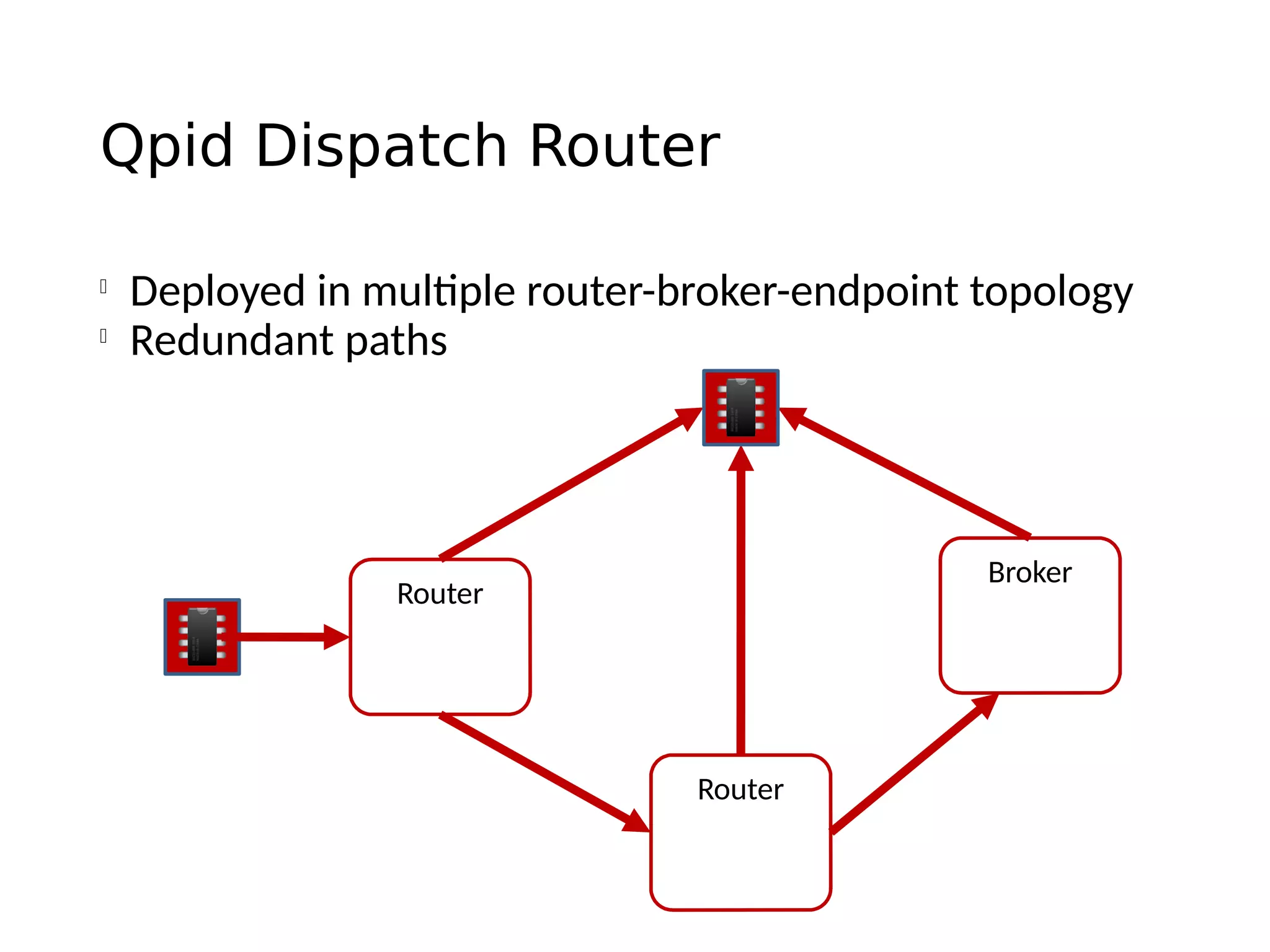
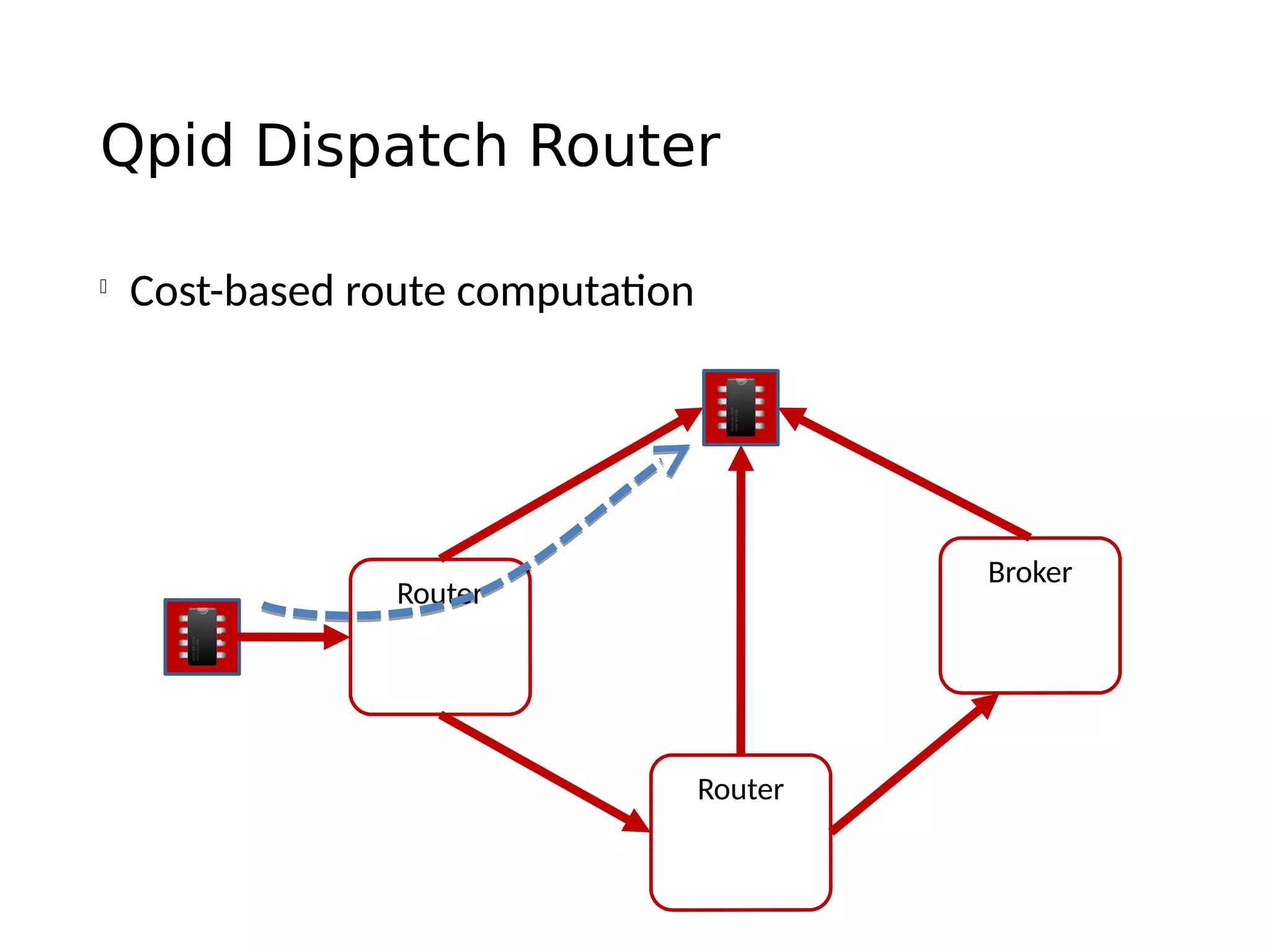
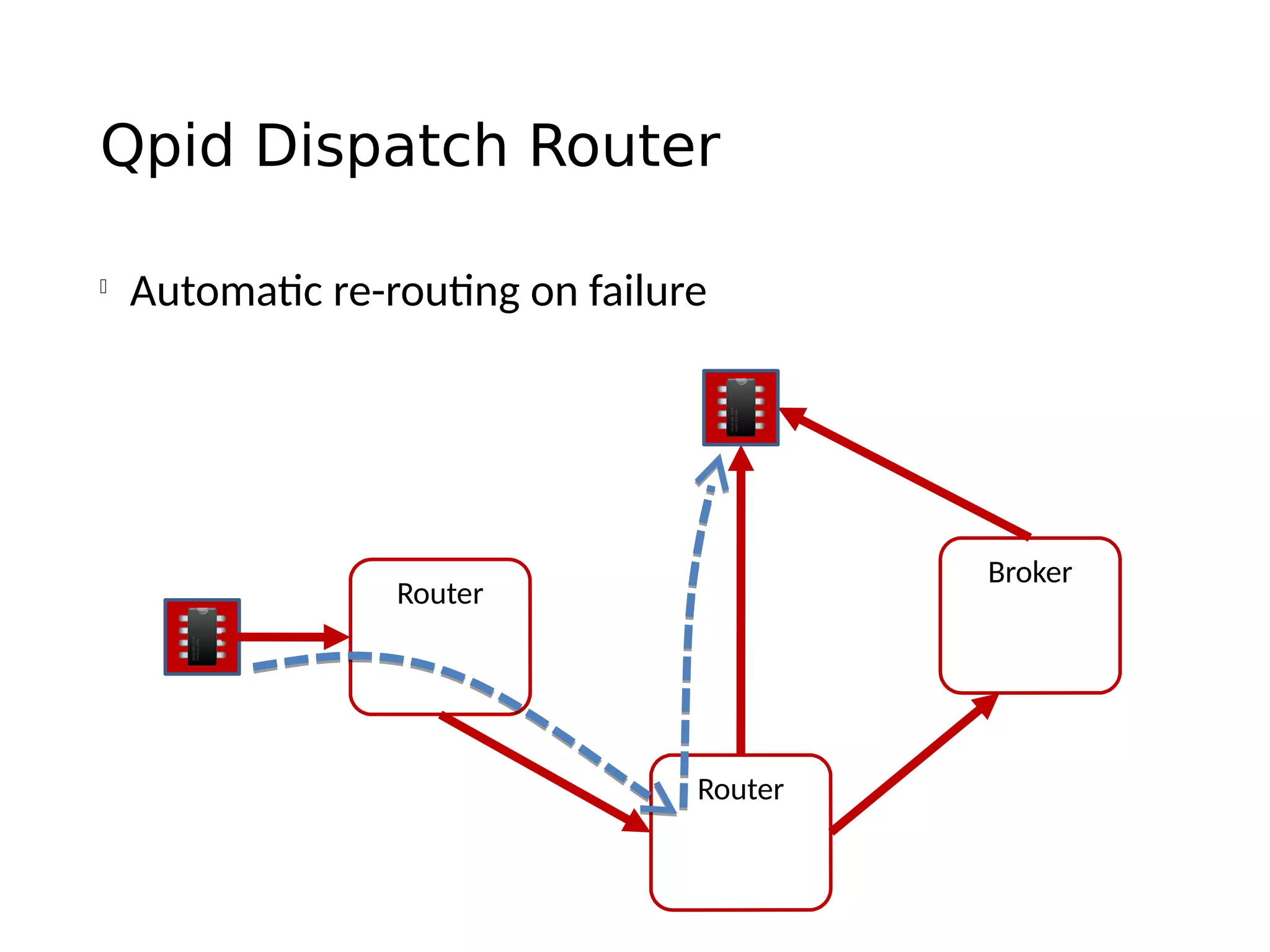
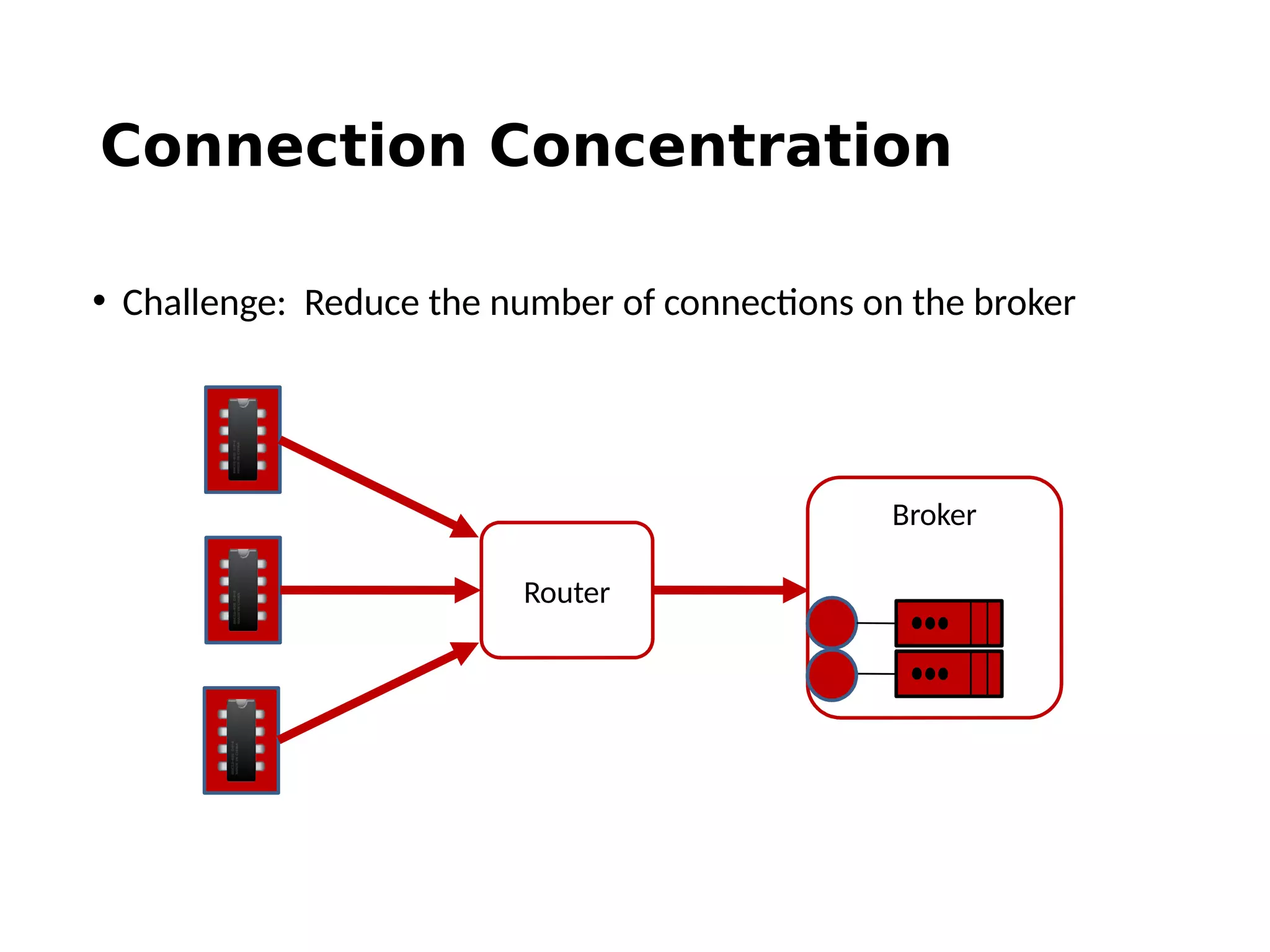
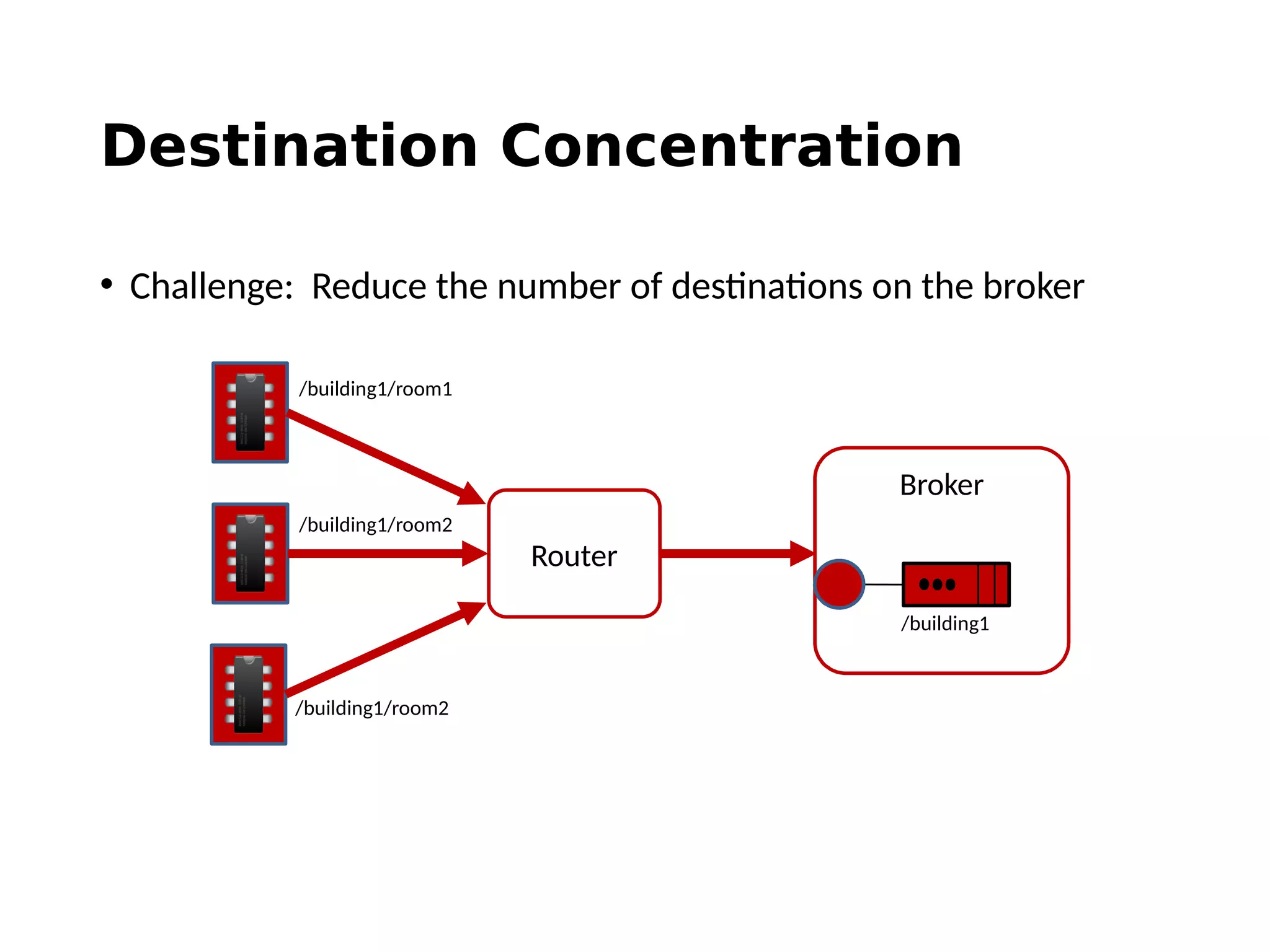
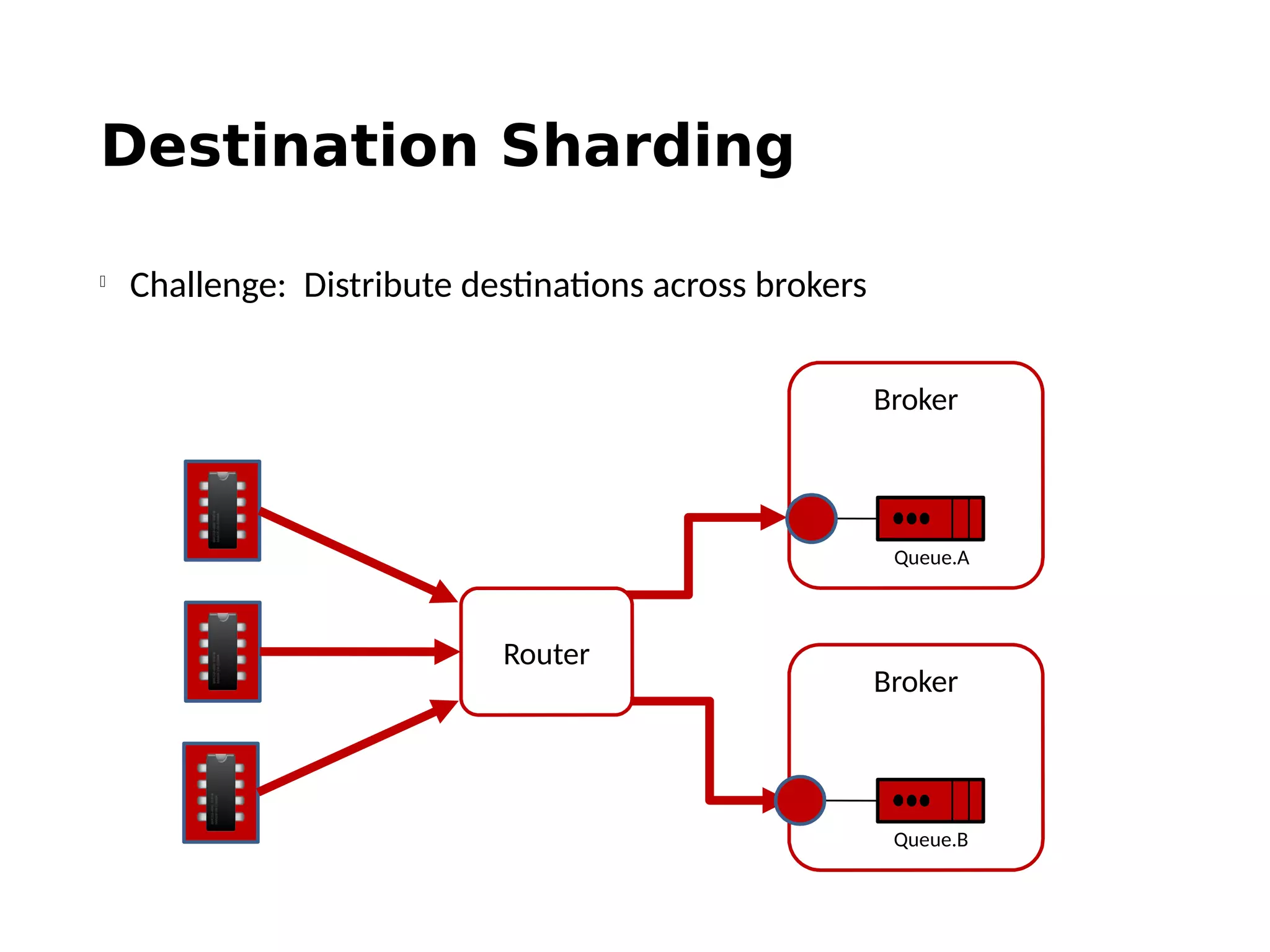
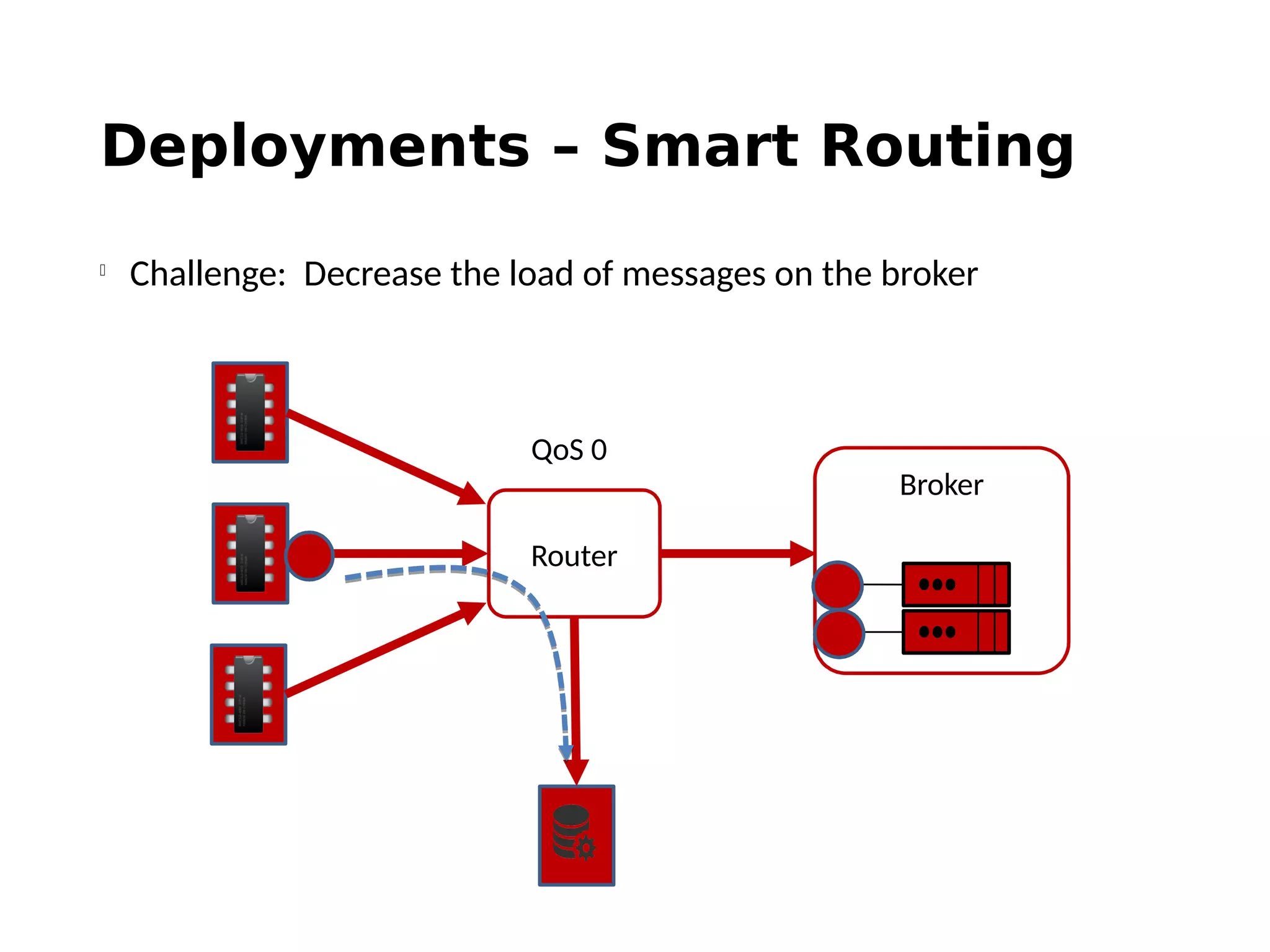
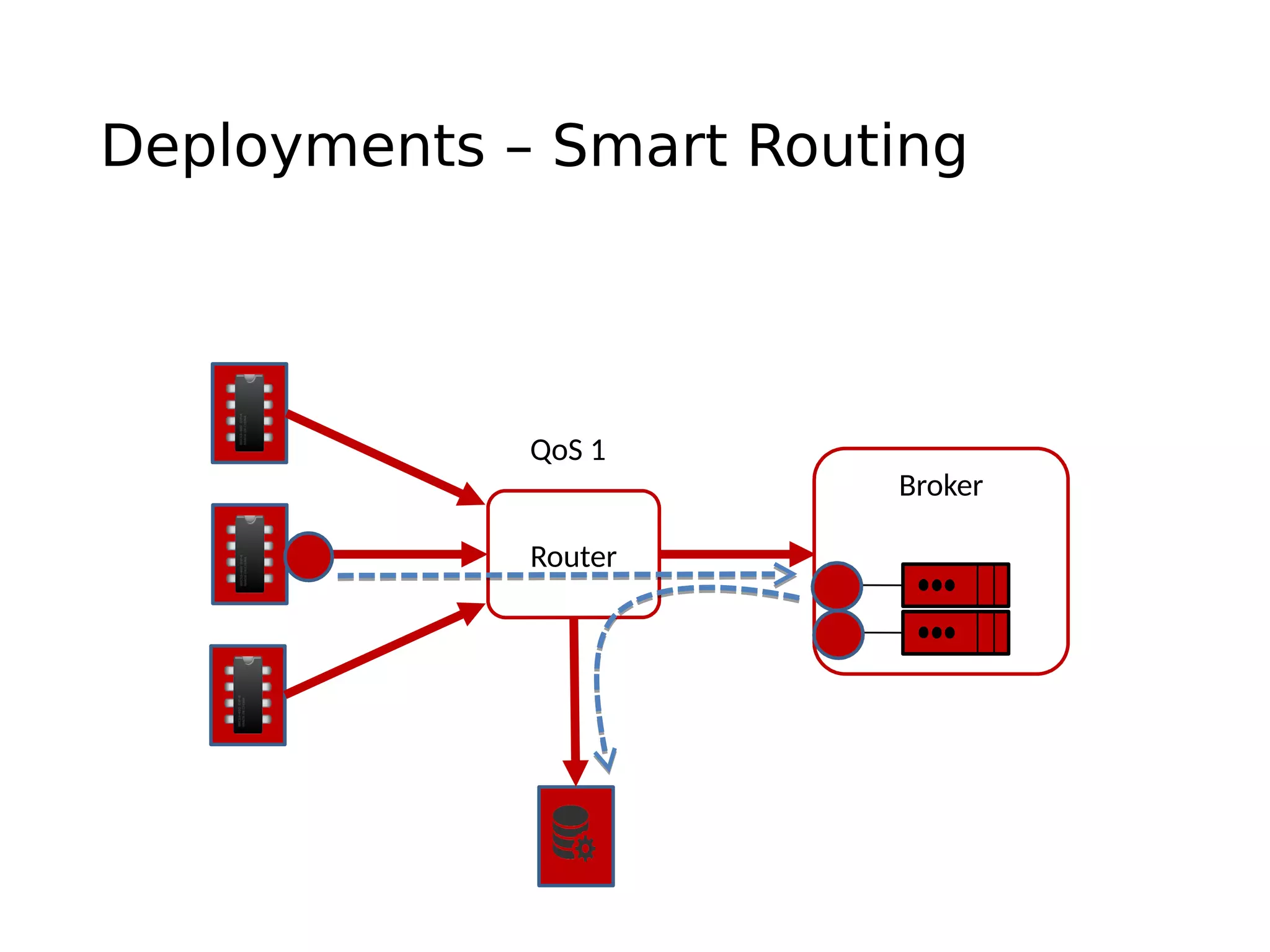
The document discusses the complexities and solutions related to messaging in the Internet of Things (IoT), focusing on the roles of protocols like JMS, MQTT, and AMQP, as well as messaging brokers such as Apache ActiveMQ and Artemis. It explores the challenges in IoT environments, including interoperability, scalability, and reliability, while outlining the advantages and limitations of various communication patterns and technologies. Additionally, it emphasizes innovative tools like the Qpid Dispatch Router that facilitate scalable deployments in IoT messaging infrastructure.