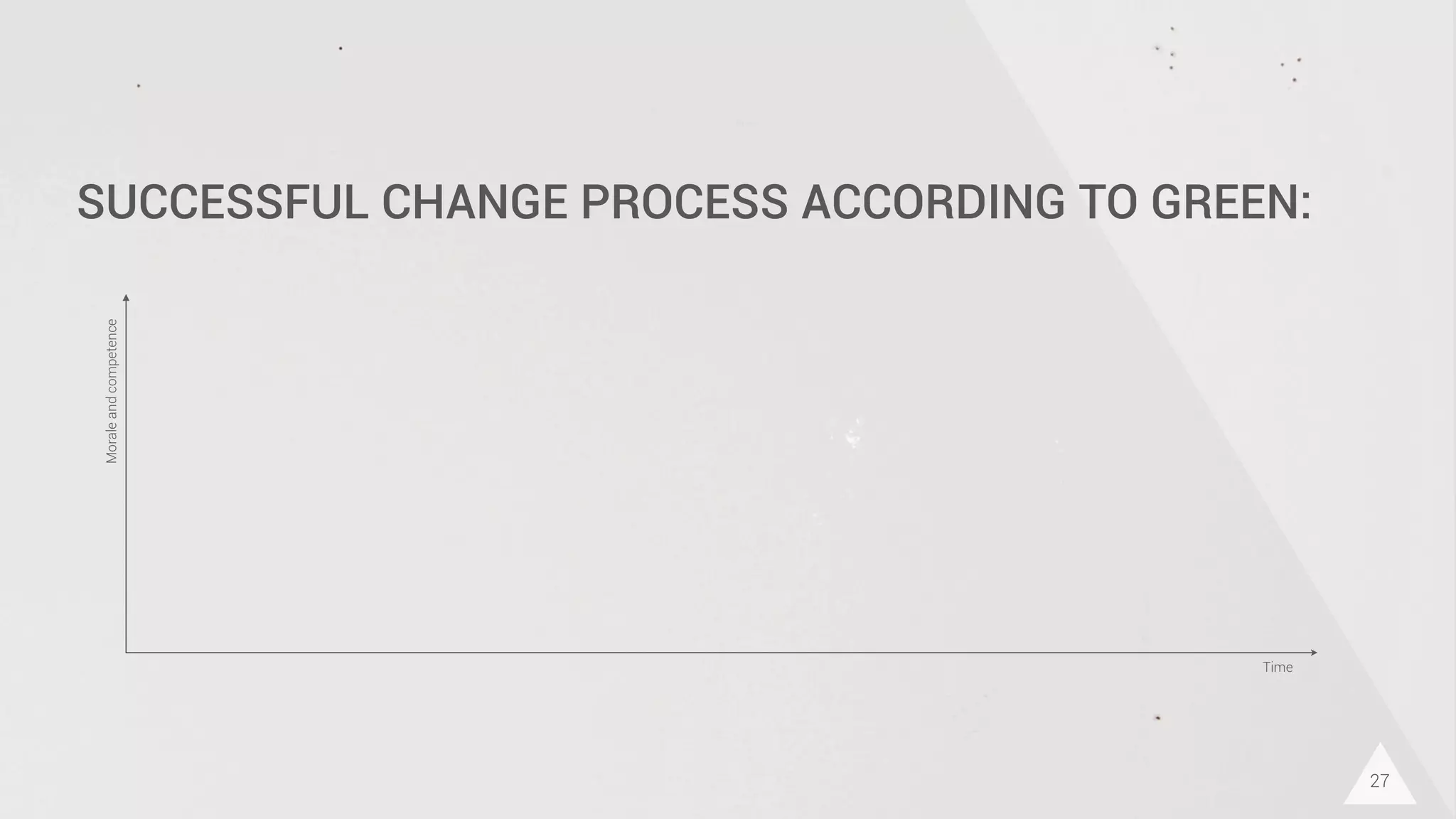
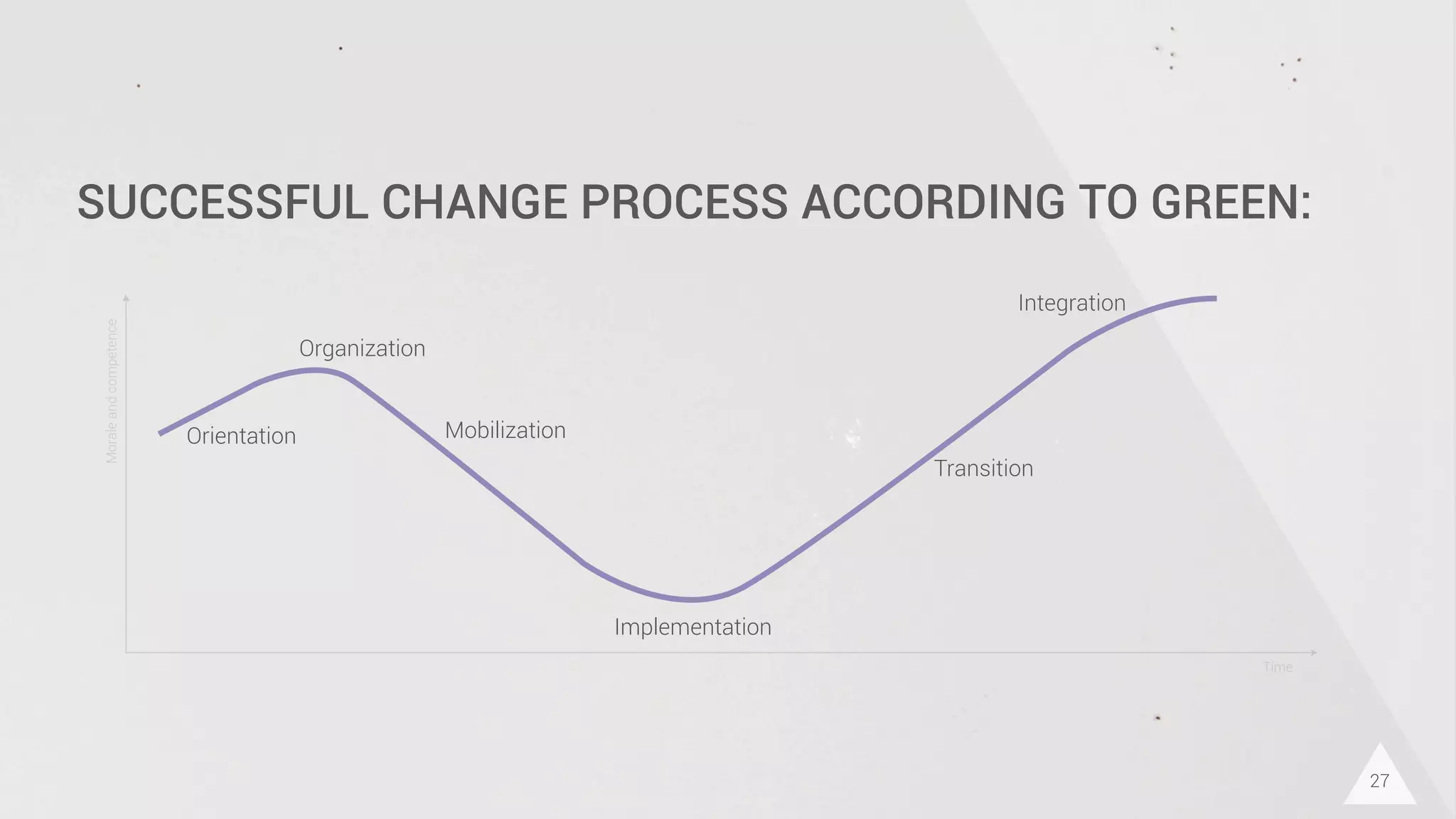
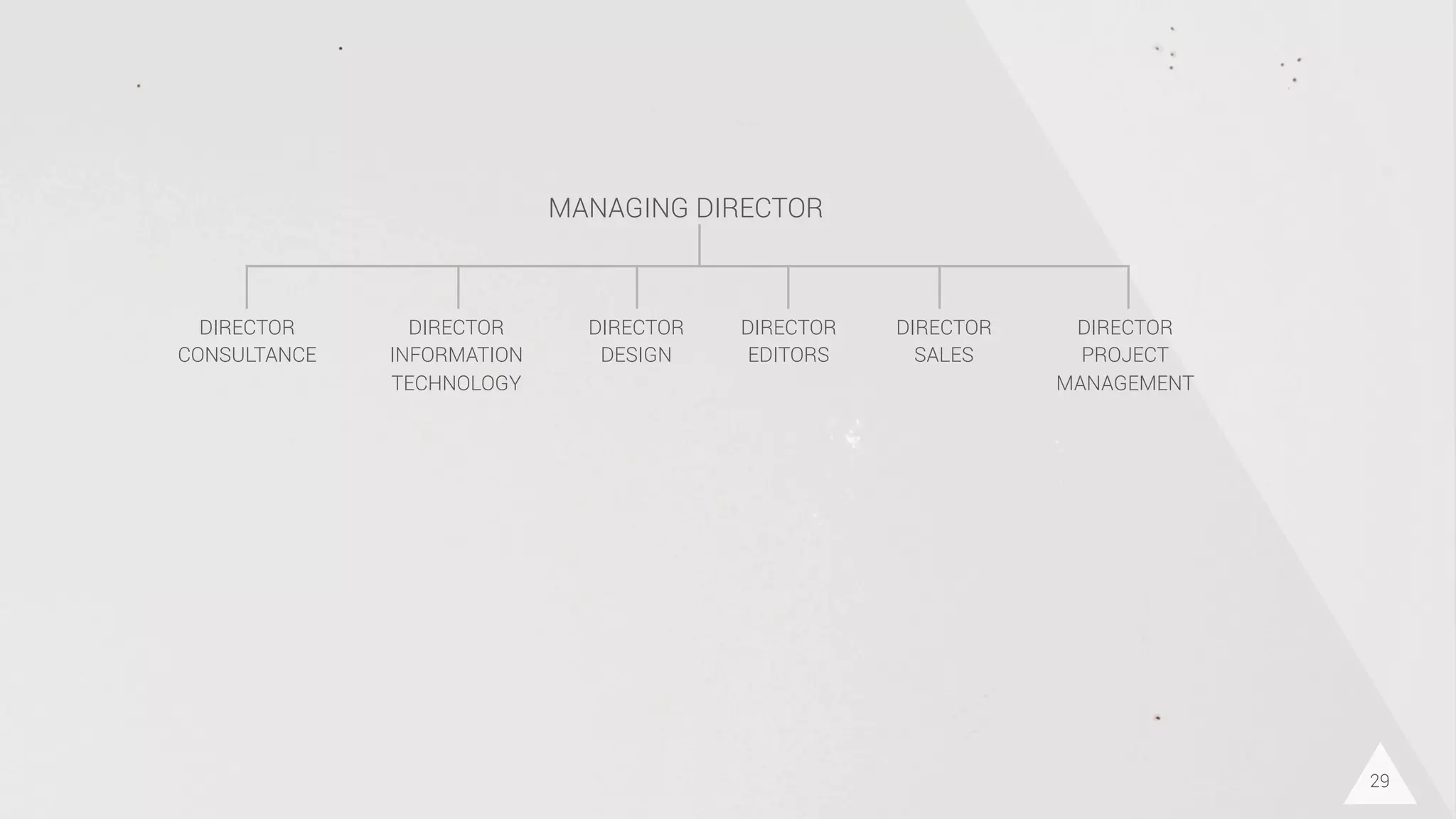
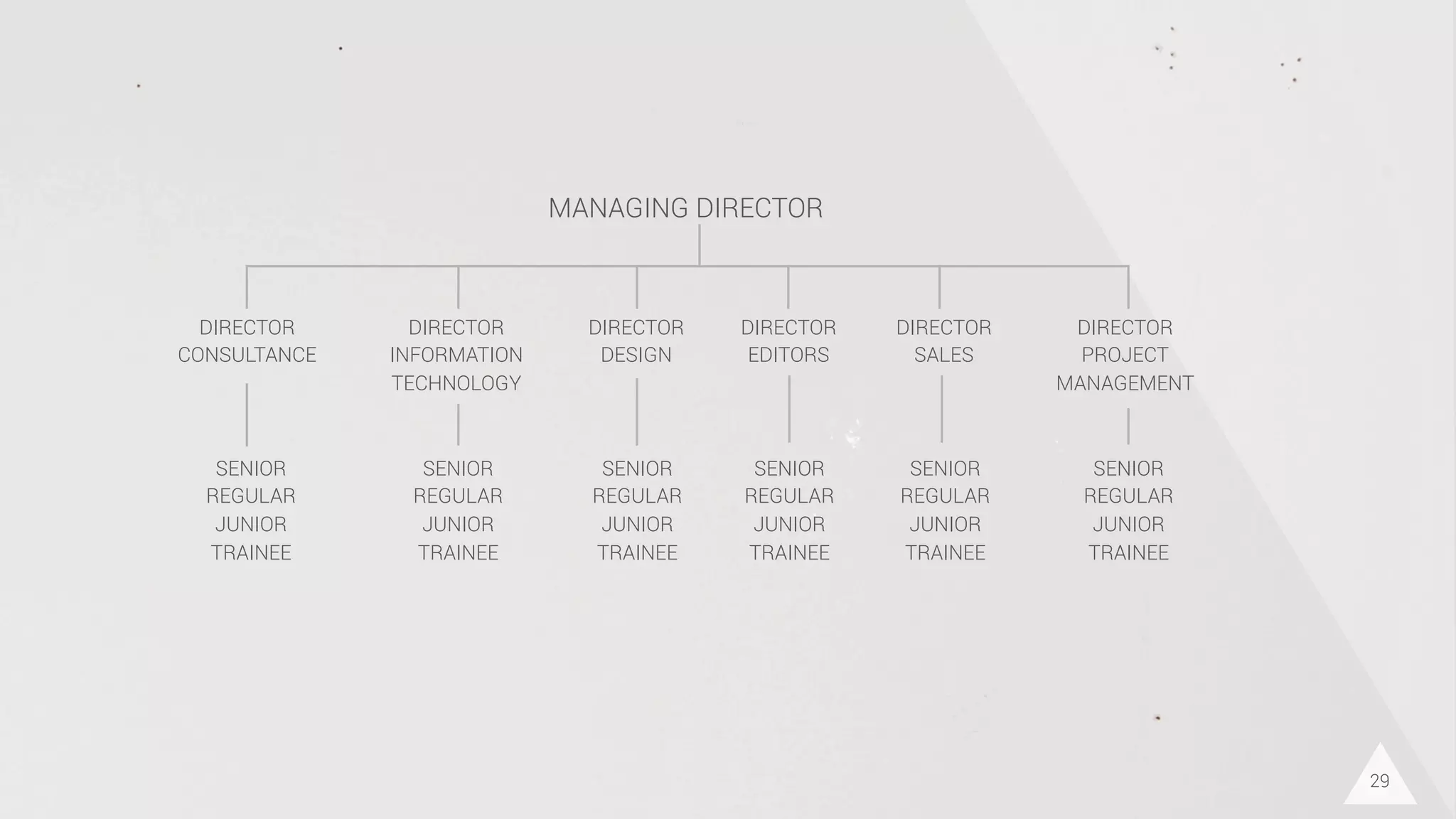
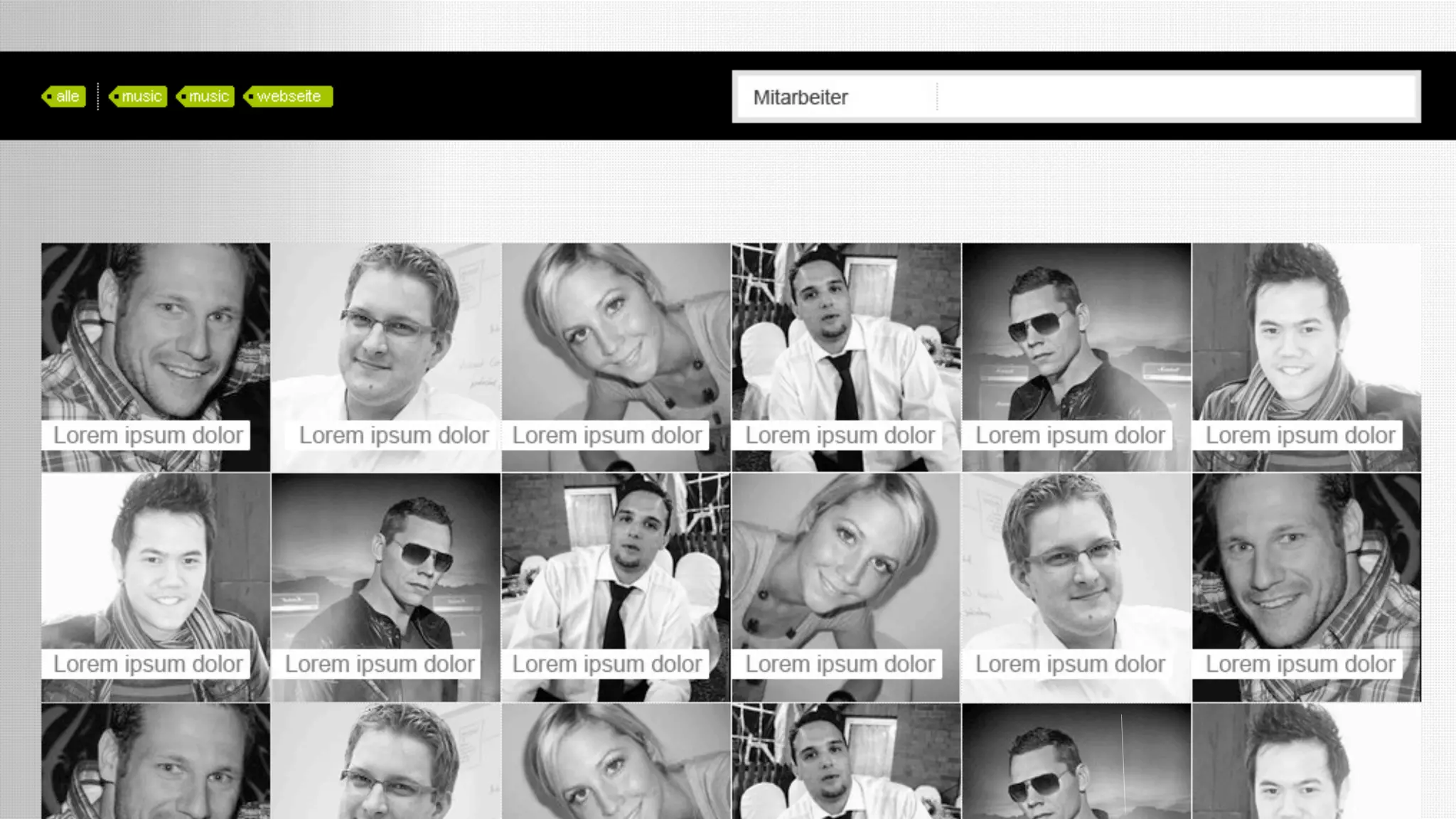
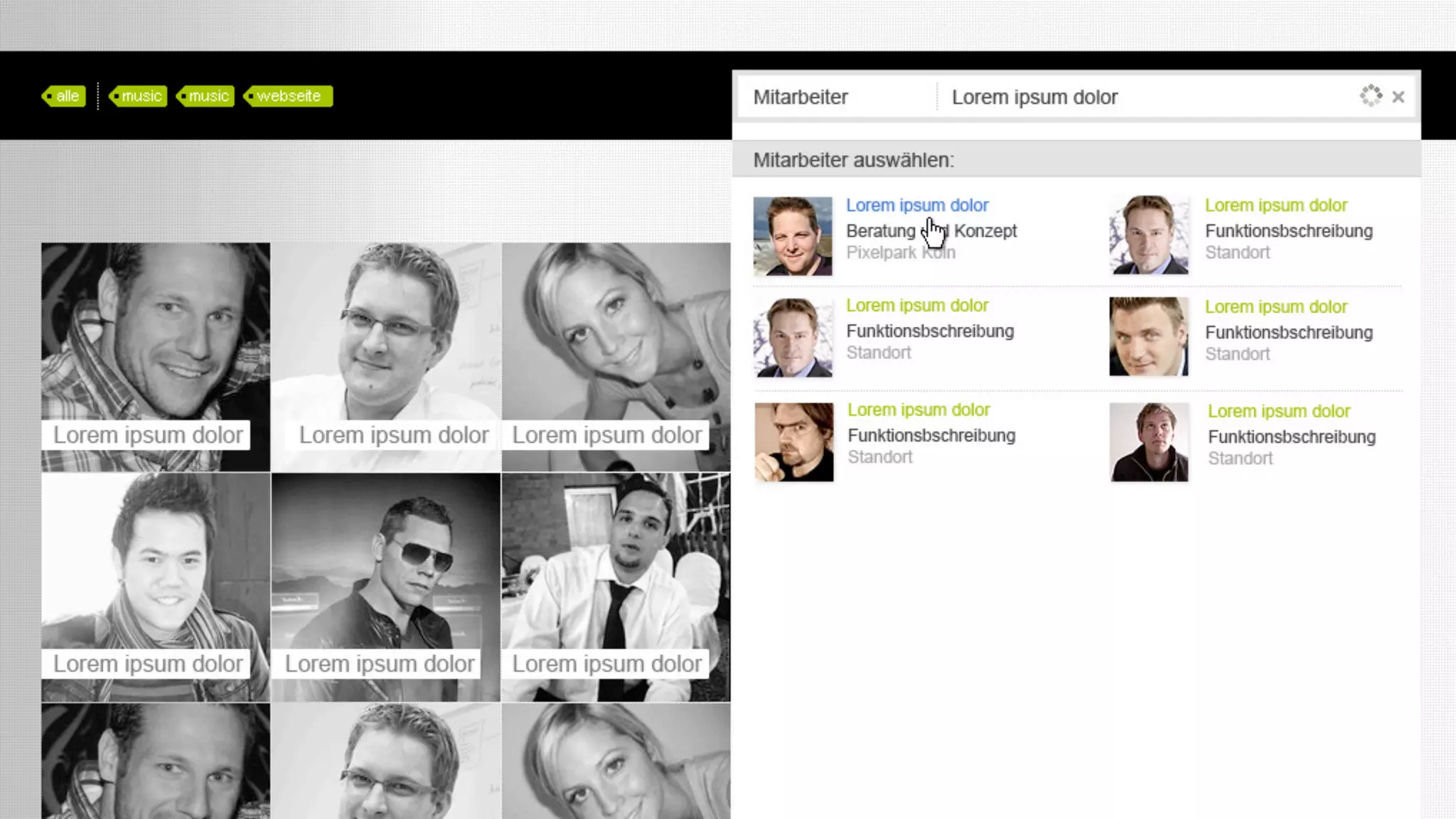
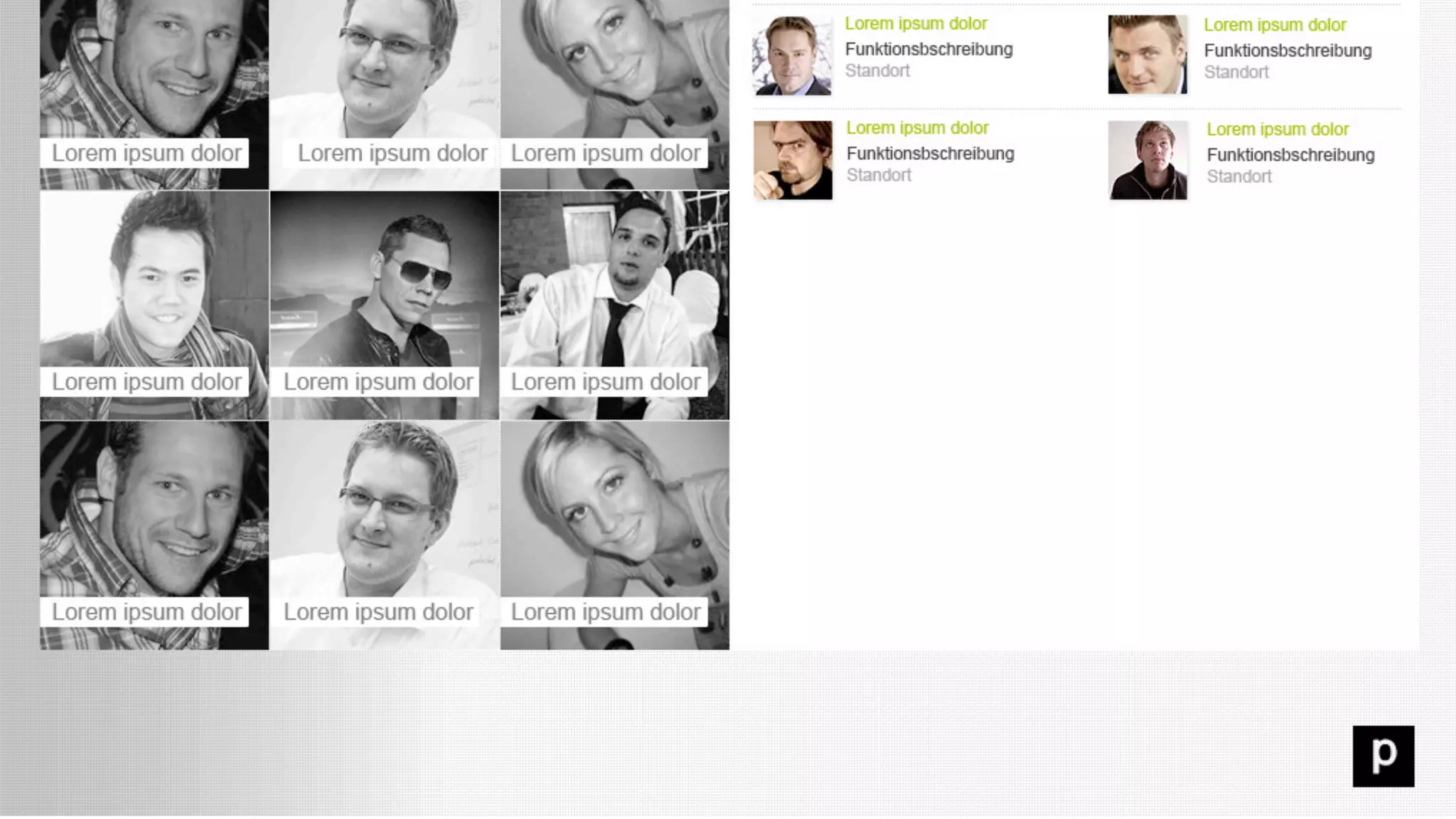
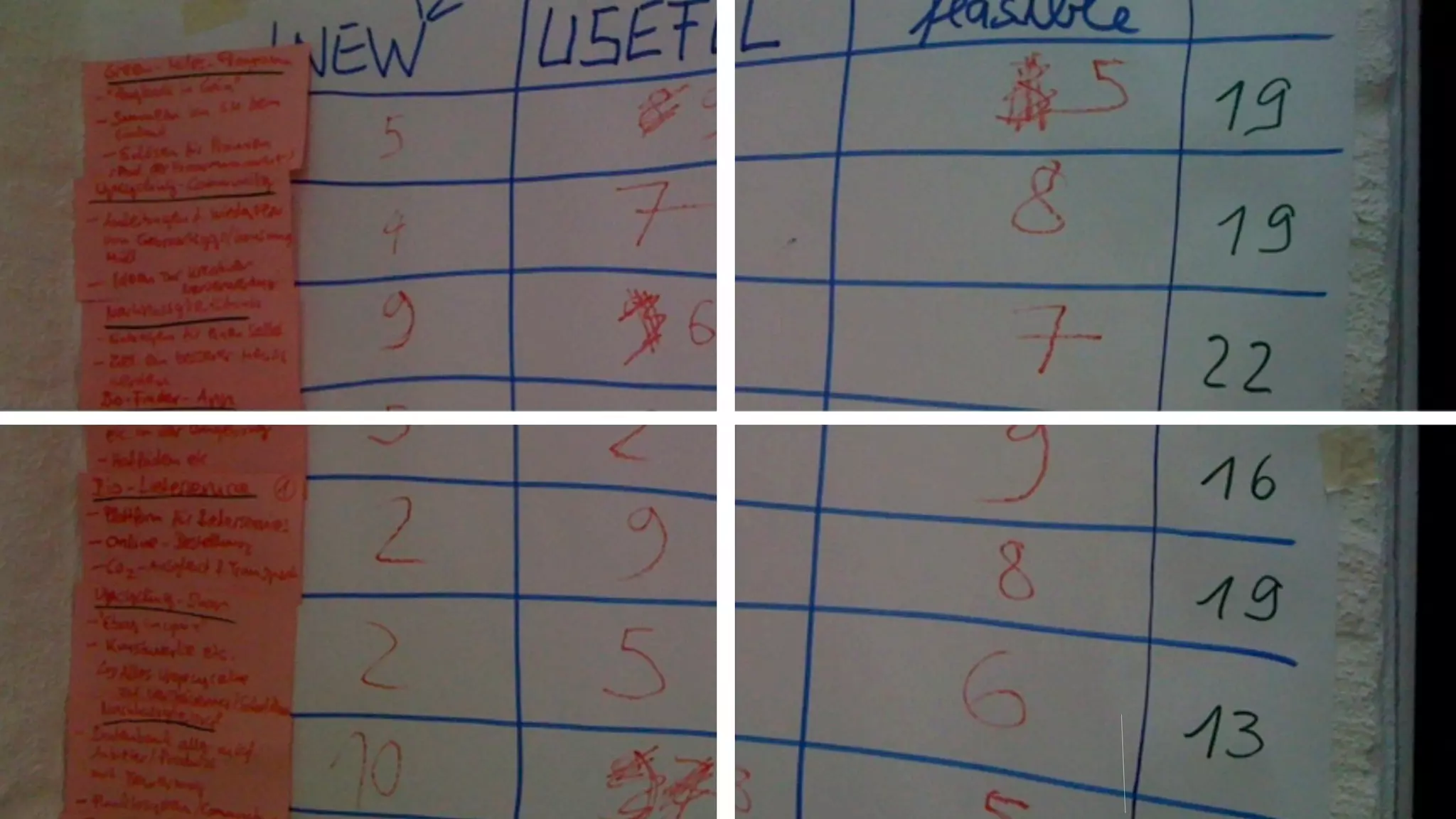
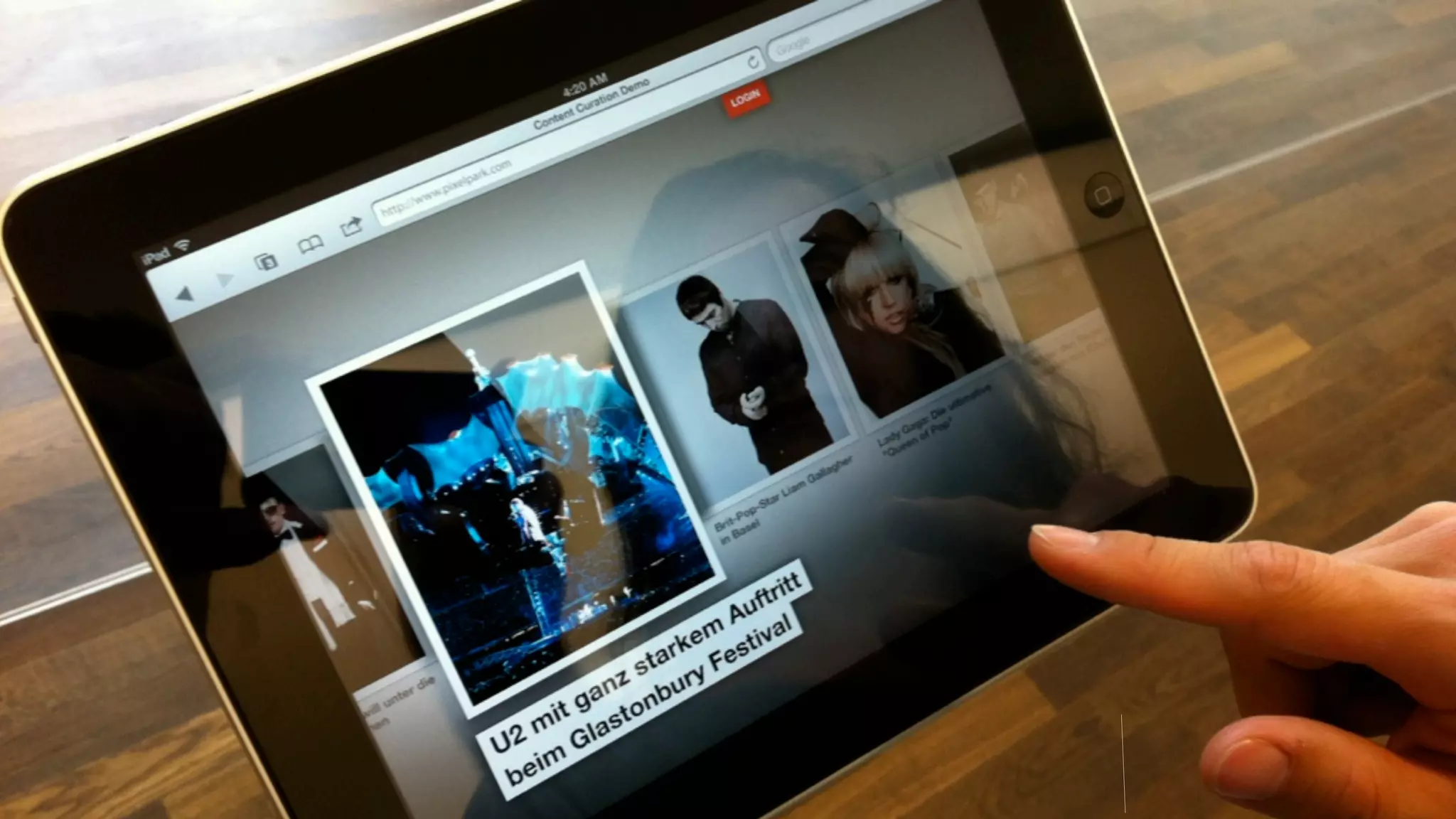
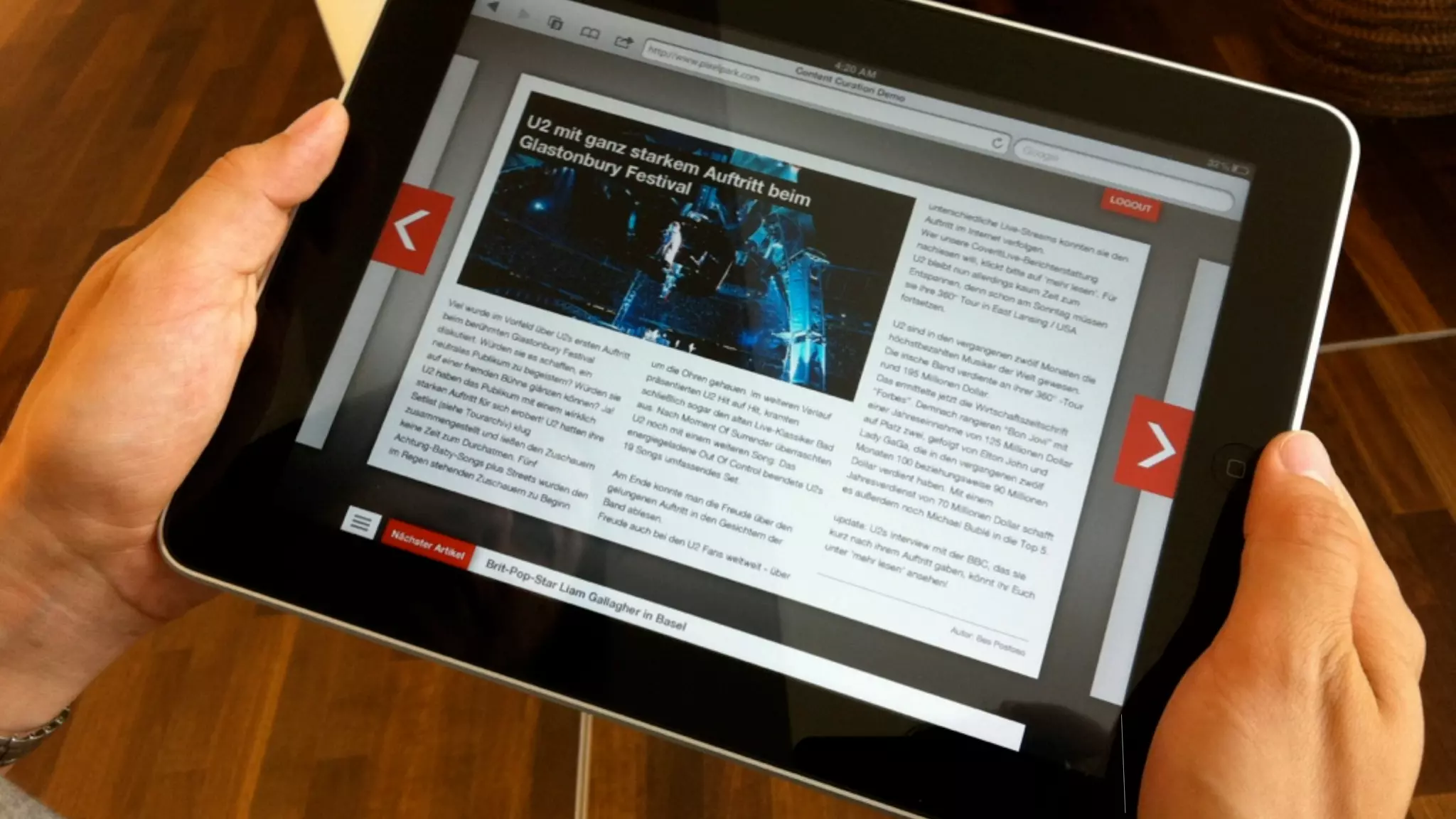
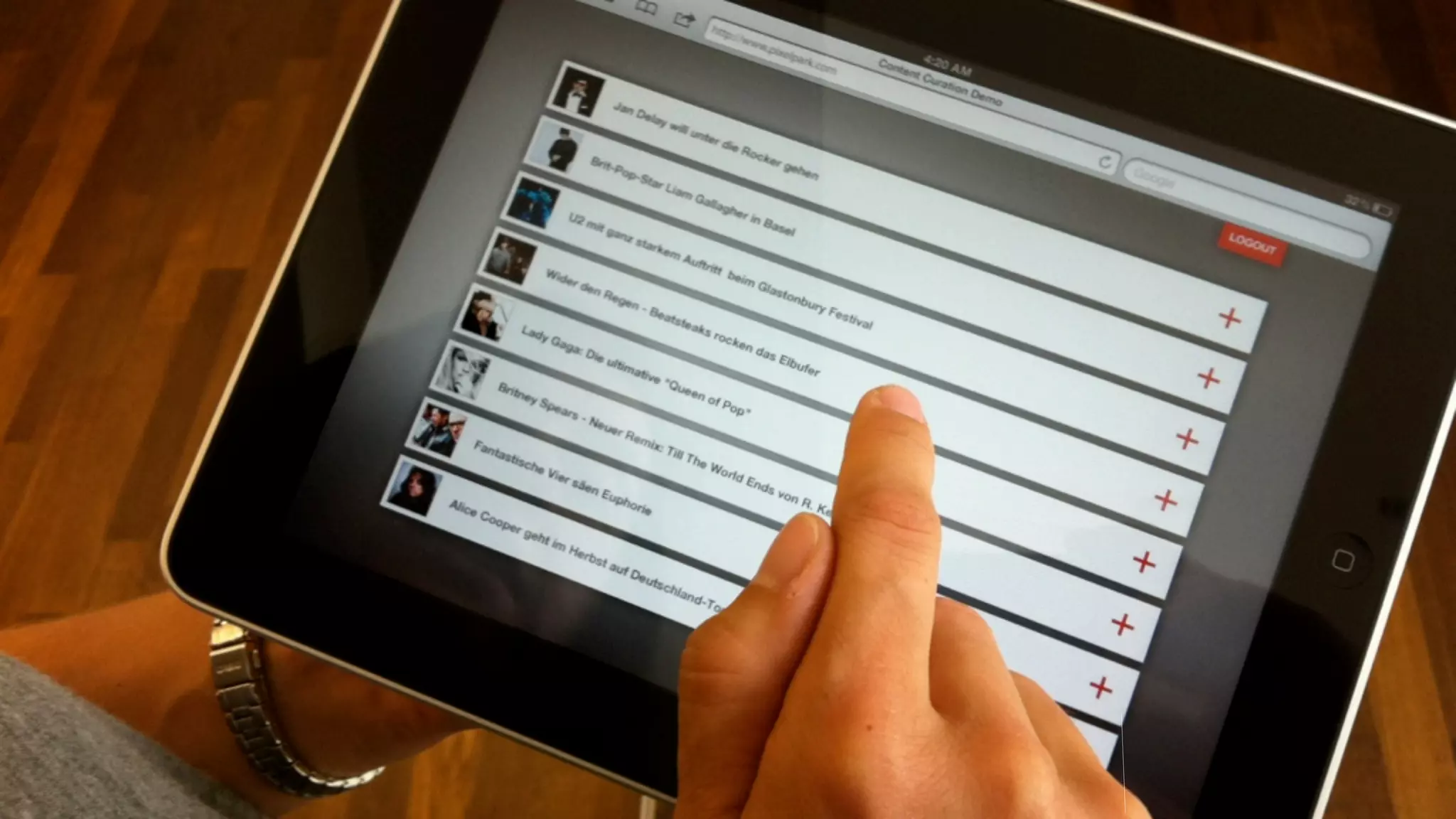
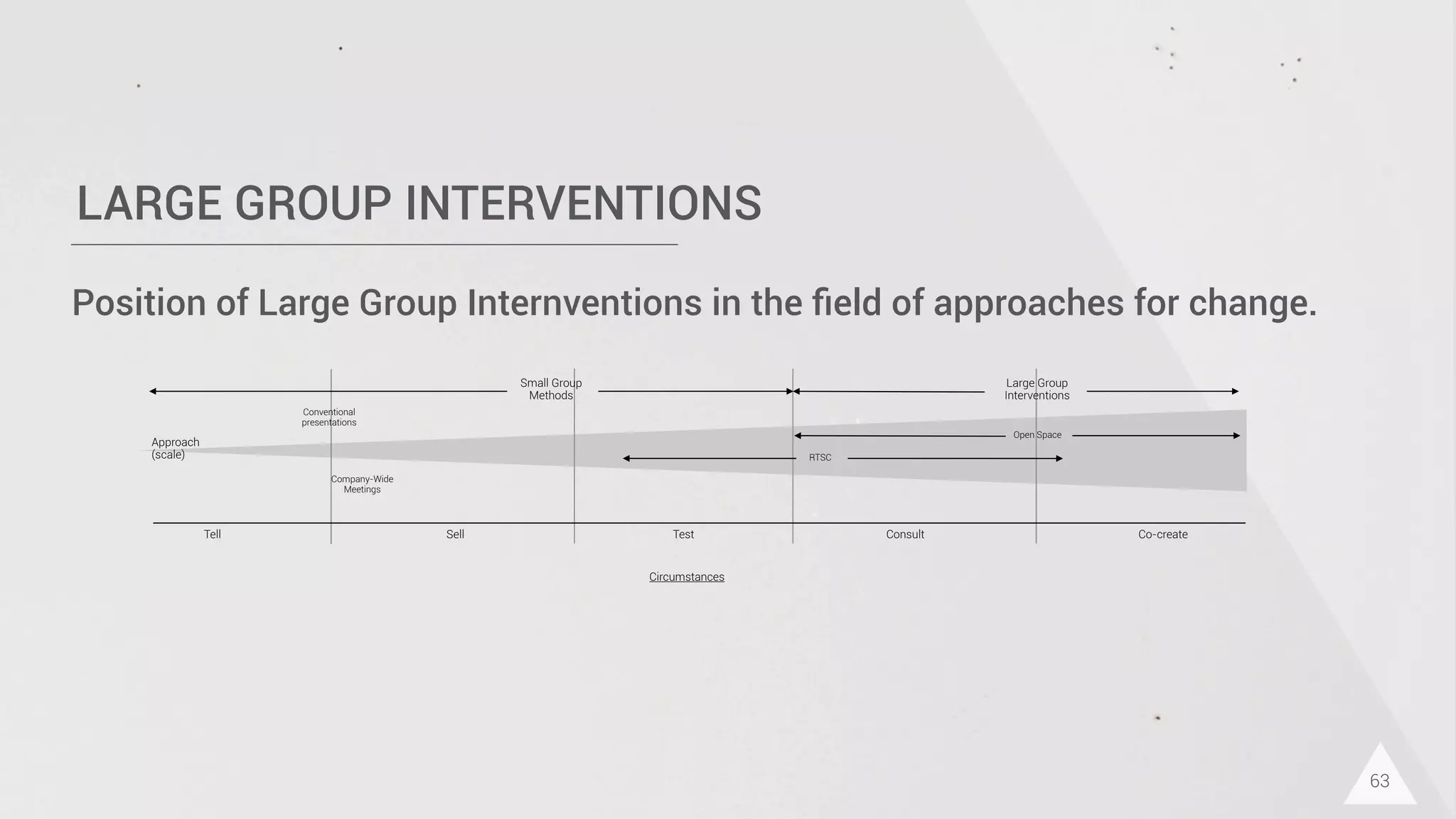
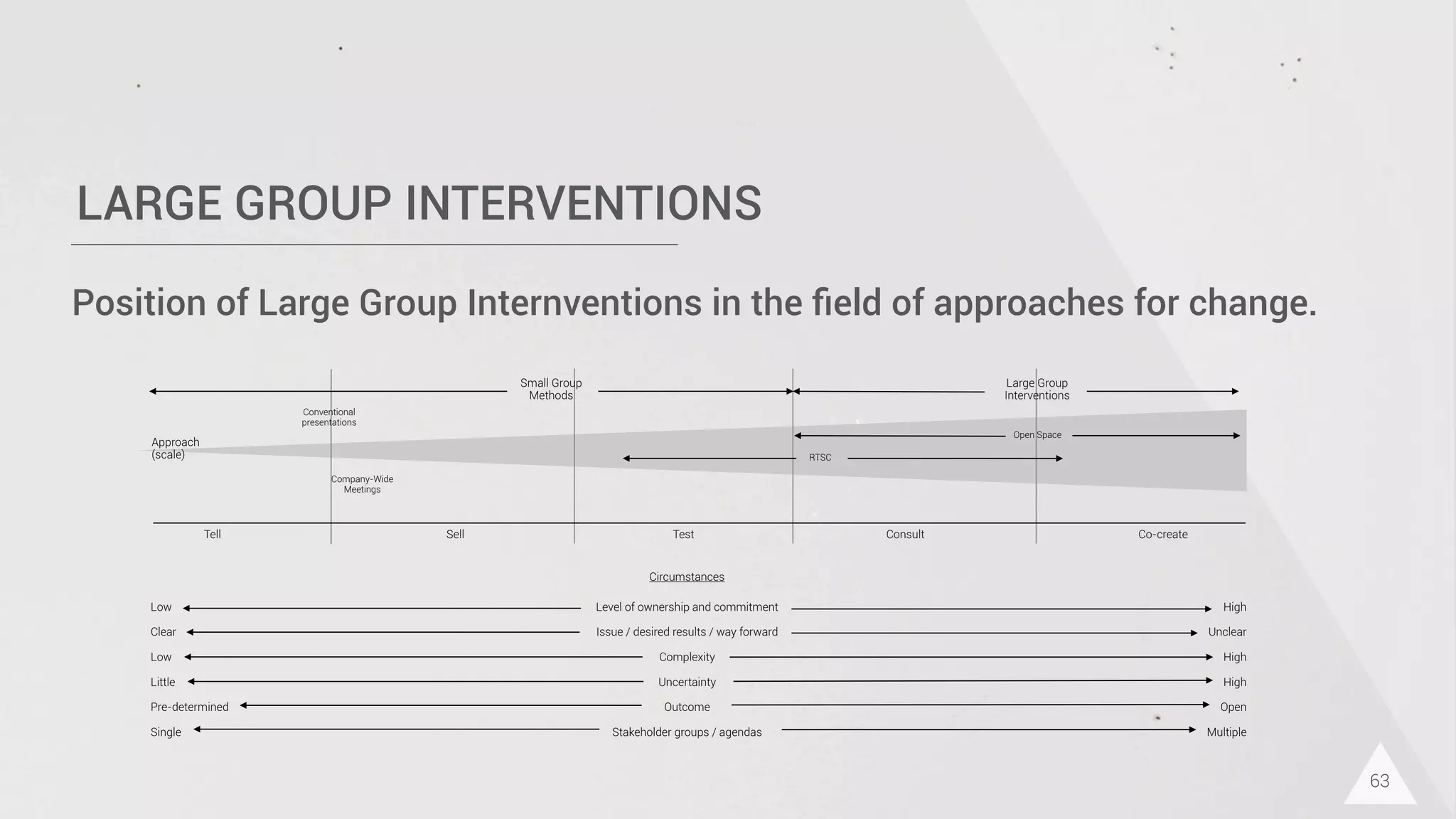
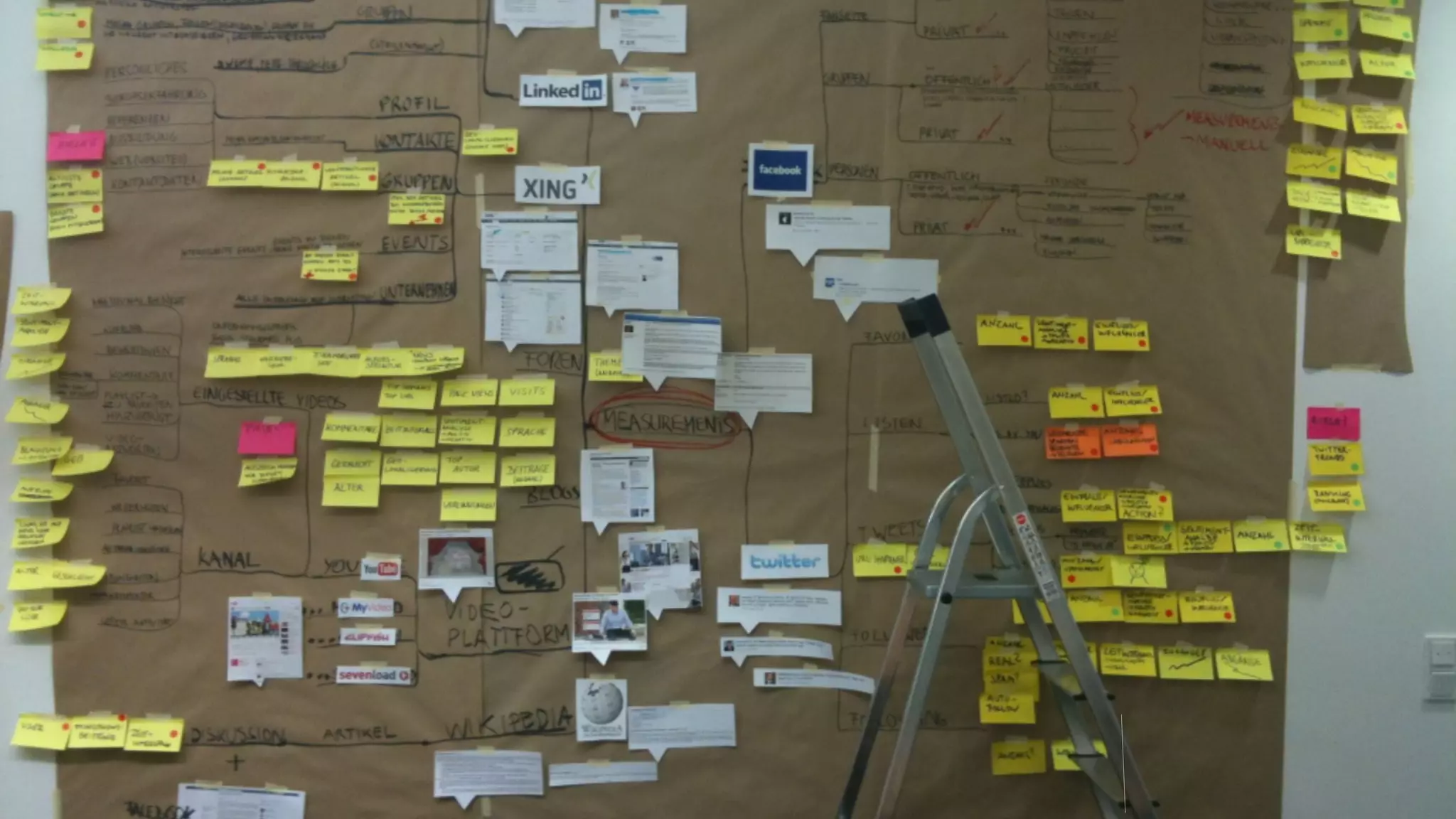
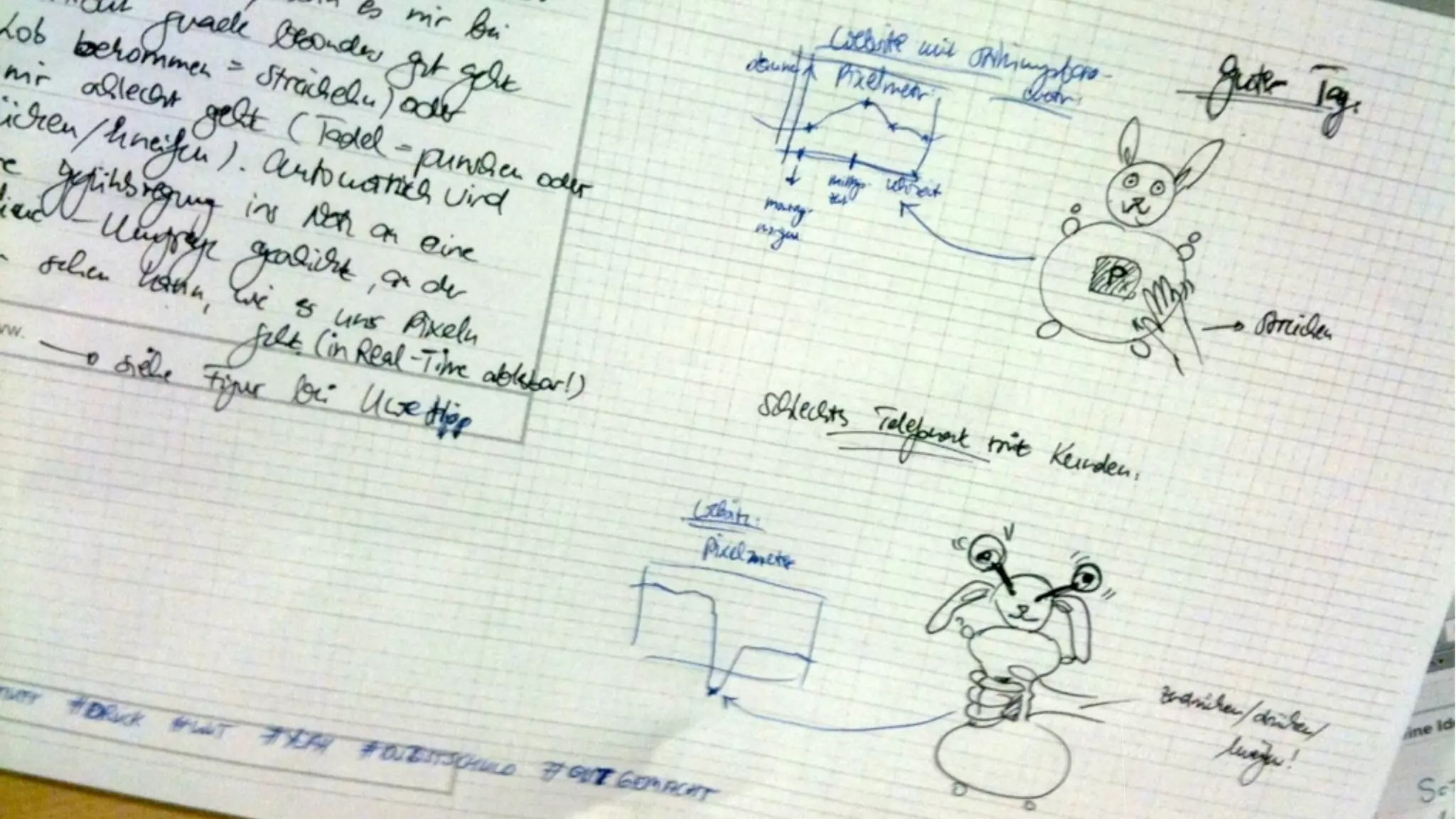
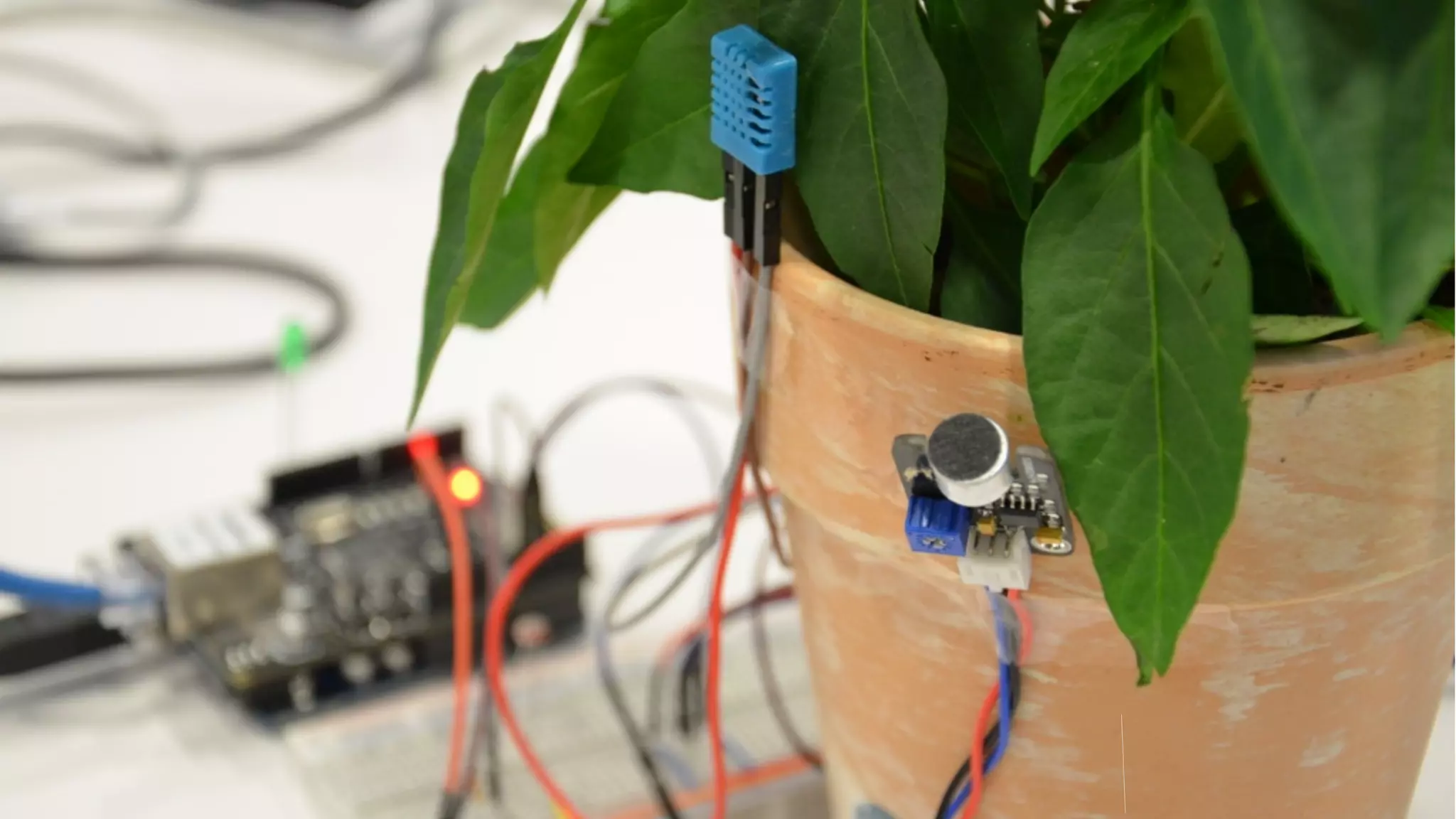
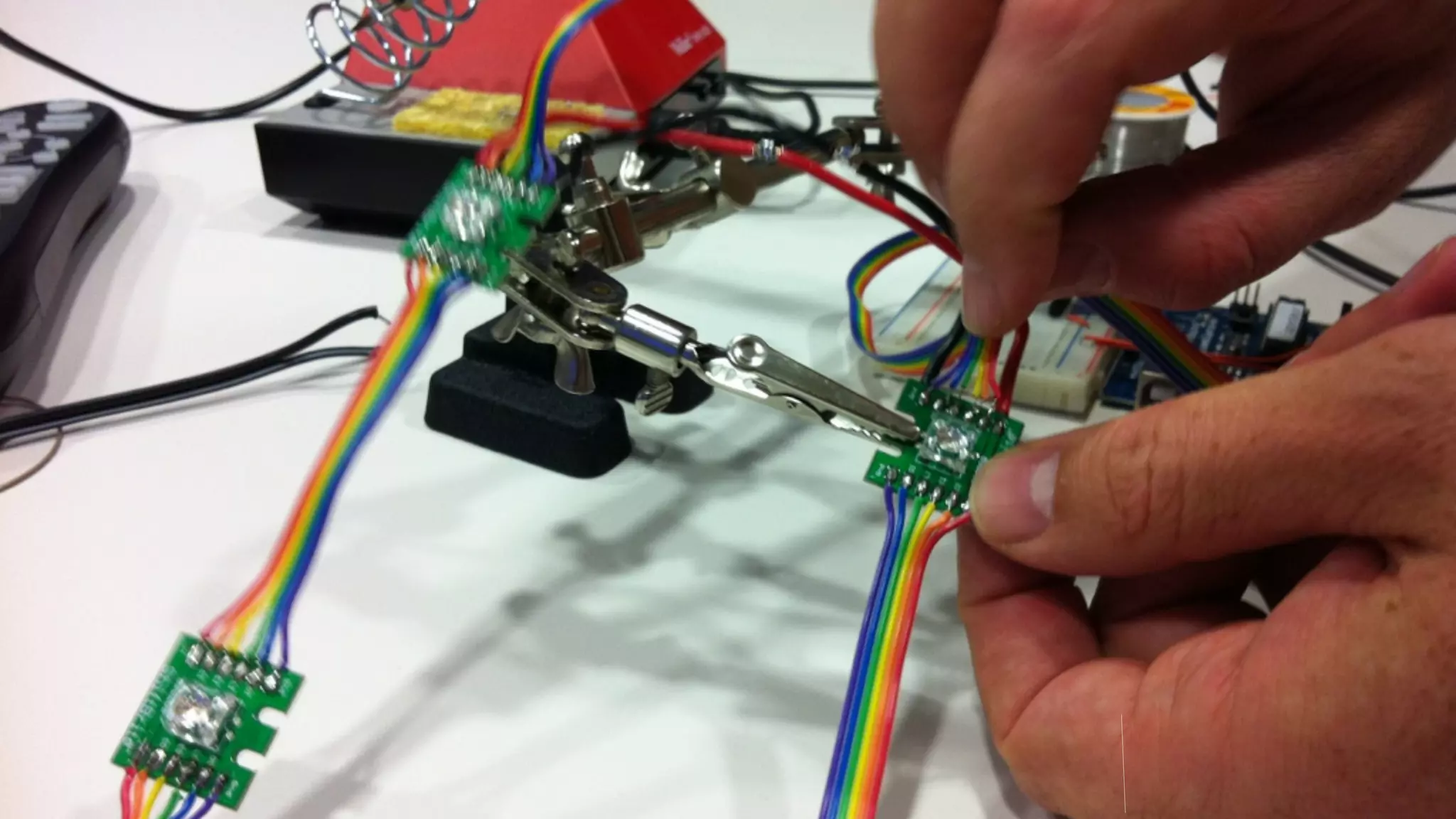
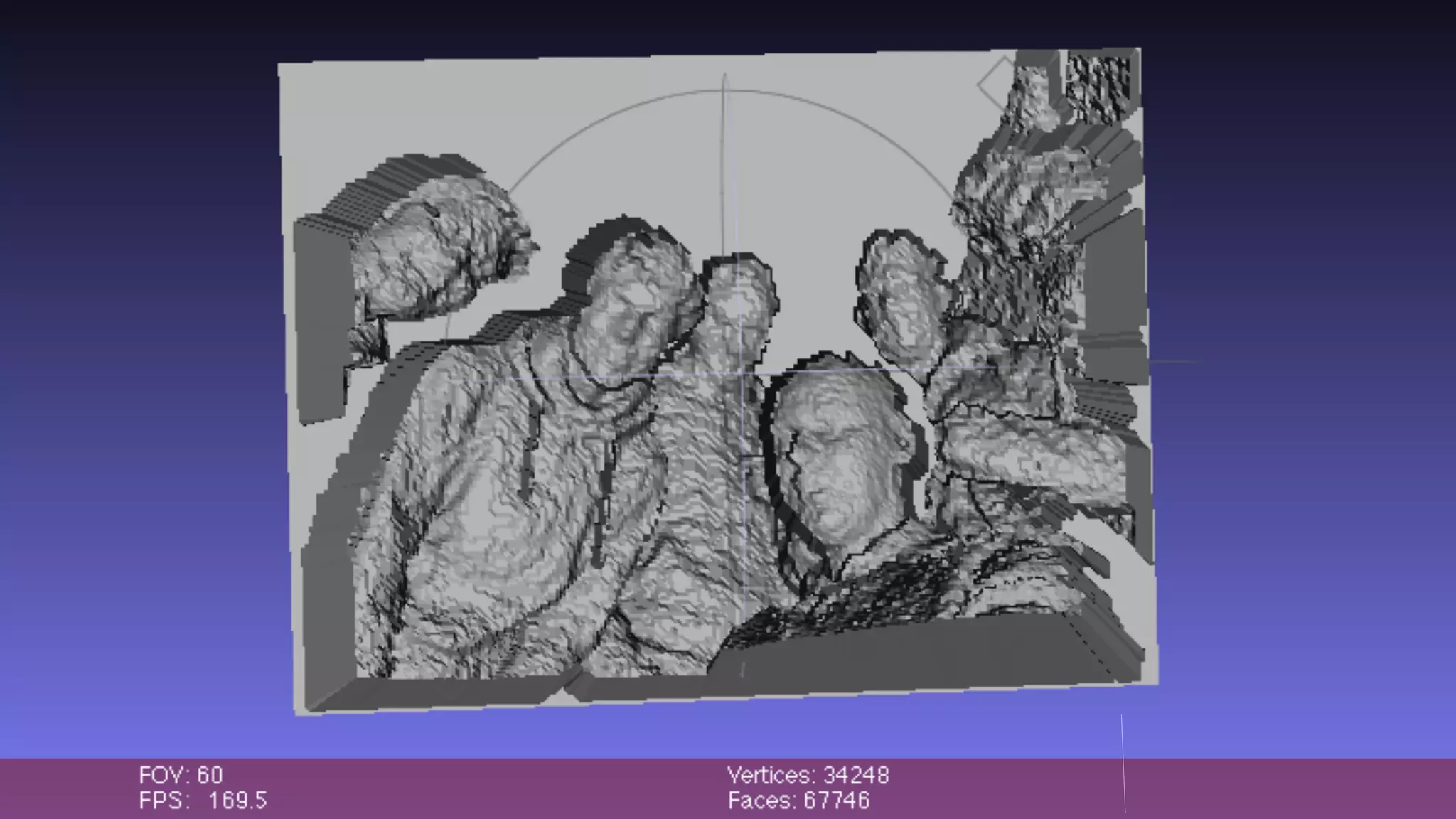
The document discusses prototyping innovation and integrating change management. It addresses why innovation is important for companies and how innovation strategies can be optimized within a company's organizational structure. The author is Axel Quack, Vice President for Innovation and Head of the Innovation Lab at Pixelpark, who discusses lessons learned about Pixelpark's innovation strategy and integrating innovation through its structure.























![APPLE
17
The company is a prime example of an innovator, which change the perception for a personal computer
from a cumbersome machine into an elegant accessory. Apple did not invent the computer. Other people
did. Moreover, businesses had been already using computers before Apple entered the market for
computers. However, Apple revolutionized this market by „[popularizing] the microcomputer.“ Apple
succeeded because the large mainframe computers of the time were hard to use. IBM dominated the
mainframe market, but it did not lead the way to smaller computers. DEC developed a minicomputer – but
even DEC „didn’t develop and popularize the microcomputer – Apple did.“ It took an existing product, shrunk
it, redesigned it and made it simpler to use.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axelquackmidemprototypinginnovation-130917074531-phpapp02/75/Midem-Prototyping-Innovation-24-2048.jpg)
![APPLE
18
The company is a prime example of an innovator, which change the perception for a personal computer
from a cumbersome machine into an elegant accessory. Apple did not invent the computer. Other people
did. Moreover, businesses had been already using computers before Apple entered the market for
computers. However, Apple revolutionized this market by „[popularizing] the microcomputer.“ Apple
succeeded because the large mainframe computers of the time were hard to use. IBM dominated the
mainframe market, but it did not lead the way to smaller computers. DEC developed a minicomputer – but
even DEC „didn’t develop and popularize the microcomputer – Apple did.“ It took an existing product, shrunk
it, redesigned it and made it simpler to use.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axelquackmidemprototypinginnovation-130917074531-phpapp02/75/Midem-Prototyping-Innovation-25-2048.jpg)
![APPLE
19
The company is a prime example of an innovator, which change the perception for a personal computer
from a cumbersome machine into an elegant accessory. Apple did not invent the computer. Other people
did. Moreover, businesses had been already using computers before Apple entered the market for
computers. However, Apple revolutionized this market by „[popularizing] the microcomputer.“ Apple
succeeded because the large mainframe computers of the time were hard to use. IBM dominated the
mainframe market, but it did not lead the way to smaller computers. DEC developed a minicomputer – but
even DEC „didn’t develop and popularize the microcomputer – Apple did.“ It took an existing product, shrunk
it, redesigned it and made it simpler to use.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/axelquackmidemprototypinginnovation-130917074531-phpapp02/75/Midem-Prototyping-Innovation-26-2048.jpg)