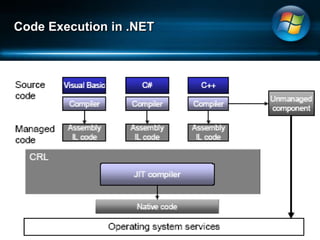
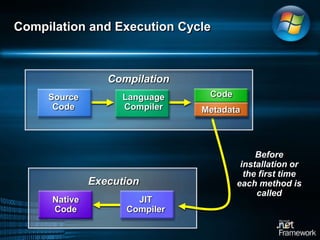
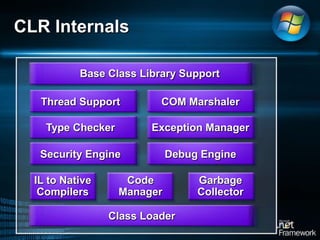
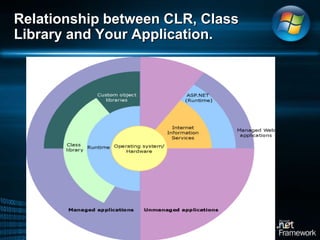
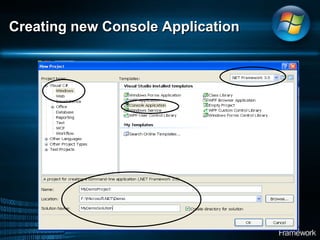
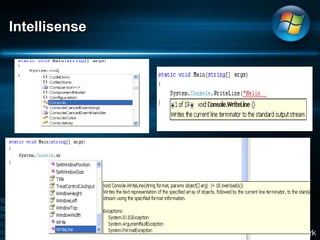
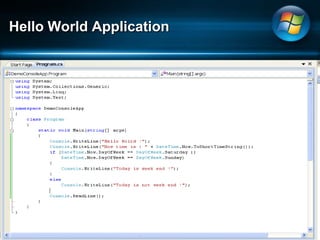
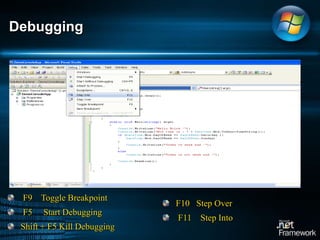
The document discusses Microsoft .NET Framework, which is a set of technologies that allows for software integration and the development of applications that can run across different operating systems and devices. It provides a common language runtime and class libraries. The .NET Framework aims to make applications more scalable, accessible from any device, and allow software to be compiled once and run on any system that supports .NET. It discusses the various versions of .NET Framework and the technologies they include like Windows Forms, ASP.NET, and ADO.NET. Visual Studio is the integrated development environment that can be used to create .NET applications using languages like C# and VB.NET.