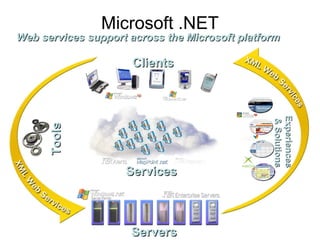
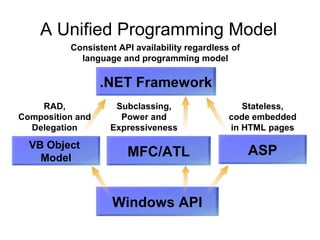
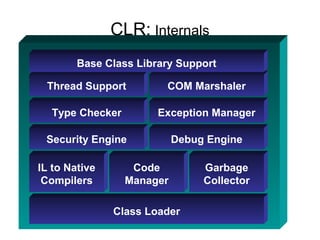
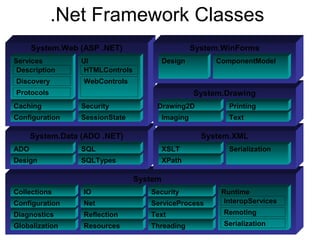
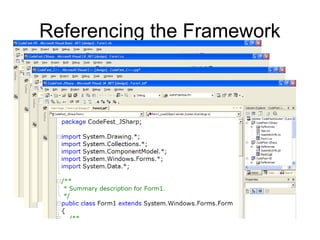
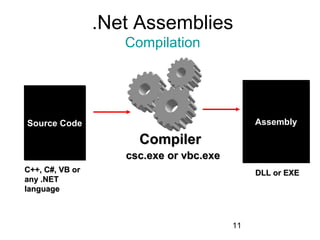
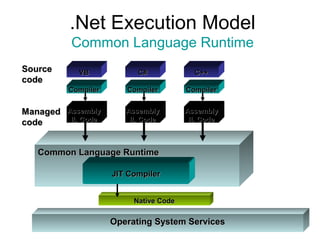
The document introduces Microsoft .NET and its tools and frameworks for building web services and mobile applications. It discusses the .NET Framework which includes a common language runtime, base class library, and languages like C# and VB.NET. It also summarizes web forms, web services, Windows forms, and how .NET applications can be built and deployed across platforms in an interoperable way using open standards.














![• Built-in Support for Developing and
Consuming Web Services
– Based entirely on open standards
– Automatically generates WSDL
– Automatically provides test page
– Attribute based – No heavy coding needed
Software as a Service
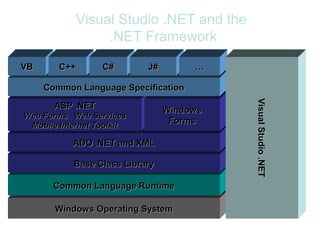
Visual Studio .Net and the Net Framework
Public Function HelloWorld() as String
return “Hello World”
End Function
[WebMethod]
WSDLWSDL
Web
Service
Object
Web
Service
Object
Test
Page
Test
Page
Compiler](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dotnet-140720050847-phpapp02/85/asp-23-320.jpg)


