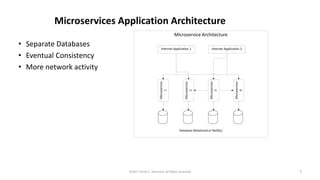
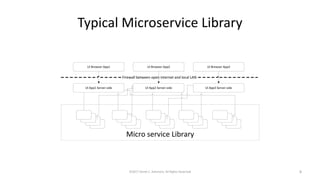
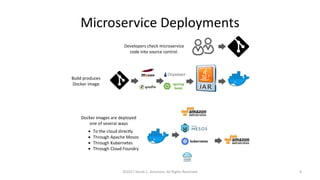
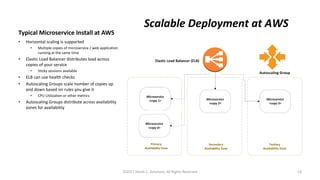
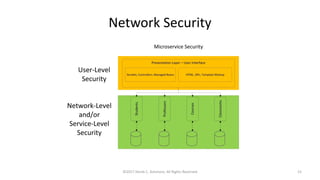
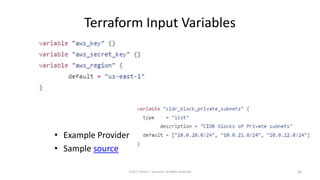
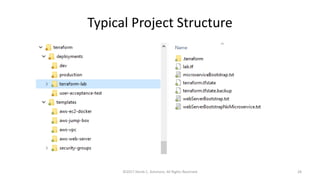
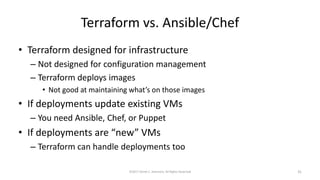
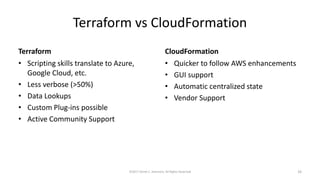
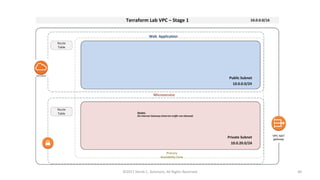
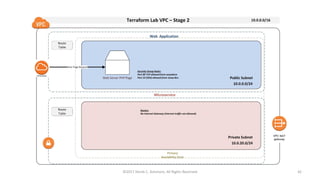
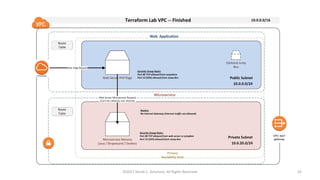
This document summarizes a presentation on managing microservices using Terraform, Docker, and cloud infrastructure. The presentation covered microservices and containerization with Docker, deploying microservices to the cloud with AWS using infrastructure as code with Terraform. It also compared Terraform to other configuration management tools and outlined an accompanying hands-on lab for attendees to deploy a sample Java microservice to AWS using Terraform.