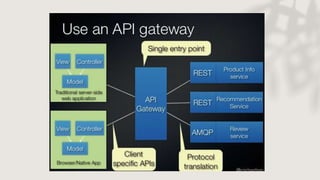
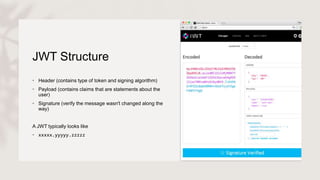
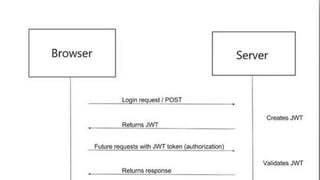
Microservices face significant security challenges due to their distributed nature and larger attack surface, making them more vulnerable than monolithic applications. Effective strategies such as using OAuth for user access control and implementing an API gateway can help secure microservices by centralizing access and screening requests for security issues. Additionally, JWT (JSON Web Token) can be utilized for token-based authentication, ensuring the integrity and legitimacy of API requests.