Embed presentation
Download to read offline



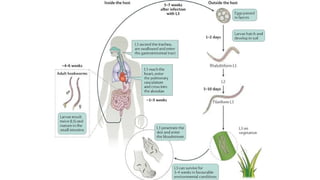
Hookworms are parasitic nematodes that infect the human small intestine, primarily species ancylostoma duodenale and necator americanus. The life cycle includes eggs excreted in feces, larval development in soil, skin penetration by infective larvae, migration through the body, and eventual intestinal infection where adult worms lay more eggs.



