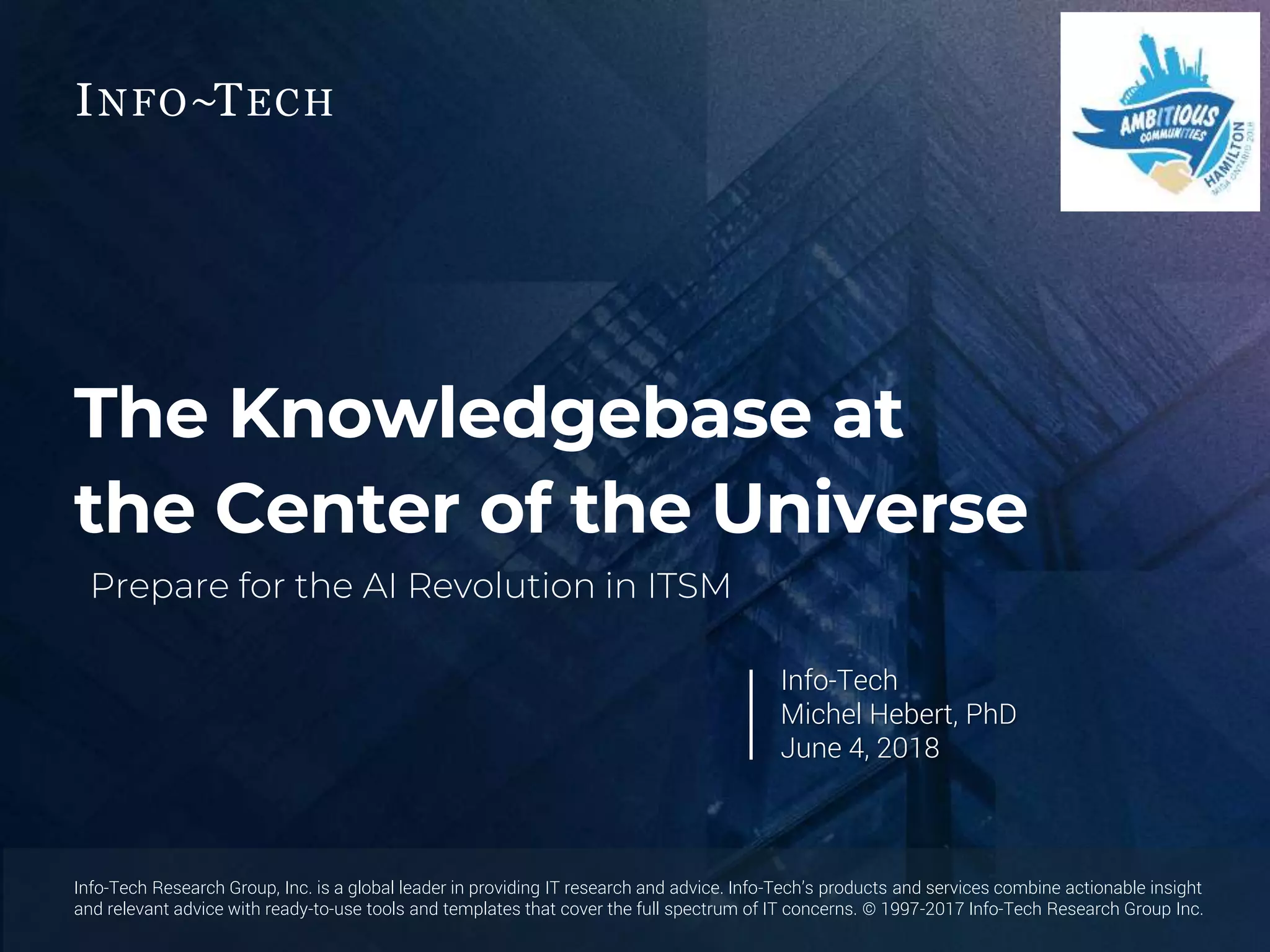
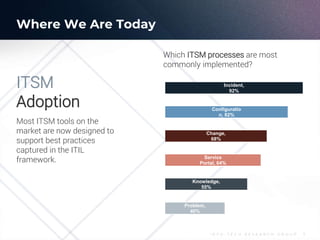
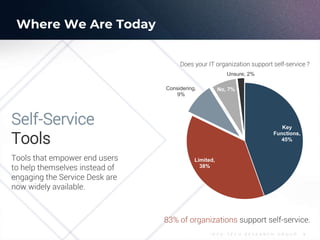
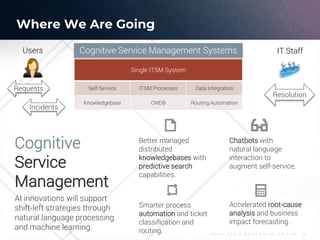
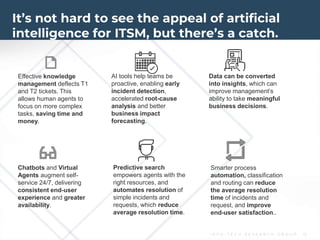
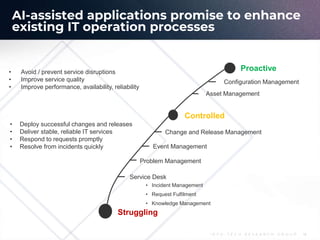
The document outlines the evolution and current state of IT Service Management (ITSM) as it prepares for the integration of AI technologies. It emphasizes the importance of focusing on problem-solving, standardizing ITSM processes, building targeted knowledgebases, and fostering a self-service culture. Additionally, it discusses the shift-left strategy for improving service efficiency and highlights the potential benefits of AI innovations in enhancing IT operations and user satisfaction.