This document discusses the personnel/payroll cycle and accounting information systems used to manage employee data and payroll processing. It covers:
- The key activities in the personnel/payroll cycle like hiring, training, compensation, and termination
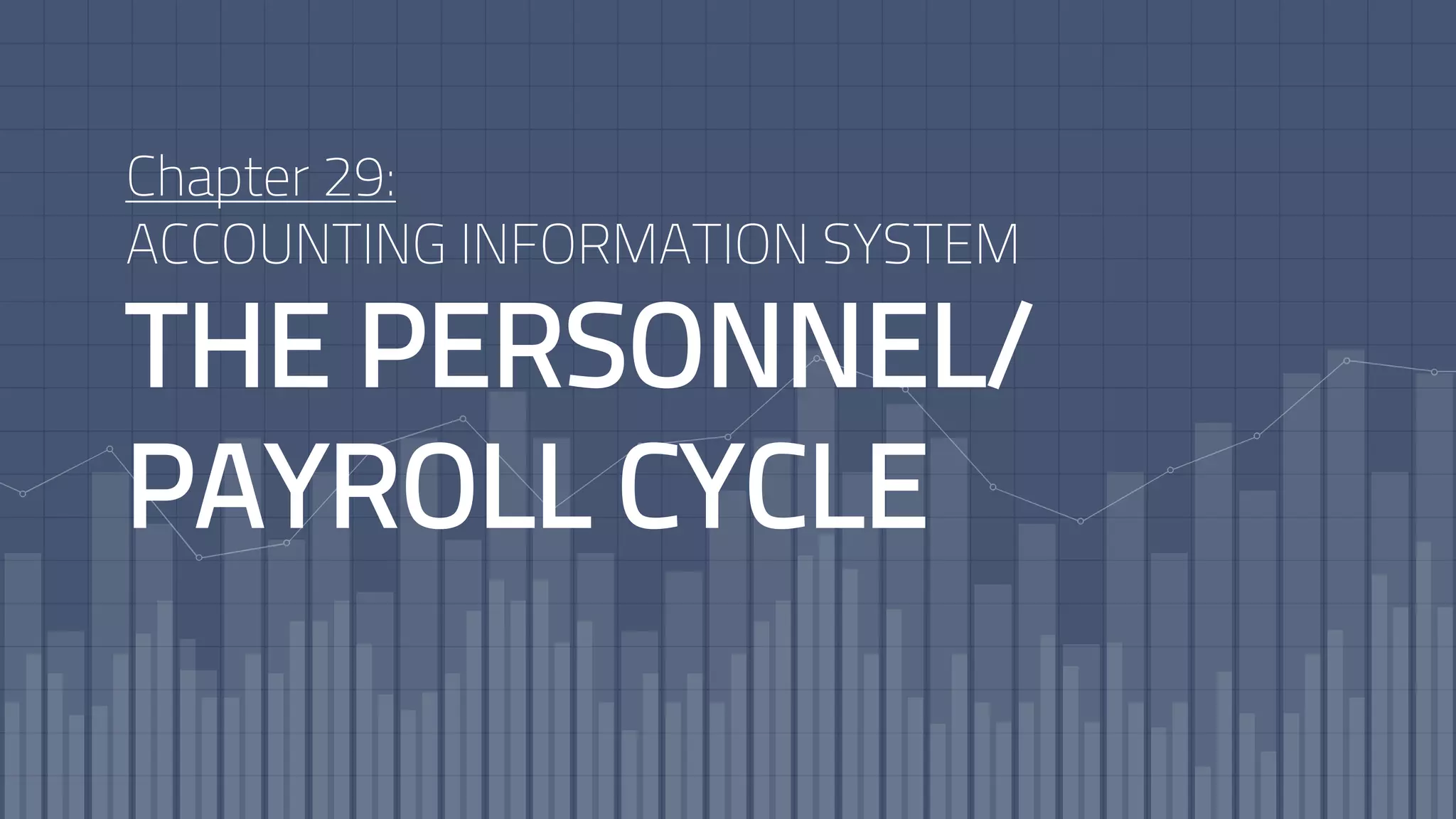
- How HR and payroll systems record and process employee data and payroll transactions
- The main functions and responsibilities of personnel management executives
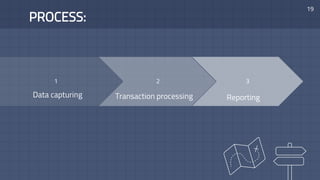
- How payroll data is collected, transactions are processed, and accounting entries are recorded for payroll in both manual and computer-based systems
- Important control objectives and procedures for payroll processing like proper authorization, transaction accuracy, and file maintenance
- Typical reports produced by payroll systems like registers, taxes withheld, and employee performance reports