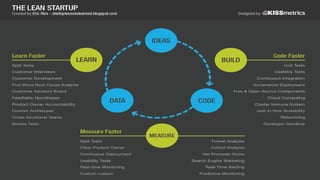
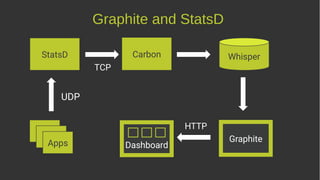
This document discusses metrics and how to use them effectively. It covers what metrics are, why they are important, and provides examples of metrics to measure things like acquisition, activation, retention, and revenue for products. It also discusses visualizing metrics, potential tools to use, and some pitfalls to avoid like vanity metrics, useless metrics, and weaponized metrics that are used for harm rather than good. The overall message is that metrics should be used to guide improvements, identify constraints, and measure outcomes, not just for their own sake or in ways that don't reflect the true performance of a business.