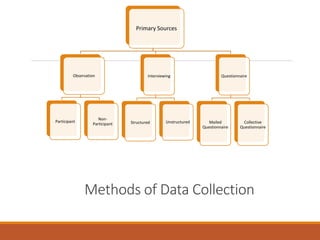
This document discusses various primary methods of data collection, including observation, interviews, and questionnaires. Observation can be participant or non-participant and is useful for studying interactions and behaviors. Interviews can be structured with predetermined questions or unstructured with open-ended questions. Questionnaires are written lists of questions that respondents self-administer and provide anonymity but have lower response rates.





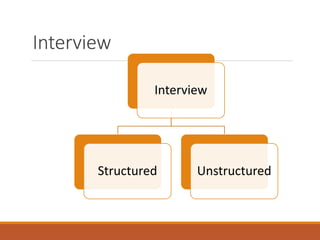
![Unstructured Interview
There is complete freedom they provide in terms of content
and structure.
Questions can be posed in any order.
There is complete freedom to use word and expressions.
Questions can be raised even on the spur of the moment.
Unstructured in depth interview can be conducted to know
the person better or his perspective. [Example research to
write biography]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7methodsofdatacollection-210720173423/85/Methods-of-Data-Collection-8-320.jpg)

