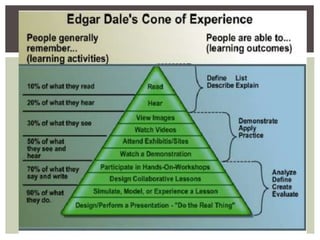
This document discusses interactive learning methods. It aims to teach participants about active learning, the need for active learning, and different types of interactive learning techniques. The document outlines objectives, levels of teaching/learning, what interactive learning is, techniques for presentations that utilize adult learning theory, classroom management strategies, understanding student behavior, why students misbehave, and possible corrective consequences.