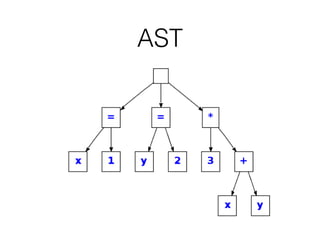
Metaprogramming allows programs to treat other programs as data by reading, generating, analyzing, transforming, or modifying other programs or even themselves at runtime. It has benefits like keeping code small, simple, DRY, lightweight, intuitive, and scalable. Metaprogramming techniques include macros, domain-specific languages, reflection, introspection, annotations, bytecode transformation, and abstract syntax tree manipulation. Many programming languages support metaprogramming through features like method missing, dynamic method definition, reflection, and abstract syntax tree transformations.









![C Macros
#include <stdio.h>
#define max_of(x, y) (x > y) ? x : y
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]){
printf("The biggest one of 2 and 5 is %dn", max_of(2, 5)); //prints 5
printf("The biggest one of 3.14 and 6.02 is %.02fn", max_of(3.14, 6.02)); //prints 6.02
printf("The biggest one of 'a' and 'z' is '%c'n", max_of('a', 'z')); //prints 'z'
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogrammingpdf-150426153312-conversion-gate01/85/Metaprogramming-10-320.jpg)

![JAVA Reflection
public class Main {
public void foo(){
System.out.println("I'm foo");
}
public void bar(){
System.out.println("I'm bar");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("Please enter a method name: ");
try {
String method_name = bf.readLine();
Object obj = Class.forName("com.metaprogramming.Main").newInstance();
Class klass = obj.getClass();
Method method = klass.getMethod(method_name, null);
method.invoke(obj, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogrammingpdf-150426153312-conversion-gate01/85/Metaprogramming-12-320.jpg)





![Introspection/Reflection:
instance variables
class Foo
def initialize
@bar = 'Bar'
end
end
f = Foo.new
f.instance_variable_get(‘@bar') #'Bar'
f.instance_variable_set(‘@baz', 'Baz')
f.instance_variable_get(‘@baz') #'Baz'
f.instance_variables #[:@bar, :@baz]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogrammingpdf-150426153312-conversion-gate01/85/Metaprogramming-19-320.jpg)
![Introspection/Reflection:
class variables
class Foo
@@bar = 'Bar'
end
Foo.class_variable_get('@@bar') #'Bar'
Foo.class_variable_defined?(‘@@bar') #true
Foo.class_variable_set('@@baz', 'Baz')
Foo.class_variable_get('@@baz') #'Baz'
Foo.class_variables #[:@@bar, :@@baz]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogrammingpdf-150426153312-conversion-gate01/85/Metaprogramming-20-320.jpg)
![Introspection: methods
class Foo
def bar; 'I'm bar' end
private
def baz; 'I'm baz' end
protected
def zoo; 'I'm zoo' end
end
f = Foo.new
f.methods #[:bar, :zoo, ...]
f.private_methods #[:baz, ...]
f.protected_methods #[:zoo, ...]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogrammingpdf-150426153312-conversion-gate01/85/Metaprogramming-21-320.jpg)






