The document discusses interprocess communication (IPC) using message queues and shared memory, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. Message queues maintain a FIFO order and are persistent in kernel space, while shared memory is faster and resides in user space. The document also includes code examples for implementing both message queues and shared memory for reading and writing data.

![11. #include<stdio.h>
12. //creatingstructure message queue:todefinetype of message andmessage data
13. struct myMessage
14. {
15. longmess_type;
16.
17. struct StdDetail
18. {
19. int Id;
20. char Name[20];
21. }stdobj;
22. };
23.
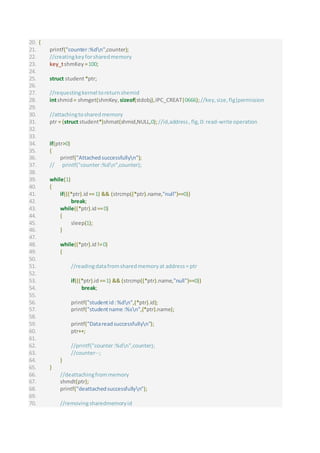
24. int main()
25. {
26. key_tkey = 8;
27.
28. //requestingfromkernel toallocate message queue inkernel space andgive messagequeueid
29.
30. intmy_id= msgget(key,IPC_CREAT|0666);
31. if(my_id==-1)
32. perror("msgget");
33. else
34. {
35. printf("Message queue createdsuccessfullyn");
36. printf("myid:%dn",my_id);
37. }
38.
39. struct myMessage msg;//creatingobjectformessage queue structure
40.
41. char choice;
42. printf("Doyouwanttoinsertdata inmessage queue 1.y:Yes, 2. n : Non");
43. while(1)
44. {
45. scanf("%c",&choice);
46.
47. if(choice == 'y')
48. {
49. printf("entermessage type(kindlyenterintvale) :");
50. scanf("%d",&msg.mess_type);
51. printf("Enterstudentid:");
52. scanf("%d",&msg.stdobj.Id);
53. printf("nEnterstudentname :");
54. scanf("%s",&msg.stdobj.Name);
55.
56. //printf("id:%d",msg.stdobj.Id);
57. //printf("%s",msg.stdobj.Name);
58. intret = msgsnd(my_id,&msg,sizeof(msg.stdobj), IPC_NOWAIT); //sending message
59.
60. if(ret== -1)
61. perror("msgsnd");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/messagequeuesharedmemory-180830174941/85/Message-queue-and-shared-memory-2-320.jpg)
![62. else
63. {
64. printf("message writtensuccessfullyn");
65. printf("Enterchoice y/n:n");
66. }
67.
68.
69. }
70. if(choice == 'n')
71. {
72. break;
73. }
74. }
75.
76. return 0;
77. }
Program to read messages from queue: ReadFrom_messageQueue.c
1. /*
2.
3. NarayanLal Menariya:August28,2018
4.
5. * */
6.
7. #include<sys/types.h>
8. #include<sys/ipc.h>
9. #include<sys/msg.h>
10. #include<string.h>
11. #include<stdio.h>
12. //creatingstructure message queue:todefinetype of message andmessage data
13.
14. struct myMessage
15. {
16. longmess_type;
17.
18. struct StdDetail
19. {
20. int Id;
21. char Name[20];
22. }stdobj;
23. };
24.
25.
26.
27. int main()
28. {
29. key_tkey = 8;
30. struct myMessage msg;//creatingobjectformessage queue structure
31.
32. //requestingfromkernel togive message queue id
33. intmy_id= msgget(key,IPC_CREAT|0666);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/messagequeuesharedmemory-180830174941/85/Message-queue-and-shared-memory-3-320.jpg)

![4.
5. #include<stdio.h>
6. #include<sys/shm.h>
7. #include<sys/ipc.h>
8. #include<string.h>
9. #include "file.h"
10.
11. int counter;
12.
13.
14. struct student
15. {
16. intid;
17. char name[20];
18. }stdobj;
19.
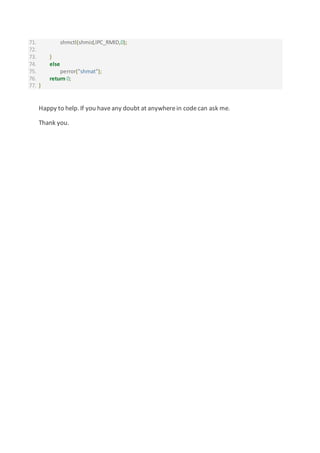
20. int main()
21. {
22. counter=0;
23. //creatingkeyforsharedmemory
24. key_tshmKey =100;
25. char choice;
26. char msg[20];
27.
28. struct student*ptr;
29.
30. //requestingkernel toallocate sharedmemoryandreturnshmid
31. intshmid = shmget(shmKey,sizeof(stdobj),IPC_CREAT|0666);//key,size, flg|permission
32.
33. //attachingtosharedmemory
34. ptr = (struct student*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);//id,address,flg,0: read-write operation
35.
36. if(ptr> 0)
37. {
38. printf("Attachedsuccessfullyn");
39. printf("Doyouwantto write insharedmemory1.y:yes,2. n:non");
40. while(1)
41. {
42. scanf("%c",&choice);
43. if(choice =='y')
44. {
45. //ptr = &stdobj;
46. printf("enterstudentid:n");
47. scanf("%d",&stdobj.id);
48. printf("enterstudentname :n");
49. scanf("%s",&stdobj.name);
50.
51. printf("name :%sn",stdobj.name);
52. printf("id:%dn",stdobj.id);
53.
54. (*ptr).id= stdobj.id;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/messagequeuesharedmemory-180830174941/85/Message-queue-and-shared-memory-5-320.jpg)
![55. strcpy((*ptr).name,stdobj.name);
56.
57. //printf("Name :%s",(*ptr).name);
58.
59. printf("nDatawrittensuccessfullyn");
60. ptr++;
61.
62.
63. increment();
64. // counter++;
65. printf("writechoice y/n:");
66. }
67. if(choice =='n')
68. {
69. (*ptr).id= 1;
70. strcpy(stdobj.name,"null");
71. strcpy((*ptr).name,stdobj.name);
72. break;
73. }
74.
75. }
76.
77. //deattachingfrommemory
78. shmdt(ptr);
79. printf("deattachedsuccessfullyn");
80.
81. }
82. else
83. perror("shmat");
84. return 0;
code: readFrom_sharedMemory.c
1. /*
2. Narayan Lal Menariya:August28,2018
3.
4.
5. * */
6.
7. #include<stdio.h>
8. #include<sys/shm.h>
9. #include<sys/ipc.h>
10. #include "file.h"
11. int counter;
12.
13. struct student
14. {
15. intid;
16. char name[20];
17. }stdobj;
18.
19. int main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/messagequeuesharedmemory-180830174941/85/Message-queue-and-shared-memory-6-320.jpg)