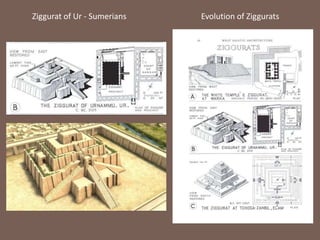
Mesopotamia was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers and was the cradle of early civilizations like the Sumerians, Assyrians, and Babylonians. Cities in Mesopotamia like Ur, Assur, Khorsabad, Nimrud, Nineveh, and Babylon contained temples, palaces, and houses built from sun-dried mud bricks due to the lack of stone. Temples evolved from simple platform structures to zigurats with multiple stacked platforms and palaces had colorful wall carvings and sculptures. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World consisting of trees and plants on elevated pillars with underground water systems.