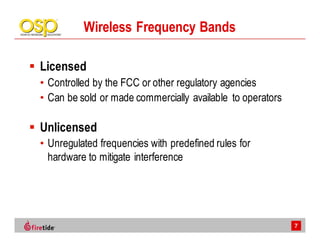
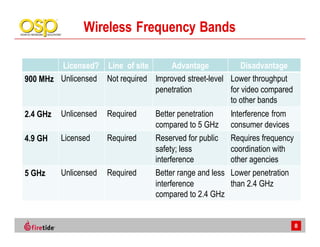
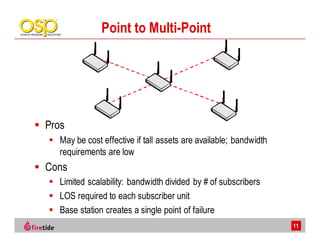
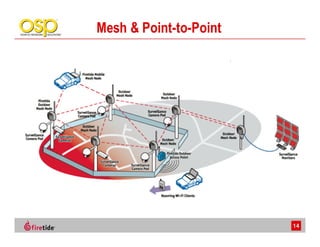
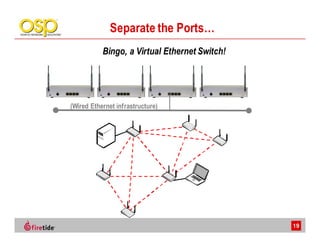
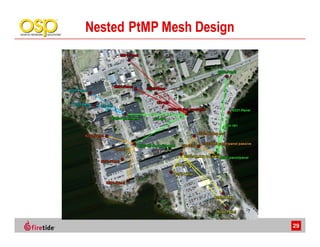
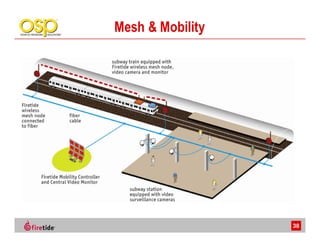
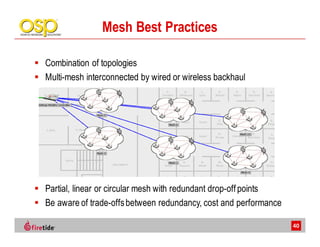
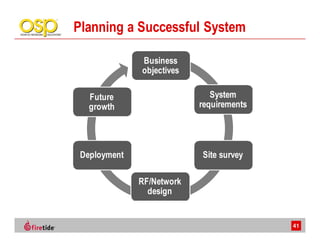
This document discusses the advantages of wireless mesh systems for outdoor surveillance projects. It reviews different wireless options and considerations for high-performance wireless networks. Wireless mesh networks can deploy virtually anywhere, extend wired infrastructure, and provide redundancy. However, they require more expertise than point-to-point or point-to-multipoint systems. The document examines wireless frequencies, topologies, throughput capabilities, security aspects, and best practices for planning and deploying a successful wireless mesh network for video surveillance and other applications.