Embed presentation


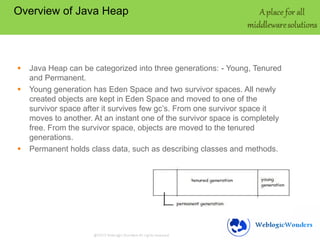



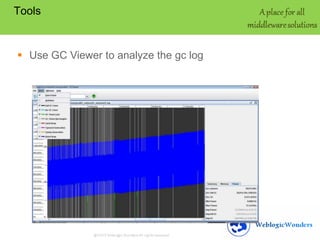

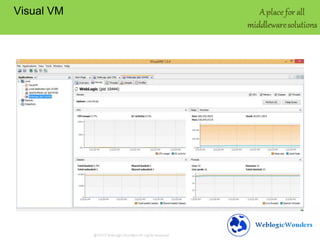


This document discusses memory leaks in Java. It provides an overview of the Java heap and generations. A memory leak occurs when objects are not removed from the heap even when no longer needed. Symptoms include frequent full garbage collections and a decreasing free heap over time. Tools like GCViewer and JProfiler can analyze garbage collection logs and heap usage to troubleshoot leaks. Best practices to avoid leaks include monitoring heap usage, freeing unnecessary objects, closing connections, and limiting session data.










