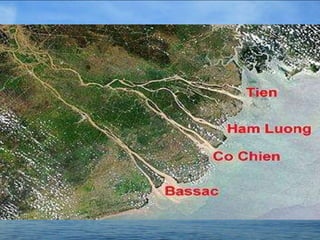
The Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in Southeast Asia that flows through China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam. It is an important resource for the 60 million people who live in its lower basin, providing water, irrigation, transport and food. However, the river is also facing threats from pollution, habitat destruction, and large hydroelectric dams which could disrupt the ecosystem. Managing development while protecting the environment and livelihoods of those who rely on the Mekong River is an ongoing challenge.