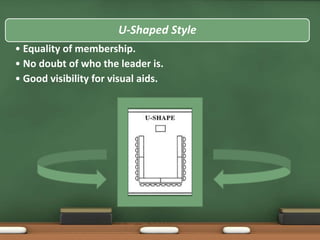
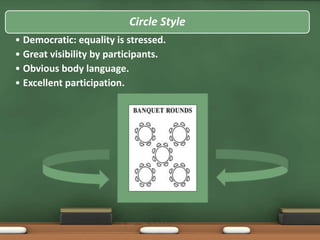
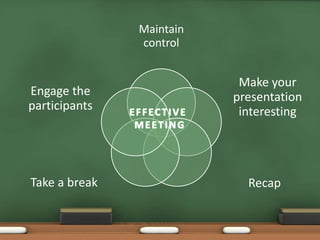
The document discusses the importance of meetings, classifying them into types such as information giving, information taking, and problem solving, while outlining the roles and responsibilities of participants. It emphasizes the need for preparation, agenda setting, time management, and proper documentation of meeting outcomes. Additionally, the document highlights strategies for effective meetings, including participant selection, establishing ground rules, and evaluating the meeting process.